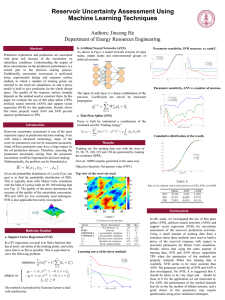
PDF - Timetree.org
... Mosses are distinguished by multicellular gametophytic rhizoids, gametophytic leaves, and a particular spermatozoid ultrastructure. Hornworts posses many unique features, including a distinctively shaped apical cell, a pyrenoid in chloroplasts, mucilage cells and cavities in the talus, and an interc ...
... Mosses are distinguished by multicellular gametophytic rhizoids, gametophytic leaves, and a particular spermatozoid ultrastructure. Hornworts posses many unique features, including a distinctively shaped apical cell, a pyrenoid in chloroplasts, mucilage cells and cavities in the talus, and an interc ...
Using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) - bio-bio-1
... Like FASTA, the BLAST algorithm increases the speed of sequence alignment by searching first for common words or k-tuples in the query sequence and each database sequence. Whereas FASTA searches for all possible words of the same length, BLAST confines the search to the words that are the most sign ...
... Like FASTA, the BLAST algorithm increases the speed of sequence alignment by searching first for common words or k-tuples in the query sequence and each database sequence. Whereas FASTA searches for all possible words of the same length, BLAST confines the search to the words that are the most sign ...
chapter8
... process time that is memory less. • Weibull: time to failure for components. • Discrete or continuous uniform: models complete uncertainty. • Triangular: a process for which only the minimum, most likely, and maximum values are known. • Empirical: resample's from the actual data collected ...
... process time that is memory less. • Weibull: time to failure for components. • Discrete or continuous uniform: models complete uncertainty. • Triangular: a process for which only the minimum, most likely, and maximum values are known. • Empirical: resample's from the actual data collected ...
Bayesian analysis of genetic population structure using BAPS
... parameter (= choosing clustering model in BAPS) 3. Individuals sampled fairly continuously from the population with relevant known geographical coordinates. Choose ’Spatial clustering of individuals’. 4. Groups of individuals known to belong to the same deme are sampled with relevant known geographi ...
... parameter (= choosing clustering model in BAPS) 3. Individuals sampled fairly continuously from the population with relevant known geographical coordinates. Choose ’Spatial clustering of individuals’. 4. Groups of individuals known to belong to the same deme are sampled with relevant known geographi ...
Perspective Motion Segmentation via Collaborative Clustering
... of the camera projection, and its multi-frame extension does not suffer from the restriction of requiring features to be present in all frames. While projective factorization [17] extends the camera model to perspective, it needs an iterative process that alternates between the estimation of the de ...
... of the camera projection, and its multi-frame extension does not suffer from the restriction of requiring features to be present in all frames. While projective factorization [17] extends the camera model to perspective, it needs an iterative process that alternates between the estimation of the de ...
The emergence of individual species
... recipient cell’s genome”. HGT is common between bacteria and causes rapid evolution of bacteria, because they can acquire mutations from multiple parents (4). HGT was thought to be merely a secondary mechanism of evolution, but now it is clear that HGT has strong influence in terms of distribution o ...
... recipient cell’s genome”. HGT is common between bacteria and causes rapid evolution of bacteria, because they can acquire mutations from multiple parents (4). HGT was thought to be merely a secondary mechanism of evolution, but now it is clear that HGT has strong influence in terms of distribution o ...
b. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
... Results shows that using the same amount of training data, SVR and ANN always outperform TPS when the parameters of the methods are properly selected. When less training data is available, SVR seems to be more accurate than ANN. The parameter sensitivity of SVR and ANN is also investigated. For SVR, ...
... Results shows that using the same amount of training data, SVR and ANN always outperform TPS when the parameters of the methods are properly selected. When less training data is available, SVR seems to be more accurate than ANN. The parameter sensitivity of SVR and ANN is also investigated. For SVR, ...
Level Ancestor Level Ancestor
... • Data structure. For each node v, store pointers to ancestors at distance 1,2,4, .. ...
