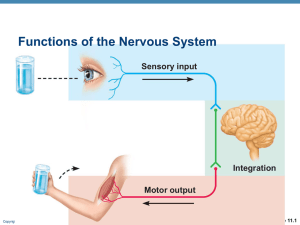
Functions of the Nervous System
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...
ppt - Castle High School
... The presynaptic neuron releases acetylcholine (ACh) from its axon terminals (boutons) when vesicles fuse with the membrane. ...
... The presynaptic neuron releases acetylcholine (ACh) from its axon terminals (boutons) when vesicles fuse with the membrane. ...
The Electrotonic Transformation: a Tool for Relating Neuronal Form
... transformation to the study of associative interactions between “teacher” and “student” synapses by analyzing this cell from the viewpoint of a “student” synapse located in the apical dendrites (Fig. 4A), contrasting this result with a different cell that had a bifurcated primary apical dendrite (ce ...
... transformation to the study of associative interactions between “teacher” and “student” synapses by analyzing this cell from the viewpoint of a “student” synapse located in the apical dendrites (Fig. 4A), contrasting this result with a different cell that had a bifurcated primary apical dendrite (ce ...
Gated Channels
... channels regenerate the action potential at each point along the axon, so voltage does not decay. Conduction is slow because movements of ions and of the gates of channel proteins take time and must occur before voltage regeneration occurs. Stimulus Myelin sheath ...
... channels regenerate the action potential at each point along the axon, so voltage does not decay. Conduction is slow because movements of ions and of the gates of channel proteins take time and must occur before voltage regeneration occurs. Stimulus Myelin sheath ...
Neurology
... Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS. The nervous system consists of two types of cells. Nerve cells are called neurons. The typical neuron is an elongated cell that consists of a cell body, containing the nucleus. Various support cells are associated with the neurons, most typi ...
... Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS. The nervous system consists of two types of cells. Nerve cells are called neurons. The typical neuron is an elongated cell that consists of a cell body, containing the nucleus. Various support cells are associated with the neurons, most typi ...
My Big List Thing
... Cardiac arrythmia (dysrythmia): electric over- or underactivity in heart; beats too slowly or too quickly; can kill or be harmless depending on severity; disposes towards stroke/embolus Cell junction: protein complexes binding cells together, especially common in endothelium Chondrocyte: only cells ...
... Cardiac arrythmia (dysrythmia): electric over- or underactivity in heart; beats too slowly or too quickly; can kill or be harmless depending on severity; disposes towards stroke/embolus Cell junction: protein complexes binding cells together, especially common in endothelium Chondrocyte: only cells ...
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION I Tim Murphy NRSC 500, 2011
... • Therefore Kd=koff/kon, assuming a diffusion limited kon of 5x108 M –1 s –1 then koff must be 5x104 s-1 if the Kd is 100 mM. • To estimate the dissociation time constant take 1/(koff +kon*[Ca]) or 20 ms. Note after the channels close [Ca2+] is ~ 1x10-7 and the kon*[Ca] is small compared to koff. Th ...
... • Therefore Kd=koff/kon, assuming a diffusion limited kon of 5x108 M –1 s –1 then koff must be 5x104 s-1 if the Kd is 100 mM. • To estimate the dissociation time constant take 1/(koff +kon*[Ca]) or 20 ms. Note after the channels close [Ca2+] is ~ 1x10-7 and the kon*[Ca] is small compared to koff. Th ...
Commentary on slides for lecture 15
... of the SR (via voltage gated calcium channels) and causes the myosin and actin filaments to slide past one another and contract. Energy is required for muscle fibers to relax, hence rigor mortis. 2. An adult mammalian muscle fiber is innervated by one presynaptic terminal. If sufficient neurotransmi ...
... of the SR (via voltage gated calcium channels) and causes the myosin and actin filaments to slide past one another and contract. Energy is required for muscle fibers to relax, hence rigor mortis. 2. An adult mammalian muscle fiber is innervated by one presynaptic terminal. If sufficient neurotransmi ...
Neural Induction
... • In Amphibian, the involuting mesoderm (dorsal lip of the blastopore) induces neuronal differentiation of the ectoderm • Transplant of a dorsal blastopore gives rise to a new body axis. Therefore the dorsal lip of the blastopore “organize” the formation of a new body axis. This structure has recei ...
... • In Amphibian, the involuting mesoderm (dorsal lip of the blastopore) induces neuronal differentiation of the ectoderm • Transplant of a dorsal blastopore gives rise to a new body axis. Therefore the dorsal lip of the blastopore “organize” the formation of a new body axis. This structure has recei ...
Nervous System • Steers, controls and watches over our bodily
... The efferent pathway also consists of two neurons – one down the spinal cord to the required level of the spine, the second from the ventral section of the spinal cord to the effector tissue (muscle, organ or gland). The final connection between this second effector neuron (motor neuron) and the req ...
... The efferent pathway also consists of two neurons – one down the spinal cord to the required level of the spine, the second from the ventral section of the spinal cord to the effector tissue (muscle, organ or gland). The final connection between this second effector neuron (motor neuron) and the req ...
