Chapter 13
... • Cell body – main cell where organelles and nuclei reside • Dendrite – many, short extensions that carry impulses to a cell body • Receive signals from sensory receptors or other neurons • Signals result in nerve impulses that are conducted by an axon ...
... • Cell body – main cell where organelles and nuclei reside • Dendrite – many, short extensions that carry impulses to a cell body • Receive signals from sensory receptors or other neurons • Signals result in nerve impulses that are conducted by an axon ...
Sam Wangdescribes some of the physics of our most complex organ
... laptop computer. In this sense, we are all dim bulbs. However, efficiency comes at a cost. Synaptic strength may change in an all-or-nothing fashion, but that is only true for measurements of strength averaged over dozens of signalling events. At any given moment, a single synapse can be remarkably ...
... laptop computer. In this sense, we are all dim bulbs. However, efficiency comes at a cost. Synaptic strength may change in an all-or-nothing fashion, but that is only true for measurements of strength averaged over dozens of signalling events. At any given moment, a single synapse can be remarkably ...
12 Physiology of autonomic nervous system
... Generally the two divisions have chains of two motor neurons that innervate same visceral organs but cause essentially opposite effects If one division stimulates certain smooth muscle to contract or a gland to secrete, the other division inhibits that action Through this process of duel innervation ...
... Generally the two divisions have chains of two motor neurons that innervate same visceral organs but cause essentially opposite effects If one division stimulates certain smooth muscle to contract or a gland to secrete, the other division inhibits that action Through this process of duel innervation ...
Nervous system
... Neurons are comprised of a dendrite, a cell body and an axon. Neurons have the amazing ability to gather and transmit electrochemical signals -- they are something like the gates and wires in a computer. pulses travel to the dendrite into the cell body and then onto the axon. Some nerves are covered ...
... Neurons are comprised of a dendrite, a cell body and an axon. Neurons have the amazing ability to gather and transmit electrochemical signals -- they are something like the gates and wires in a computer. pulses travel to the dendrite into the cell body and then onto the axon. Some nerves are covered ...
introduction the neuron doctrine
... nervous system. In some diseases, long stretches of DNA that contain several genes are missing; in others, genes are duplicated, leading to overexpression of specific proteins. These sorts of mishaps, called gene copy number variations, often occur at the moment of conception when paternal and mater ...
... nervous system. In some diseases, long stretches of DNA that contain several genes are missing; in others, genes are duplicated, leading to overexpression of specific proteins. These sorts of mishaps, called gene copy number variations, often occur at the moment of conception when paternal and mater ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 The Central Nervous
... branch is found a terminal knob. Synaptic vesicles (bundles of neurotransmitters) are located within each terminal knob. That portion of the terminal knob that faces the synaptic cleft is thickened and is called the presynaptic membrane. This is the membrane through that neurotransmitters pass to en ...
... branch is found a terminal knob. Synaptic vesicles (bundles of neurotransmitters) are located within each terminal knob. That portion of the terminal knob that faces the synaptic cleft is thickened and is called the presynaptic membrane. This is the membrane through that neurotransmitters pass to en ...
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.131: Introduction to Neuroscience
... potentials—near the resting potential—to evoke vesicle release. c. The receptor potential is very large, peaking near +10 mV, which can open ...
... potentials—near the resting potential—to evoke vesicle release. c. The receptor potential is very large, peaking near +10 mV, which can open ...
The First Open International Symposium
... understood. The Drosophila larval peristalsis is generated by a traveling wave of motor activity from the posterior to anterior segments. The pattern of peristalsis, including rhythm and speed, is remarkably stereotypic, providing an excellent system in which to investigate motor control. We used ca ...
... understood. The Drosophila larval peristalsis is generated by a traveling wave of motor activity from the posterior to anterior segments. The pattern of peristalsis, including rhythm and speed, is remarkably stereotypic, providing an excellent system in which to investigate motor control. We used ca ...
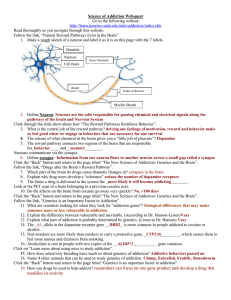
Science of Addiction WebquestKEY
... 2. Define Neuron: Neurons are the cells responsible for passing chemical and electrical signals along the pathways of the brain and Nervous System Click through the slide show about how “The Reward Pathways Reinforce Behavior”. 3. What is the central job of the reward pathway? driving our feelings o ...
... 2. Define Neuron: Neurons are the cells responsible for passing chemical and electrical signals along the pathways of the brain and Nervous System Click through the slide show about how “The Reward Pathways Reinforce Behavior”. 3. What is the central job of the reward pathway? driving our feelings o ...
Body Systems - Bishop Ireton High School
... of the eye) which has an opening called the pupil. Just behind the pupil is the lens, that refracts incoming light. The eyeball itself consists of a large chamber filled with jellylike fluid, the ...
... of the eye) which has an opening called the pupil. Just behind the pupil is the lens, that refracts incoming light. The eyeball itself consists of a large chamber filled with jellylike fluid, the ...
Cognitive Psychology
... properties of neurons, how they share information and what-not, and try to understand how these properties can lead to complex computations. (opponent processes, how feature detectors are calculated). • Computational modeling - Neural networks are computer models of how groups of neurons behave. Use ...
... properties of neurons, how they share information and what-not, and try to understand how these properties can lead to complex computations. (opponent processes, how feature detectors are calculated). • Computational modeling - Neural networks are computer models of how groups of neurons behave. Use ...