... • Data structure. For each node v, store pointers to ancestors at distance 1,2,4, .. ...
arthropod-success-and-phylogeny 224 kb arthropod-success
... But are these features convergent and analogous, or derived homologies? Originally, taxonomists presumed several distinct lineages had undergone ‘arthropodisation’. For example, the insects and myriapods were thought to be part of the phylum Onychophora (velvet worms), and arthropods in general were ...
... But are these features convergent and analogous, or derived homologies? Originally, taxonomists presumed several distinct lineages had undergone ‘arthropodisation’. For example, the insects and myriapods were thought to be part of the phylum Onychophora (velvet worms), and arthropods in general were ...
NETADIS Research Project Overview The first list below gives the
... used in order to decide which molecular pathway or network structure is more likely to describe a certain biological function in light of a limited amount of experimental data. A Bayesian inference approach in which all unobserved quantities (reaction parameters, states) conditioned on the observati ...
... used in order to decide which molecular pathway or network structure is more likely to describe a certain biological function in light of a limited amount of experimental data. A Bayesian inference approach in which all unobserved quantities (reaction parameters, states) conditioned on the observati ...
CMPS101: Homework #1 Solutions
... The binding of n to internal nodes was simply our choice. Similar proofs may be found in which n represents either the number of leaves or the total number of nodes. These proofs will have different sets of base cases, but the intuition behind the inductive case is identical, namely that the number ...
... The binding of n to internal nodes was simply our choice. Similar proofs may be found in which n represents either the number of leaves or the total number of nodes. These proofs will have different sets of base cases, but the intuition behind the inductive case is identical, namely that the number ...
Lecture 8: Advanced Clustering
... The k-means algorithm has two steps at each iteration: ◦ Expectation Step (E-step): Given the current cluster centers, each object is assigned to the cluster whose center is closest to the object: An object is expected to belong to the closest cluster ◦ Maximization Step (M-step): Given the cluster ...
... The k-means algorithm has two steps at each iteration: ◦ Expectation Step (E-step): Given the current cluster centers, each object is assigned to the cluster whose center is closest to the object: An object is expected to belong to the closest cluster ◦ Maximization Step (M-step): Given the cluster ...
Girdling Roots: A Problem of Shade Trees Trees can slowly weaken
... tree affected by the girdling root will slowdown in growth. Injury may eventually show up as weakened top growth, short terminal twigs, and smaller, lighter green leaves. The branches will eventually become weakened by strangulation and the tree may die over a period of 5 to 15 years. Good cultural ...
... tree affected by the girdling root will slowdown in growth. Injury may eventually show up as weakened top growth, short terminal twigs, and smaller, lighter green leaves. The branches will eventually become weakened by strangulation and the tree may die over a period of 5 to 15 years. Good cultural ...
Clustering Time-Course Gene
... • Nearest neighbor: Distance between two clusters is the minimum of all distances between all pairs of curves, one from each cluster • Furthest neighbor: Distance between two cluster is the maximum of all distances between all pairs of curves, one from each cluster • Average linkage: Distance betwee ...
... • Nearest neighbor: Distance between two clusters is the minimum of all distances between all pairs of curves, one from each cluster • Furthest neighbor: Distance between two cluster is the maximum of all distances between all pairs of curves, one from each cluster • Average linkage: Distance betwee ...
Archetypal Analysis for Machine Learning
... A and S be orthogonal, in ICA statistical independence is assumed for S and in SC a penalty term is introduced that measures deviation from sparsity on S, while in NMF all variables are constrained non-negative. In hard clustering by K-means S is constrained to be a binary assignment matrix such tha ...
... A and S be orthogonal, in ICA statistical independence is assumed for S and in SC a penalty term is introduced that measures deviation from sparsity on S, while in NMF all variables are constrained non-negative. In hard clustering by K-means S is constrained to be a binary assignment matrix such tha ...
File
... • A graph is a collection of vertices (also called nodes) and edges that connect these vertices. • A graph is often viewed as a generalization of the tree structure, where instead of a having a purely parent-to-child relationship between tree nodes, any kind of complex relationships between the node ...
... • A graph is a collection of vertices (also called nodes) and edges that connect these vertices. • A graph is often viewed as a generalization of the tree structure, where instead of a having a purely parent-to-child relationship between tree nodes, any kind of complex relationships between the node ...