Changes to Earth`s Surface Vocabulary Builder
... 15. fault - a break in Earth’s crust where rocks can slide past each other 16. earthquake - the snap and slide of rocks as energy is released in Earth’s crust 17. focus - the point inside Earth where and earthquake begins 18. epicenter - the point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an ea ...
... 15. fault - a break in Earth’s crust where rocks can slide past each other 16. earthquake - the snap and slide of rocks as energy is released in Earth’s crust 17. focus - the point inside Earth where and earthquake begins 18. epicenter - the point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an ea ...
History of Earth Study Guide
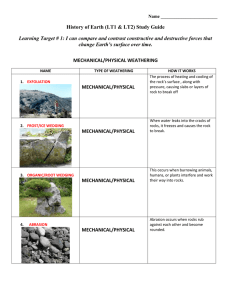
... 2. Define WEATHERING. Wearing or breaking down; physical and chemical 3. Define EROSION. Moving or carrying away sediment; Sand Dunes and Loess are a result of erosion 4. Define DEPOSITION. Settling or laying down sediment 5. How does deposition play a role at the mouth of a river? A river will wide ...
... 2. Define WEATHERING. Wearing or breaking down; physical and chemical 3. Define EROSION. Moving or carrying away sediment; Sand Dunes and Loess are a result of erosion 4. Define DEPOSITION. Settling or laying down sediment 5. How does deposition play a role at the mouth of a river? A river will wide ...
unit 4 landscape development
... 2. _______________________Forces which lower the elevation of the Earth’s surface through subsidence and erosion. - the major cause of leveling is gravity ...
... 2. _______________________Forces which lower the elevation of the Earth’s surface through subsidence and erosion. - the major cause of leveling is gravity ...
review 2nd sem EOC- WIG
... 4. Sketch a river meander and illustrate a point on both sides of the river channel where erosion and deposition occur. Also include on the sketch a cutoff and an oxbow lake. ...
... 4. Sketch a river meander and illustrate a point on both sides of the river channel where erosion and deposition occur. Also include on the sketch a cutoff and an oxbow lake. ...
Tectonics, Dynamics and Geomorphology of the Eastern Tibetan
... with a crustal thickness approaching 70 km, nearly double the thickness of normal continental crust. Large-scale crustal shortening features are absent at the surface and the crust appears to have thickened by eastward flow of weak material within a deep crustal channel, without significant disrupti ...
... with a crustal thickness approaching 70 km, nearly double the thickness of normal continental crust. Large-scale crustal shortening features are absent at the surface and the crust appears to have thickened by eastward flow of weak material within a deep crustal channel, without significant disrupti ...
Getting to Know: Formation of the Earth
... how Earth formed, when it formed, and how it has changed ...
... how Earth formed, when it formed, and how it has changed ...
Unit 1
... Igneous – crystalizing and solidifying of hot molten magma Sedimentary – formed from pre-existing rock pieces or organisms Metamorphic – rocks that have been changed by heat and/or pressure ...
... Igneous – crystalizing and solidifying of hot molten magma Sedimentary – formed from pre-existing rock pieces or organisms Metamorphic – rocks that have been changed by heat and/or pressure ...
molten rock inside the earth`s surface the process of breaking rock
... beneath the crust filled with molten rock ...
... beneath the crust filled with molten rock ...
Physical and Ecological Processes
... A seismograph is a device that detects if an earthquake has occurred. The Richter Scale is a scale used for measuring the intensity of an earthquake. ...
... A seismograph is a device that detects if an earthquake has occurred. The Richter Scale is a scale used for measuring the intensity of an earthquake. ...
Our Changing Earth - Bal Bharati Public School
... Q1. What is the difference between weathering and erosion? Weathering is the breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s surface. Erosion is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind, and ice. Q2. What are endogenic and enogenic forces? The forces which act in the interior o ...
... Q1. What is the difference between weathering and erosion? Weathering is the breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s surface. Erosion is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind, and ice. Q2. What are endogenic and enogenic forces? The forces which act in the interior o ...