Unit 1 – Nervous and Endocrine System
... Number the following events of the reflex arc in the correct order. ____ Motor neuron activates the muscle cell to contract. ____Sensory information is received by interneurons in the spinal cord. ____Sensory information is relayed to the motor neuron. ____Sensory information is relayed from the sen ...
... Number the following events of the reflex arc in the correct order. ____ Motor neuron activates the muscle cell to contract. ____Sensory information is received by interneurons in the spinal cord. ____Sensory information is relayed to the motor neuron. ____Sensory information is relayed from the sen ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... potential cannot produce another action potential behind it. Action potentials are therefore prevented from traveling back toward the cell body. Thus, an action potential that starts at one end of an axon moves in only one direction—toward the synaptic terminals. ...
... potential cannot produce another action potential behind it. Action potentials are therefore prevented from traveling back toward the cell body. Thus, an action potential that starts at one end of an axon moves in only one direction—toward the synaptic terminals. ...
RetinaCircuts
... • Higher convergence of rods than cones – Average of 120 rods to one ganglion cell – Average of 6 cones to one ganglion cell – Cones in fovea have 1 to 1 relation to ...
... • Higher convergence of rods than cones – Average of 120 rods to one ganglion cell – Average of 6 cones to one ganglion cell – Cones in fovea have 1 to 1 relation to ...
VI. The vertebrate nervous system is a hierarchy of structural and
... ⇒ Dendrites convey signals to the cell body; are short, numerous and extensively branched to increase surface area where the cell is most likely to be stimulated. ⇒ Axons conduct impulses away from the cell body; are long, single processes. ◊ Vertebrate axons in PNS are wrapped in concentric layers ...
... ⇒ Dendrites convey signals to the cell body; are short, numerous and extensively branched to increase surface area where the cell is most likely to be stimulated. ⇒ Axons conduct impulses away from the cell body; are long, single processes. ◊ Vertebrate axons in PNS are wrapped in concentric layers ...
Mechanisms of response homeostasis during retinocollicular map
... patterned retinal waves in β2−/− mice prevents the normal developmental strengthening of retinocollicular synapses. Interestingly, the capacity for LTP is preserved in these immature and weak synapses (Shah & Crair, 2008). These results reveal that dynamic, activity-dependent regulation of the capac ...
... patterned retinal waves in β2−/− mice prevents the normal developmental strengthening of retinocollicular synapses. Interestingly, the capacity for LTP is preserved in these immature and weak synapses (Shah & Crair, 2008). These results reveal that dynamic, activity-dependent regulation of the capac ...
MS Word doc here
... Numerous specializations occur in this simple basic organization, so that in fact the muscle spindle is one of the most complex receptor organs in the body. Only three of these specializations are described here; their overall effect is to make the muscle spindle adjustable and give it a dual functi ...
... Numerous specializations occur in this simple basic organization, so that in fact the muscle spindle is one of the most complex receptor organs in the body. Only three of these specializations are described here; their overall effect is to make the muscle spindle adjustable and give it a dual functi ...
Handout_Master_11
... height by age 2. If the continued to grow throughout their life as quickly as they do in the first two years, they would end up more than 12 feet tall. 3. True. The average infant has many more neurons and neural connections than we do, but about half of the neurons produced early in life die. The n ...
... height by age 2. If the continued to grow throughout their life as quickly as they do in the first two years, they would end up more than 12 feet tall. 3. True. The average infant has many more neurons and neural connections than we do, but about half of the neurons produced early in life die. The n ...
Lecture Outline
... potential cannot produce another action potential behind it. Action potentials are therefore prevented from traveling back toward the cell body. Thus, an action potential that starts at one end of an axon moves in only one direction—toward the synaptic terminals. ...
... potential cannot produce another action potential behind it. Action potentials are therefore prevented from traveling back toward the cell body. Thus, an action potential that starts at one end of an axon moves in only one direction—toward the synaptic terminals. ...
Central Nervous System
... the central nervous system. These nerves coordinate messages between all parts of the body and the central nervous system (brain and spine) ...
... the central nervous system. These nerves coordinate messages between all parts of the body and the central nervous system (brain and spine) ...
NERVE SYSTEM The nervous system is divided anatomically into
... folium, forming a sort of tree – extensively branching dendritic system which arborizes into the outer molecular layer (Fig.7). A relatively fine axon extends down through the granular layer to form inhibitory synaptic connections releasing gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) as the neurotransmitter with ...
... folium, forming a sort of tree – extensively branching dendritic system which arborizes into the outer molecular layer (Fig.7). A relatively fine axon extends down through the granular layer to form inhibitory synaptic connections releasing gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) as the neurotransmitter with ...
The Nervous System
... activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
... activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
The Nervous System
... activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
... activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
Document
... participate in the immune response of the brain scar tissue formation following neuronal loss storage of glycogen as an energy reserve in the brain uptake and release of neuroactive compounds buffering of the extracellular ion homeostasis (spatial buffering of K+ ions) participate in the formation o ...
... participate in the immune response of the brain scar tissue formation following neuronal loss storage of glycogen as an energy reserve in the brain uptake and release of neuroactive compounds buffering of the extracellular ion homeostasis (spatial buffering of K+ ions) participate in the formation o ...