The skin performs all of the following except
... Explain what an action potential is? K+ ions are entering the neuron Negatively charged proteins are leaving the neuron Na+ ions are entering the neuron The myelin coat has broken down and ions are ...
... Explain what an action potential is? K+ ions are entering the neuron Negatively charged proteins are leaving the neuron Na+ ions are entering the neuron The myelin coat has broken down and ions are ...
Nerve Impulses and Action Potential
... 6 Initial ionic conditions restored. The ionic conditions of the resting state are restored later by the activity of the sodium-potassium pump. Three sodium ions are ejected for every two potassium ions carried back into the cell. ...
... 6 Initial ionic conditions restored. The ionic conditions of the resting state are restored later by the activity of the sodium-potassium pump. Three sodium ions are ejected for every two potassium ions carried back into the cell. ...
The Muscular System
... The Human Muscular System • a human has 600 muscles making up over 40% of your total body weight!! • the overall responsibility of the muscles is to provide movement, but also ...
... The Human Muscular System • a human has 600 muscles making up over 40% of your total body weight!! • the overall responsibility of the muscles is to provide movement, but also ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... From the Retina to the Visual Cortex The axons of ganglion cells in the retina assemble to form the optic nerves that carry nerve impulses from the eyes to the optic chiasma. The optic tracts synapse with neurons in nuclei within the thalamus, which then take nerve impulses to the visual area within ...
... From the Retina to the Visual Cortex The axons of ganglion cells in the retina assemble to form the optic nerves that carry nerve impulses from the eyes to the optic chiasma. The optic tracts synapse with neurons in nuclei within the thalamus, which then take nerve impulses to the visual area within ...
Nervous System - An-Najah Staff - An
... • Channel-linked receptors that open ion channels, leading to fast changes in membrane potential, or • G protein–coupled receptors that oversee slow synaptic responses mediated by G proteins and intracellular second messengers. Second messengers most often activate kinases, which in turn act on io ...
... • Channel-linked receptors that open ion channels, leading to fast changes in membrane potential, or • G protein–coupled receptors that oversee slow synaptic responses mediated by G proteins and intracellular second messengers. Second messengers most often activate kinases, which in turn act on io ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM GENERALITY – INTRODUCTION
... • maintaining the bloodblood-brain barrier that isolates the CNS • creating a 3-dimensional framework for the CNS • repairing damaged neural tissue • guiding neuron development • controlling the interstitial environment ...
... • maintaining the bloodblood-brain barrier that isolates the CNS • creating a 3-dimensional framework for the CNS • repairing damaged neural tissue • guiding neuron development • controlling the interstitial environment ...
Pain
... Guidance cues for growth cones advancing to their synaptic targets Interactions between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells that organize development of the neuromuscular junction Elimination of polysynaptic innervation during development Similarities and dissimilarities between development of c ...
... Guidance cues for growth cones advancing to their synaptic targets Interactions between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells that organize development of the neuromuscular junction Elimination of polysynaptic innervation during development Similarities and dissimilarities between development of c ...
Part 1: From Ion Channels to behavior, HT2009 Course
... Guidance cues for growth cones advancing to their synaptic targets Interactions between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells that organize development of the neuromuscular junction Elimination of polysynaptic innervation during development Similarities and dissimilarities between development of c ...
... Guidance cues for growth cones advancing to their synaptic targets Interactions between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells that organize development of the neuromuscular junction Elimination of polysynaptic innervation during development Similarities and dissimilarities between development of c ...
Printable version
... A. basic principles of electricity 1. the difference in two voltages is called the potential 2. in the body, electrical charges are provided by ions B. resting membrane potential 1. a resting neuron has an internal potential of about -70mV 2. the potential is due to the difference in the sodium and ...
... A. basic principles of electricity 1. the difference in two voltages is called the potential 2. in the body, electrical charges are provided by ions B. resting membrane potential 1. a resting neuron has an internal potential of about -70mV 2. the potential is due to the difference in the sodium and ...
CORTEX I. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS a. Cerebral cortex = grey
... ii. Layers 2 &3 – small pyramidal cells – do not project outside of cortex For each layer, know: iii. Layer 4 – many small spiny stellate cells; main input layer for thalamocortical 1) What cells axons; do not project out of cortex (project to other nearby layers) 2) Input *Striate (primary visual c ...
... ii. Layers 2 &3 – small pyramidal cells – do not project outside of cortex For each layer, know: iii. Layer 4 – many small spiny stellate cells; main input layer for thalamocortical 1) What cells axons; do not project out of cortex (project to other nearby layers) 2) Input *Striate (primary visual c ...
Document
... – olfactory hairs neurons with 20 cilia • bind odor molecules in thin layer of mucus ...
... – olfactory hairs neurons with 20 cilia • bind odor molecules in thin layer of mucus ...
Chapter 16 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... – olfactory hairs neurons with 20 cilia • bind odor molecules in thin layer of mucus ...
... – olfactory hairs neurons with 20 cilia • bind odor molecules in thin layer of mucus ...
Nervous and Muscular System
... information from the rest of the body to the cerebral cortex; regulates autonomic functions (body temperature, heart rate and blood pressure); expression of emotions; and regulation of food and water intake ...
... information from the rest of the body to the cerebral cortex; regulates autonomic functions (body temperature, heart rate and blood pressure); expression of emotions; and regulation of food and water intake ...