Resting Potential
... • Saltatory conduction – impulse jumps from 1 node of Ranvier to another; why? • Myelin covering – • channels - are located at nodes of Ranvier for ions to diffuse in & out • Myelinated axons (white matter) - ...
... • Saltatory conduction – impulse jumps from 1 node of Ranvier to another; why? • Myelin covering – • channels - are located at nodes of Ranvier for ions to diffuse in & out • Myelinated axons (white matter) - ...
Ch11AB
... Graded potentials are _________________, ____________________ changes in the membrane potential. Graded potentials can be __________________or _______________________. The ___________________ of a graded potential varies directly (is graded) with stimulus strength. (Slide 10) The ___________________ ...
... Graded potentials are _________________, ____________________ changes in the membrane potential. Graded potentials can be __________________or _______________________. The ___________________ of a graded potential varies directly (is graded) with stimulus strength. (Slide 10) The ___________________ ...
Biology 12 - Excretion
... part of the CNS, relays information to brain and instruction to body CNS tissue containing mostly myelinated nerve fibers and support cells CNS tissue containing cell bodies and short, non-myelinated fibers highway through which information from body is sorted before being sent to cerbebrum ancient ...
... part of the CNS, relays information to brain and instruction to body CNS tissue containing mostly myelinated nerve fibers and support cells CNS tissue containing cell bodies and short, non-myelinated fibers highway through which information from body is sorted before being sent to cerbebrum ancient ...
Biology 3201
... Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between schwann cells. ...
... Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between schwann cells. ...
Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by
... Sensory – take impulses from sensory receptor to CNS o Interneurons – receive information in the CNS and send it to a motor neuron These essentially connect the sensory and motor neurons o Motor – take impulses from the CNS to an effector (i.e. gland or muscle fiber) Nerve impulses move from the ...
... Sensory – take impulses from sensory receptor to CNS o Interneurons – receive information in the CNS and send it to a motor neuron These essentially connect the sensory and motor neurons o Motor – take impulses from the CNS to an effector (i.e. gland or muscle fiber) Nerve impulses move from the ...
Topic 6
... because the range of different chemicals in the numerous different regions of the brain and spinal cord make isolation very difficult. One technique that can be used to approximate the study of CNS transmitter release to a REGION (not an individual neuron) of the brain or spinal cord involves in vit ...
... because the range of different chemicals in the numerous different regions of the brain and spinal cord make isolation very difficult. One technique that can be used to approximate the study of CNS transmitter release to a REGION (not an individual neuron) of the brain or spinal cord involves in vit ...
document
... Proprioceptors and the Control of Movement In the tendons, muscles and joints there are receptors called proprioceptors which provide sensory information about muscle contraction, position of the limbs, and posture and balance. ...
... Proprioceptors and the Control of Movement In the tendons, muscles and joints there are receptors called proprioceptors which provide sensory information about muscle contraction, position of the limbs, and posture and balance. ...
Chapter 13: The Nervous System
... potential? How are organisms containing neurons without a myelin sheath cell’s structured to speed up transmission? ...
... potential? How are organisms containing neurons without a myelin sheath cell’s structured to speed up transmission? ...
Nervous Tissue - MrsSconyersAnatomy
... Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, developing embryo advantages: Faster – don’t have to “jump the gap” Synchronization – allows groups of cell’s to work together – heart beating ...
... Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, developing embryo advantages: Faster – don’t have to “jump the gap” Synchronization – allows groups of cell’s to work together – heart beating ...
Slide ()
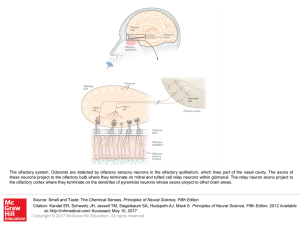
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
30 - HistologyforMedStudents
... 7. Multiple sclerosis is an auto-immune disorder which leads to demyleination of axons and disruption of signal transduction. The Schwann cell myelinates axons in the peripheral nervous system. What cell performs the same function in the CNS? ...
... 7. Multiple sclerosis is an auto-immune disorder which leads to demyleination of axons and disruption of signal transduction. The Schwann cell myelinates axons in the peripheral nervous system. What cell performs the same function in the CNS? ...
