Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Once released neurotransmitter molecules are picked up by receptors - structures that appear on cellular surfaces that pick up molecules that fit into them like a "lock and key" ...
... Once released neurotransmitter molecules are picked up by receptors - structures that appear on cellular surfaces that pick up molecules that fit into them like a "lock and key" ...
CH 48 Nervous systemnotes2010
... 2. interneuron- a nerve cell within the central nervous system responsible for the integration of neural input and output 3. motor neuron transmits signals from the brain or spinal column to muscles or glands How do nerve cells send impulses along itself? All deals with membrane potentials it’s the ...
... 2. interneuron- a nerve cell within the central nervous system responsible for the integration of neural input and output 3. motor neuron transmits signals from the brain or spinal column to muscles or glands How do nerve cells send impulses along itself? All deals with membrane potentials it’s the ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... An electric Signal that is conducted along an axon to a synapse. Refractory Period The time following an action potential in which new action potential cannot be initiated. Terminal Buttons Knoblike structures that branch out from an axon. Neurotransmitters Chemicals that transmit information across ...
... An electric Signal that is conducted along an axon to a synapse. Refractory Period The time following an action potential in which new action potential cannot be initiated. Terminal Buttons Knoblike structures that branch out from an axon. Neurotransmitters Chemicals that transmit information across ...
Slide ()
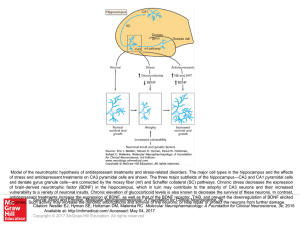
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
Neuroplasticity - University of Michigan–Flint
... • When climbing fiber increases its activity, mossy fiber signals to Purkinje cells is reduced, which change the synaptic strength for the circuit ...
... • When climbing fiber increases its activity, mossy fiber signals to Purkinje cells is reduced, which change the synaptic strength for the circuit ...
The Nervous System
... terminals) and join (make connections with) many different neurons Small vesicles containing chemicals called neurotransmitters are located in the end plates of axons. When the nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon it causes the chemicals to be released into the synaptic cleft. Chemicals d ...
... terminals) and join (make connections with) many different neurons Small vesicles containing chemicals called neurotransmitters are located in the end plates of axons. When the nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon it causes the chemicals to be released into the synaptic cleft. Chemicals d ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I
... 5. The calcium inside the synaptic knob initiates a series of events that causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane, releasing the neurotransmitter by exocytosis. 6. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and react with specific receptors on the postsynaptic ...
... 5. The calcium inside the synaptic knob initiates a series of events that causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane, releasing the neurotransmitter by exocytosis. 6. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and react with specific receptors on the postsynaptic ...
Chapter 28: Nervous System
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
I. Introduction to class
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
Na+ - cloudfront.net
... Na+ channels open and Na+ rushes inside K+ channels open to let K+ out Causes other Na+ channels to open, like a chain ...
... Na+ channels open and Na+ rushes inside K+ channels open to let K+ out Causes other Na+ channels to open, like a chain ...
Chapter 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
... button and causes the _22_ (2 words), the storage sacs for the neurotransmitter, to fuse with the membrane at the end of the axon and spill its contents into the synaptic cleft. ...
... button and causes the _22_ (2 words), the storage sacs for the neurotransmitter, to fuse with the membrane at the end of the axon and spill its contents into the synaptic cleft. ...
Nervous System
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
... causing the microtubules to constrict, pulling the synaptic vesicles towards the presynaptic membrane. These fuse to the membrane which then empty their contents (neurotransmitter substance) into the synaptic cleft. This substance diffuses across the cleft to the receptor sites in the post synaptic ...
... causing the microtubules to constrict, pulling the synaptic vesicles towards the presynaptic membrane. These fuse to the membrane which then empty their contents (neurotransmitter substance) into the synaptic cleft. This substance diffuses across the cleft to the receptor sites in the post synaptic ...
Motor Neuron
... region of the membrane • Na+ ions rush into the cell and K+ ions rush out depolarizing the region of the membrane • This region of depolarization is an Action Potential • An action potential in one region stimulates adjacent regions to depolarize and the action potential moves away from the point of ...
... region of the membrane • Na+ ions rush into the cell and K+ ions rush out depolarizing the region of the membrane • This region of depolarization is an Action Potential • An action potential in one region stimulates adjacent regions to depolarize and the action potential moves away from the point of ...
Katie Newhall Synchrony in stochastic pulse-coupled neuronal network models
... Synchrony in stochastic pulse-coupled neuronal network models Many pulse-coupled dynamical systems possess synchronous attracting states. Even stochastically driven model networks of Integrate and Fire neurons demonstrate synchrony over a large range of parameters. We study the interplay between ...
