PDF
... During postnatal growth, satellite cells (skeletal muscle stem cells) divide to provide new myonuclei for growing muscle fibres, but in adult muscle they are maintained in an undifferentiated quiescent state except during muscle regeneration. Notch signalling regulates stem cells in many tissues, in ...
... During postnatal growth, satellite cells (skeletal muscle stem cells) divide to provide new myonuclei for growing muscle fibres, but in adult muscle they are maintained in an undifferentiated quiescent state except during muscle regeneration. Notch signalling regulates stem cells in many tissues, in ...
PDF
... During postnatal growth, satellite cells (skeletal muscle stem cells) divide to provide new myonuclei for growing muscle fibres, but in adult muscle they are maintained in an undifferentiated quiescent state except during muscle regeneration. Notch signalling regulates stem cells in many tissues, in ...
... During postnatal growth, satellite cells (skeletal muscle stem cells) divide to provide new myonuclei for growing muscle fibres, but in adult muscle they are maintained in an undifferentiated quiescent state except during muscle regeneration. Notch signalling regulates stem cells in many tissues, in ...
PDF
... During postnatal growth, satellite cells (skeletal muscle stem cells) divide to provide new myonuclei for growing muscle fibres, but in adult muscle they are maintained in an undifferentiated quiescent state except during muscle regeneration. Notch signalling regulates stem cells in many tissues, in ...
... During postnatal growth, satellite cells (skeletal muscle stem cells) divide to provide new myonuclei for growing muscle fibres, but in adult muscle they are maintained in an undifferentiated quiescent state except during muscle regeneration. Notch signalling regulates stem cells in many tissues, in ...
Slide 1
... The second action potential causes depolarization in its adjacent region, triggering yet another action potential. This sequence continues all the way to the end of the axon at full strength. ...
... The second action potential causes depolarization in its adjacent region, triggering yet another action potential. This sequence continues all the way to the end of the axon at full strength. ...
Lab Report
... Objective: You will observe different cell types found in living organisms and compare the cell structure to its function. You will explain the similarities and differences amongst these cell types and describe how their structure relates to their function. Part One: Skeletal (Striated) Muscle There ...
... Objective: You will observe different cell types found in living organisms and compare the cell structure to its function. You will explain the similarities and differences amongst these cell types and describe how their structure relates to their function. Part One: Skeletal (Striated) Muscle There ...
Abstract Background Preliminary Data Hypothesis
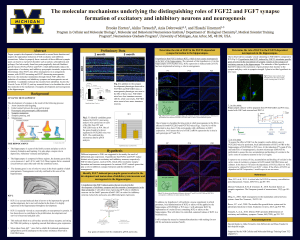
... active zone of excitatory neurons in the CA3 region. I expect to see a rescue of size, accumulation and docking of vesicles in the active zone of excitatory synapses in IGF2 treated FGF22KO mice and cultures. In the future I will assess the dependence of FGF22 effects on IGF2 ...
... active zone of excitatory neurons in the CA3 region. I expect to see a rescue of size, accumulation and docking of vesicles in the active zone of excitatory synapses in IGF2 treated FGF22KO mice and cultures. In the future I will assess the dependence of FGF22 effects on IGF2 ...
Document
... • Most postnatal brain growth occurs within 3 to 4 years • But changes in myelination occurs well into aging, as late as 70-80 years ...
... • Most postnatal brain growth occurs within 3 to 4 years • But changes in myelination occurs well into aging, as late as 70-80 years ...
In This Issue - The Journal of Cell Biology
... leading to shorter axons. Microtubules are also essential for fundamental cellular processes such as mitotic spindle assembly, so it is unclear how pmn mutant mice manage to develop normally. One possibility is that neuron-specific isoforms of tubulin may have a more stringent requirement for CofE d ...
... leading to shorter axons. Microtubules are also essential for fundamental cellular processes such as mitotic spindle assembly, so it is unclear how pmn mutant mice manage to develop normally. One possibility is that neuron-specific isoforms of tubulin may have a more stringent requirement for CofE d ...
Chapter 3
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
... Figure 3.10 Integration of Excitatory and Inhibitory Inputs ...
... Figure 3.10 Integration of Excitatory and Inhibitory Inputs ...
neurons
... Note the similarities in the above brain regions, which are all engaged in information processing. ...
... Note the similarities in the above brain regions, which are all engaged in information processing. ...
Structures and Functions Lecture 2
... • Synaptotagmin protein binds Ca2+ and promotes fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
... • Synaptotagmin protein binds Ca2+ and promotes fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
New Insights into Neuron-Glia Communication
... environment shared by these two cell types. Advanced imaging methods, which allow observation of changes in intracellular and extracellular signaling molecules in real time, show that glia communicate with one another and with neurons primarily through chemical signals rather than electrical signals ...
