Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... cells, neurons of the retina, and sensory neurons of the inner ear. c. Unipolar neurons have only a single process leading away from the soma; they are represented by the neurons that carry sensory signals to the spinal cord. i. They are also called pseudounipolar because they start out embryonicall ...
... cells, neurons of the retina, and sensory neurons of the inner ear. c. Unipolar neurons have only a single process leading away from the soma; they are represented by the neurons that carry sensory signals to the spinal cord. i. They are also called pseudounipolar because they start out embryonicall ...
Psy101 Brain.lst
... Explain the anatomy of a neuron including: dendrite, soma, axon, myelin sheath, axon terminal, terminal buttons/synaptic vesicles and synapse. Give an example of how a message travels through the neuron. ...
... Explain the anatomy of a neuron including: dendrite, soma, axon, myelin sheath, axon terminal, terminal buttons/synaptic vesicles and synapse. Give an example of how a message travels through the neuron. ...
Neuroscience - Instructional Resources
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
Histology of Nerve the Nervous System
... system,consisting of the brain and the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system,composed of nerve fibers and small aggregates of nerve cells called nerve ganglia Structurally,nerve tissue consists of two cell types:nerve cells,or neurons, Usually show numerous long processes, and several types ...
... system,consisting of the brain and the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system,composed of nerve fibers and small aggregates of nerve cells called nerve ganglia Structurally,nerve tissue consists of two cell types:nerve cells,or neurons, Usually show numerous long processes, and several types ...
Properties of Neuronal circuits
... –6o order –Innervated by simple cells –Straight bars or borders at specific angles –Do not have topographically fixed RF •Correct stimulus anywhere on retina –Bars of specific orientation –On one side/off other –Border moving in only one direction ...
... –6o order –Innervated by simple cells –Straight bars or borders at specific angles –Do not have topographically fixed RF •Correct stimulus anywhere on retina –Bars of specific orientation –On one side/off other –Border moving in only one direction ...
File
... There is always more than one neuron involved in the transmission of a nerve impulse from its origin to its destination, whether it is sensory or motor. There is no physical contact between these neurons. The point at which the nerve impulse passes from one to another is the synapse. There are the j ...
... There is always more than one neuron involved in the transmission of a nerve impulse from its origin to its destination, whether it is sensory or motor. There is no physical contact between these neurons. The point at which the nerve impulse passes from one to another is the synapse. There are the j ...
Packet 6- The neuron
... The action potential is a rapid change in the membrane potential that spreads quickly along the cell membrane of a neuron. A signal is transmitted when a STIMULUS triggers a neuron…and causes an ACTION POTENTIAL (aka nerve impulse). The action potential was discovered in 1952 by Huxley and Hodgkin a ...
... The action potential is a rapid change in the membrane potential that spreads quickly along the cell membrane of a neuron. A signal is transmitted when a STIMULUS triggers a neuron…and causes an ACTION POTENTIAL (aka nerve impulse). The action potential was discovered in 1952 by Huxley and Hodgkin a ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... •Neurotransmitters are synthesized and packaged into vesicles within the varicosities. •Presynaptic receptors can modulate release. Facilitate or inhibit it. •Substances are co-released along with transmitters. ...
... •Neurotransmitters are synthesized and packaged into vesicles within the varicosities. •Presynaptic receptors can modulate release. Facilitate or inhibit it. •Substances are co-released along with transmitters. ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary and Nervous Systems
... Cell body – contains nucleus and other cell organelles, helps pass impulse along Axon – extension off cell body which impulse travels down Terminal branches – contains synaptic knobs Synaptic knobs – impulse is released here across the synapse to another neuron Myelin sheath – layer of fat that insu ...
... Cell body – contains nucleus and other cell organelles, helps pass impulse along Axon – extension off cell body which impulse travels down Terminal branches – contains synaptic knobs Synaptic knobs – impulse is released here across the synapse to another neuron Myelin sheath – layer of fat that insu ...
The peripheral nerves
... Type A fibers carry sensory information to the CNS concerning position, balance, and delicate touch and pressure sensations from the surface of the skin. The motor neurons that control skeletal muscles also send their commands over large, myelinated Type A axons. Type B fibers and Type C fibers carr ...
... Type A fibers carry sensory information to the CNS concerning position, balance, and delicate touch and pressure sensations from the surface of the skin. The motor neurons that control skeletal muscles also send their commands over large, myelinated Type A axons. Type B fibers and Type C fibers carr ...
nervous system 2 notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... certain stimulus (you have NO control over it). ...
... certain stimulus (you have NO control over it). ...