... Synchrony in stochastic pulse-coupled neuronal network models Many pulse-coupled dynamical systems possess synchronous attracting states. Even stochastically driven model networks of Integrate and Fire neurons demonstrate synchrony over a large range of parameters. We study the interplay between ...
Chapter 48: Nervous Systems Overview: Command and Control
... • The speed of an action potential increases with the diameter of an axon • In vertebrates, axons are myelinated, which also causing the speed of an action potential to increase – Gaps between the myelination are known as ______________________________ Neurons communicate with other cells at synapse ...
... • The speed of an action potential increases with the diameter of an axon • In vertebrates, axons are myelinated, which also causing the speed of an action potential to increase – Gaps between the myelination are known as ______________________________ Neurons communicate with other cells at synapse ...
Name
... B. motor nerves. C. mixed nerves. D. Schwann nerves. 25. In the human nervous system, what percentage of cells are neurons? A. 10% B. 50% C. 90% D. the ratio is unknown due to complexity of nervous system Following are steps in the conduction of an impulse at a synapse. Place them in proper sequence ...
... B. motor nerves. C. mixed nerves. D. Schwann nerves. 25. In the human nervous system, what percentage of cells are neurons? A. 10% B. 50% C. 90% D. the ratio is unknown due to complexity of nervous system Following are steps in the conduction of an impulse at a synapse. Place them in proper sequence ...
Ling411-02-Neurons - OWL-Space
... distinctions of the world’s languages By 11 months the child recognizes only those of the language of its environment At 20 months the left hemisphere is favored for most newly acquired linguistic information Brain mass nears adult size by age six yrs • Female brain grows faster than male duri ...
... distinctions of the world’s languages By 11 months the child recognizes only those of the language of its environment At 20 months the left hemisphere is favored for most newly acquired linguistic information Brain mass nears adult size by age six yrs • Female brain grows faster than male duri ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Cell body — nucleus and metabolic center of the cell (main part of nerve cell) • Processes — fibers that extend from the cell body – can be microscopic or up to 3-4 feet in length ...
... • Cell body — nucleus and metabolic center of the cell (main part of nerve cell) • Processes — fibers that extend from the cell body – can be microscopic or up to 3-4 feet in length ...
Part 2 of Unit Test 4
... Question 1: Nervous systems of animals contain thousands of neurons, all needing to quickly and effectively communicate with one another to function properly. In four sentences or less, relate the 3 steps of a signal transduction pathway to the process of neural communication across the synapse from ...
... Question 1: Nervous systems of animals contain thousands of neurons, all needing to quickly and effectively communicate with one another to function properly. In four sentences or less, relate the 3 steps of a signal transduction pathway to the process of neural communication across the synapse from ...
225.1 Bogenmann
... signal pathway induces NB differentiation. Hence, we hypothesized that signaling pathway(s) that regulate normal neuronal maturation also control NB cell differentiation and therefore may open new treatment modalities for patients with high-risk NB. Here, we demonstrate that activation of the RET re ...
... signal pathway induces NB differentiation. Hence, we hypothesized that signaling pathway(s) that regulate normal neuronal maturation also control NB cell differentiation and therefore may open new treatment modalities for patients with high-risk NB. Here, we demonstrate that activation of the RET re ...
Microscopic Nervous System and Reflexes with answers
... 5. What are the 2 subdivisions of the efferent nerves and the function of each? Somatic NS which is voluntary and controls the skeletal muscles and the autonomic NS which is involuntary and controls the heart, smooth muscles and glands 6. Name the 2 types of nervous tissue found in the nervous syste ...
... 5. What are the 2 subdivisions of the efferent nerves and the function of each? Somatic NS which is voluntary and controls the skeletal muscles and the autonomic NS which is involuntary and controls the heart, smooth muscles and glands 6. Name the 2 types of nervous tissue found in the nervous syste ...
1 NOTES – CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System – LECTURE
... a. Afferent division 1) transmits impulses from sensory organs to the CNS 2) Afferent fibers/neurons – nerve fibers that transmit action potentials from the periphery to the CNS b. Efferent (motor) division 1) transmits impulses from the CNS to effectors a) effectors include muscles or glands 2) Eff ...
... a. Afferent division 1) transmits impulses from sensory organs to the CNS 2) Afferent fibers/neurons – nerve fibers that transmit action potentials from the periphery to the CNS b. Efferent (motor) division 1) transmits impulses from the CNS to effectors a) effectors include muscles or glands 2) Eff ...