module b6: brain and mind – overview
... How the human brain functions remains largely unknown. Neuroscience is an area at the frontiers of medical research, and has huge potential impact for an aging population. This module begins by looking at how, in order to survive, simple organisms respond to changes in their environment. The nervous ...
... How the human brain functions remains largely unknown. Neuroscience is an area at the frontiers of medical research, and has huge potential impact for an aging population. This module begins by looking at how, in order to survive, simple organisms respond to changes in their environment. The nervous ...
lecture-4-post
... Neurons are cells that communicate within the nervous system 10-100 billion in the brain alone, each communicating with thousands of others ...
... Neurons are cells that communicate within the nervous system 10-100 billion in the brain alone, each communicating with thousands of others ...
ADAM Nervous System Ion Channels Use this program only if you
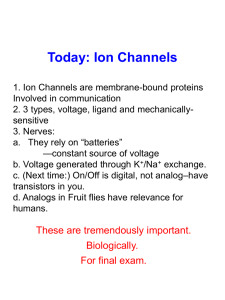
... 3. What is the numerical value and unit for the resting membrane potential? 4. What is the “job” of the Na/K pump in a neuron membrane? Action Potential 5. What is an action potential? 6. What causes the action potential? 7. What is depolarization? 8. Diagram the positive feedback loop that causes t ...
... 3. What is the numerical value and unit for the resting membrane potential? 4. What is the “job” of the Na/K pump in a neuron membrane? Action Potential 5. What is an action potential? 6. What causes the action potential? 7. What is depolarization? 8. Diagram the positive feedback loop that causes t ...
The Nervous System
... ▫ proprioceptors (muscle sense, position, movement) ▫ Motor/Efferent: carry messages from CNS to effectors; dendrites are stimulated by other neurons and axons are connected to effectors (muscles and glands); multipolar ▫ Association/Interneurons: carry impulses from one neuron to another (afferent ...
... ▫ proprioceptors (muscle sense, position, movement) ▫ Motor/Efferent: carry messages from CNS to effectors; dendrites are stimulated by other neurons and axons are connected to effectors (muscles and glands); multipolar ▫ Association/Interneurons: carry impulses from one neuron to another (afferent ...
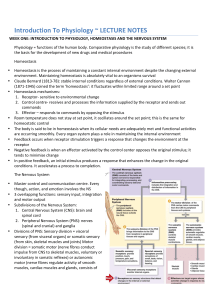
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
1 1. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the A. brain and
... usually caused by damage to the cerebrum during gestation or birth trauma but can also be hereditary. A. Conjunctivitis B. Epilepsy C. Multiple sclerosis D. Cerebral palsy E. Parkinson disease ...
... usually caused by damage to the cerebrum during gestation or birth trauma but can also be hereditary. A. Conjunctivitis B. Epilepsy C. Multiple sclerosis D. Cerebral palsy E. Parkinson disease ...
striated.
... The elongated fibers of skeletal muscle are striated. The striations are dark and light stripes along the muscle cell due to the arrangement of the protein filaments, or myofilaments within the muscle fiber. Contractions of skeletal muscle can be regulated by conscious control, therefore, it is cons ...
... The elongated fibers of skeletal muscle are striated. The striations are dark and light stripes along the muscle cell due to the arrangement of the protein filaments, or myofilaments within the muscle fiber. Contractions of skeletal muscle can be regulated by conscious control, therefore, it is cons ...
Spinal Cord - Northside Middle School
... of contractions, acts a stress hormone by increasing heart rate, triggering release of glucose from storage, increase blood flow to skeletal muscle -too much associated with schizophrenia, and too little associated with ADHD and depression ...
... of contractions, acts a stress hormone by increasing heart rate, triggering release of glucose from storage, increase blood flow to skeletal muscle -too much associated with schizophrenia, and too little associated with ADHD and depression ...
notes as
... and bind to receptor molecules in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron thus changing their shape. – This opens up holes that allow specific ions in or out. • The effectiveness of the synapse can be changed – vary the number of vesicles of transmitter – vary the number of receptor molecules. • Syn ...
... and bind to receptor molecules in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron thus changing their shape. – This opens up holes that allow specific ions in or out. • The effectiveness of the synapse can be changed – vary the number of vesicles of transmitter – vary the number of receptor molecules. • Syn ...