... environment shared by these two cell types. Advanced imaging methods, which allow observation of changes in intracellular and extracellular signaling molecules in real time, show that glia communicate with one another and with neurons primarily through chemical signals rather than electrical signals ...
m5zn_aeb235b83927ffb
... callosum facilitates communication between the hemispheres, enabling them to process information together. Under the corpus callosum, groups of neurons called the basal nuclei are important in motor coordination. If they are damaged, a person may be immobilized. Degeneration of the basal nuclei ...
... callosum facilitates communication between the hemispheres, enabling them to process information together. Under the corpus callosum, groups of neurons called the basal nuclei are important in motor coordination. If they are damaged, a person may be immobilized. Degeneration of the basal nuclei ...
REGULATION
... the outside and the polarity is returned back to that of the resting neuron. IV. Transmission at the synapse A. During impulse (electrical energy), a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine and norepinephrine, is released into the synaptic cleft (space between 2 neurons). B. The electrical impulse is now co ...
... the outside and the polarity is returned back to that of the resting neuron. IV. Transmission at the synapse A. During impulse (electrical energy), a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine and norepinephrine, is released into the synaptic cleft (space between 2 neurons). B. The electrical impulse is now co ...
Central Nervous System Honors Biology Mr. Lee Room 320
... dendrite or cell body of another – Neurotransmitters: • Chemicals that are released in the synaptic cleft • They cause electrical activity in the second neuron ...
... dendrite or cell body of another – Neurotransmitters: • Chemicals that are released in the synaptic cleft • They cause electrical activity in the second neuron ...
Anat3_01_Nervous_Tissue
... The axon propagates nerve impulses toward another neuron, muscle fiber, or gland cell. Long, thin, cylindrical projection that often joins the cell body at a cone-shaped elevation called the axon hillock (= small hill). The part of the axon closest to the hillock is the initial segment. The ...
... The axon propagates nerve impulses toward another neuron, muscle fiber, or gland cell. Long, thin, cylindrical projection that often joins the cell body at a cone-shaped elevation called the axon hillock (= small hill). The part of the axon closest to the hillock is the initial segment. The ...
Handout - Science in the News
... Membrane voltage: Electrical force due to the imbalance of ions inside and outside of a neuron. This voltage is affected by neurotransmitters and changes rapidly when the neuron “fires” an action potential. Neuron: Nerve cell. Neurotransmitter: Chemicals that neurons use to send signals from one neu ...
... Membrane voltage: Electrical force due to the imbalance of ions inside and outside of a neuron. This voltage is affected by neurotransmitters and changes rapidly when the neuron “fires” an action potential. Neuron: Nerve cell. Neurotransmitter: Chemicals that neurons use to send signals from one neu ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
Document
... Solution: Cholinesterase (an enzyme released into synaptic cleft) breaks down acetylcholine. Once sodium channels close, the neuron begins recovery. ...
... Solution: Cholinesterase (an enzyme released into synaptic cleft) breaks down acetylcholine. Once sodium channels close, the neuron begins recovery. ...
1. A unicellular protest may use a contractile vacuole to expel
... 28. After the depolarization of an action potential, the fall in the membrane potential occurs due to the a. Closing of sodium inactivation gates. b. Closing of potassium and sodium channels. c. Refractory ...
... 28. After the depolarization of an action potential, the fall in the membrane potential occurs due to the a. Closing of sodium inactivation gates. b. Closing of potassium and sodium channels. c. Refractory ...
Nervous system notes - FISD Teacher Web Sites
... _____________________ - the basic structural unit of the nervous system Consists of: o _______________ - contains the nucleus o _______________ - nerve fibers (carries impulses ___________ the cell body) o _______________ - single nerve fiber (carries impulses ___________ from the cell body) The N ...
... _____________________ - the basic structural unit of the nervous system Consists of: o _______________ - contains the nucleus o _______________ - nerve fibers (carries impulses ___________ the cell body) o _______________ - single nerve fiber (carries impulses ___________ from the cell body) The N ...
A real-time model of the cerebellar circuitry underlying classical
... We have demonstrated that a model, which re#ects basic properties of the cerebellum, can acquire and retain CRs where only one parameter, the duration of the PF-Pu synapse response, can control the ISI range where e!ective acquisition can take place. We have shown that this model can be generalized ...
... We have demonstrated that a model, which re#ects basic properties of the cerebellum, can acquire and retain CRs where only one parameter, the duration of the PF-Pu synapse response, can control the ISI range where e!ective acquisition can take place. We have shown that this model can be generalized ...