Exploring the Human Nervous System
... sheaths produced by Schwann cells. Small axons lack a myelin sheath. Neurons in the PNS can regenerate because they are myelinated by Schwann cells. Neurons in the CNS are myelinated by different cells and cannot regenerate. ...
... sheaths produced by Schwann cells. Small axons lack a myelin sheath. Neurons in the PNS can regenerate because they are myelinated by Schwann cells. Neurons in the CNS are myelinated by different cells and cannot regenerate. ...
How Many Cell Types Does It Take to Wire a Brain?
... via the Cx3cr1 fractalkine receptor (left). Microglia prune elements (center) and then return to a resting state near maintained elements (right). (B) In an alternative model, fractalkine signaling globally activates microglia, but a more local, ...
... via the Cx3cr1 fractalkine receptor (left). Microglia prune elements (center) and then return to a resting state near maintained elements (right). (B) In an alternative model, fractalkine signaling globally activates microglia, but a more local, ...
embj201593518-sup-0001
... synapse. In order to measure the density of presynaptic vesicles in the CA3 region, given that some MFTs were not fully included in the image due to the high complexity of these structures in this zone, a squared region of interest (ROI) was used to count the number of vesicles and to calculate the ...
... synapse. In order to measure the density of presynaptic vesicles in the CA3 region, given that some MFTs were not fully included in the image due to the high complexity of these structures in this zone, a squared region of interest (ROI) was used to count the number of vesicles and to calculate the ...
Slide ()
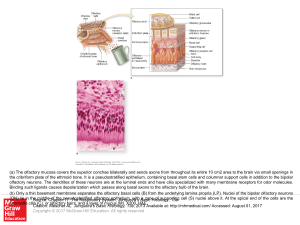
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
The Nervous System
... • Interneurons (association neurons) – Lie between motor and sensory neurons – Shuttle signals through CNS pathways; most are entirely within CNS – 99% of body's neurons – Most confined in CNS ...
... • Interneurons (association neurons) – Lie between motor and sensory neurons – Shuttle signals through CNS pathways; most are entirely within CNS – 99% of body's neurons – Most confined in CNS ...
3 Types of Muscle Tissue SKELETAL MUSCLE CARDIAC MUSCLE
... Multinucleated due to being very active Cylindrical shape Voluntary control ...
... Multinucleated due to being very active Cylindrical shape Voluntary control ...
Composition of the Nervous System
... -At the boundaries of this system are sensory cells, which through the process of transduction collect the information about the environment (external and internal) and motor neurons that via excitation – contraction coupling and muscles and glands act upon the environment. In between are the interm ...
... -At the boundaries of this system are sensory cells, which through the process of transduction collect the information about the environment (external and internal) and motor neurons that via excitation – contraction coupling and muscles and glands act upon the environment. In between are the interm ...
Nervous System ppt
... 1. Sensory: carry impulse from sense organ to spinal chord and brain 2. Motor: carry impulse from brain and spinal chord to muscles and glands 3. Interneurons: connect sensory and motor and carry impulses in between ...
... 1. Sensory: carry impulse from sense organ to spinal chord and brain 2. Motor: carry impulse from brain and spinal chord to muscles and glands 3. Interneurons: connect sensory and motor and carry impulses in between ...
Module 3:Neural conduction and transmission Lecture 13
... cytoplasm of the neuron is contained in the soma. Dentrites come out from the soma and carry message into the neurons. Dendrites have small bumps known as dendritic spines which can receive signals from other neurons. Axon is the extension carrying signals from cell body to the terminal buttons at t ...
... cytoplasm of the neuron is contained in the soma. Dentrites come out from the soma and carry message into the neurons. Dendrites have small bumps known as dendritic spines which can receive signals from other neurons. Axon is the extension carrying signals from cell body to the terminal buttons at t ...
Nervous System - mr-youssef-mci
... How do electrical signals pass through cells? Membrane Potential glial cells provide insulation for electrical ...
... How do electrical signals pass through cells? Membrane Potential glial cells provide insulation for electrical ...
Lecture 3 NS_2015
... gates conduct more readily in one direction than in another -Also transmit metabolic signals between cells -Connexon channels (2 connexons of the coupled cells, with a 1.5 nm pore) open and close randomly, with a higher probability to open when there is an elevated level of intracellular Ca2+ or H+ ...
... gates conduct more readily in one direction than in another -Also transmit metabolic signals between cells -Connexon channels (2 connexons of the coupled cells, with a 1.5 nm pore) open and close randomly, with a higher probability to open when there is an elevated level of intracellular Ca2+ or H+ ...
Frequently asked questions Psychology 1010.06M A Biologically-Oriented
... Glia support cells – provide insulation • increase speed of neurons ...
... Glia support cells – provide insulation • increase speed of neurons ...