Right vestibular nucleus
... brain via 10 to 20 afferent fibers (through a ribbon synapse) of the spiral ganglion of the 8th cranial nerve. Outer hair cells have both sensory and motor capabilities and possess electromotility that underlies their active process. They have sparse afferent innervation (5-10% of spiral ganglia neu ...
... brain via 10 to 20 afferent fibers (through a ribbon synapse) of the spiral ganglion of the 8th cranial nerve. Outer hair cells have both sensory and motor capabilities and possess electromotility that underlies their active process. They have sparse afferent innervation (5-10% of spiral ganglia neu ...
Simplified view of how a neuron sends a signal
... Note in Figure 2A that there is a very narrow space between the target cell and the tips of the neuron's dendrites. That is, the neuron's plasma membrane does not actually touch the target cell's plasma membrane. This tiny area where the two membranes lie so close together is called the synapse. Th ...
... Note in Figure 2A that there is a very narrow space between the target cell and the tips of the neuron's dendrites. That is, the neuron's plasma membrane does not actually touch the target cell's plasma membrane. This tiny area where the two membranes lie so close together is called the synapse. Th ...
Inquiry into Life, Eleventh Edition
... • Communication across synapse • Release of neurotransmitter – Presynaptic axon depolarizes – Calcium channels open and calcium moves in – Causes synaptic vesicles to bind to membrane » Neurotransmitter released into cleft » Diffuses across and binds to postsynaptic receptors • Response of postsynap ...
... • Communication across synapse • Release of neurotransmitter – Presynaptic axon depolarizes – Calcium channels open and calcium moves in – Causes synaptic vesicles to bind to membrane » Neurotransmitter released into cleft » Diffuses across and binds to postsynaptic receptors • Response of postsynap ...
SAC 1 PRACTICE TEST 2017
... 9. Which of the following statements is true regarding the somatosensory cortex? A. The somatosensory cortex receives signals from body areas. B. Nerve impulses are sent from the somatosensory cortex to skeletal muscles in the body. C. The somatosensory cortex folds in on the motor cortex, forming a ...
... 9. Which of the following statements is true regarding the somatosensory cortex? A. The somatosensory cortex receives signals from body areas. B. Nerve impulses are sent from the somatosensory cortex to skeletal muscles in the body. C. The somatosensory cortex folds in on the motor cortex, forming a ...
Lecture 1
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
Stephen Hawking
... disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord. • Motor neurons reach from the brain to the spinal cord and from the spinal cord to the muscles throughout the body. • Stephen Hawking is unable to move or speak* because of a disease called Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis ...
... disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord. • Motor neurons reach from the brain to the spinal cord and from the spinal cord to the muscles throughout the body. • Stephen Hawking is unable to move or speak* because of a disease called Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis ...
The Nervous System
... neurons and used by them to transmit signals to the other neurons A chemical message telling the next cell to fire or not to fire its own action potential More than 200 in our body all with different ...
... neurons and used by them to transmit signals to the other neurons A chemical message telling the next cell to fire or not to fire its own action potential More than 200 in our body all with different ...
hcollectors
... depolarization followed by a wave of repolarization. With the absence of the myelin, the impulse is transmitted continuously throughout the membrane. ...
... depolarization followed by a wave of repolarization. With the absence of the myelin, the impulse is transmitted continuously throughout the membrane. ...
6.5 Nervous system part1
... 5. Then the gates in the potassium channels CLOSE, and the resting potential is re-established by sodium/ potassium pumps and facilitated diffusion. This is called repolarize. ...
... 5. Then the gates in the potassium channels CLOSE, and the resting potential is re-established by sodium/ potassium pumps and facilitated diffusion. This is called repolarize. ...
Nervous System - Serrano High School AP Biology
... Neural impulses are transmitted both chemically and electrically. This can happen because the cell membrane has the ability to pump out certain molecules that have an electrical charge and allow other charged particles in. There is a great diversity of neuron shapes and functions. There are three ty ...
... Neural impulses are transmitted both chemically and electrically. This can happen because the cell membrane has the ability to pump out certain molecules that have an electrical charge and allow other charged particles in. There is a great diversity of neuron shapes and functions. There are three ty ...