Chapter 11
... h. axon depends upon the cell body for everything: organelles, proteins, and enzymes for synthesis of neurotransmitter i. anterograde transport - movement of material from cell body to synaptic knobs ii. retrograde transport - movement of material from synapse to cell body 3. myelin sheath - wrap of ...
... h. axon depends upon the cell body for everything: organelles, proteins, and enzymes for synthesis of neurotransmitter i. anterograde transport - movement of material from cell body to synaptic knobs ii. retrograde transport - movement of material from synapse to cell body 3. myelin sheath - wrap of ...
Slide ()
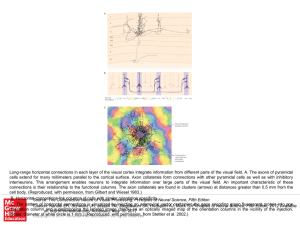
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
Nerve Tissue - Coach Frei Science
... 17. ____ Another name for a motor neuron. 18. ____ The fatty substance that fills a Schwann cell and provides protection for the axon. 19. ____ The point of close contact between the telodendrites of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron. 20. ____ Another name for a sensory neuron. 21. ____ ...
... 17. ____ Another name for a motor neuron. 18. ____ The fatty substance that fills a Schwann cell and provides protection for the axon. 19. ____ The point of close contact between the telodendrites of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron. 20. ____ Another name for a sensory neuron. 21. ____ ...
Chapter Three Study Guide
... --The average brain is about the size of a grapefruit --About 3 lbs in weight --100 billion nerve cells – each cells connects to up to 10,000 other nerve cells --At age 70, a person retains about 98% of their nerve cells --The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain s ...
... --The average brain is about the size of a grapefruit --About 3 lbs in weight --100 billion nerve cells – each cells connects to up to 10,000 other nerve cells --At age 70, a person retains about 98% of their nerve cells --The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain s ...
Chapter 12 – Introduction to the Nervous System
... Afferent vs Efferent Nervous pathways are organized into division based on the direction they carry information • Afferent division: incoming information ...
... Afferent vs Efferent Nervous pathways are organized into division based on the direction they carry information • Afferent division: incoming information ...
Functions of the Nervous System
... Conception: a kind of protein molecules that produced by the tissue( such as muscle ) and astrocytes, and is the necessary substance to the neuron survival and growth. Action mode: Neurotrophin enter into the terminal of axon by endocytosis, then reach to cell body by retrograde ...
... Conception: a kind of protein molecules that produced by the tissue( such as muscle ) and astrocytes, and is the necessary substance to the neuron survival and growth. Action mode: Neurotrophin enter into the terminal of axon by endocytosis, then reach to cell body by retrograde ...
Unit Outline_Ch17 - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
11 Func[ons of the Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System
... – Myelin sheath gaps between adjacent Schwann cells – Sites where axon collaterals can emerge ...
... – Myelin sheath gaps between adjacent Schwann cells – Sites where axon collaterals can emerge ...
Nervous System Notes
... How a Nerve Impulse Travels • Nerve impulses can travels as fast as 120 meters per second! THAT’S FAST! • Messages travel from the Cell Body, down the axon, and to the axon tips! ...
... How a Nerve Impulse Travels • Nerve impulses can travels as fast as 120 meters per second! THAT’S FAST! • Messages travel from the Cell Body, down the axon, and to the axon tips! ...
Somatic Sensory System
... • Varies 20 fold throughout body • Fingertips have highest resolution – Due to high density of mechanoreceptors – Receptor subtypes with small receptive fields – More cortical neurons dedicated to deciphering sensory information ...
... • Varies 20 fold throughout body • Fingertips have highest resolution – Due to high density of mechanoreceptors – Receptor subtypes with small receptive fields – More cortical neurons dedicated to deciphering sensory information ...
Neurotransmitters
... • At the terminal buttons, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse and passed along to the dendrites of the next neuron. • If enough neurotransmitters have been sent, the next neuron will fire. If not, the message ends. This is called the all-or-nothing ...
... • At the terminal buttons, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse and passed along to the dendrites of the next neuron. • If enough neurotransmitters have been sent, the next neuron will fire. If not, the message ends. This is called the all-or-nothing ...