8 - Balbharatipp.org
... Q1. What is the difference between weathering and erosion? Weathering is the breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s surface. Erosion is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind, and ice. Q2. What are endogenic and enogenic forces? The forces which act in the interior o ...
... Q1. What is the difference between weathering and erosion? Weathering is the breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s surface. Erosion is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind, and ice. Q2. What are endogenic and enogenic forces? The forces which act in the interior o ...
CGF 3MO - TeacherWeb
... Diagrams – label features of diagrams from last few units; waves, water, glaciers, atmosphere – no word list provided (you need to know them) TIPS FOR STUDYING – Start by taking out all of your old tests. What areas did you do well on? What types of questions gave you difficulty? Look at types o ...
... Diagrams – label features of diagrams from last few units; waves, water, glaciers, atmosphere – no word list provided (you need to know them) TIPS FOR STUDYING – Start by taking out all of your old tests. What areas did you do well on? What types of questions gave you difficulty? Look at types o ...
Chapter 13: Introduction to Landform Study
... 1. topography: surface configuration of Earth 2. landform: individual topographic feature, of whatever size 3. geomorphology: study of the characteristics, origin, and development of landforms 4. relief: difference in elevation between the highest and lowest points in an area a. maximum world relief ...
... 1. topography: surface configuration of Earth 2. landform: individual topographic feature, of whatever size 3. geomorphology: study of the characteristics, origin, and development of landforms 4. relief: difference in elevation between the highest and lowest points in an area a. maximum world relief ...
Section 1 - kjpederson
... 3. gravity: a force that moves rocks and other materials downhill; that force that pulls objects toward each other 4. mass movement: any one of several processes by which gravity moves sediment downhill 5. sediment: small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or organisms; earth materials d ...
... 3. gravity: a force that moves rocks and other materials downhill; that force that pulls objects toward each other 4. mass movement: any one of several processes by which gravity moves sediment downhill 5. sediment: small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or organisms; earth materials d ...
CHAPTER 13 Denudation, weathering and mass wasting
... principal styles of slope instability and failure, with distinctions between rock and debris slopes. The chapter includes a review of debris flow hazard, which appears to be on the increase in temperate climates through changes in land use and climate. Chapter Summary Denudation ...
... principal styles of slope instability and failure, with distinctions between rock and debris slopes. The chapter includes a review of debris flow hazard, which appears to be on the increase in temperate climates through changes in land use and climate. Chapter Summary Denudation ...
A View of Earth - Cloudfront.net
... spheres: the hydrosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, and biosphere Hydrosphere – the water portion of Earth Atmosphere – the gaseous portion of a planet; the planet’s envelope of air Geosphere – layer of Earth under both the atmosphere and the oceans Because the geosphere is not uniform, it is divided i ...
... spheres: the hydrosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, and biosphere Hydrosphere – the water portion of Earth Atmosphere – the gaseous portion of a planet; the planet’s envelope of air Geosphere – layer of Earth under both the atmosphere and the oceans Because the geosphere is not uniform, it is divided i ...
Tectonic And Surface Processes Interaction
... The exogenic processes originate externally to the solid Earth, including water, river, wind, and glacial action on land, and tides, currents, and waves in the ocean. The endogene processes originate within the Earth including volcanic activity, Earthquakes, and horizontal and vertical motions of th ...
... The exogenic processes originate externally to the solid Earth, including water, river, wind, and glacial action on land, and tides, currents, and waves in the ocean. The endogene processes originate within the Earth including volcanic activity, Earthquakes, and horizontal and vertical motions of th ...
The Living Planet PPT
... Erosion Water erosion –Water flows in streams or rivers Erode vertically and horizontally Delta: fan-like landform that occurs when a river enters the ocean –Wave action along coastline Can reduce or increase beaches ...
... Erosion Water erosion –Water flows in streams or rivers Erode vertically and horizontally Delta: fan-like landform that occurs when a river enters the ocean –Wave action along coastline Can reduce or increase beaches ...
Erosion, Transport, Deposition Key Words
... (rocks and stones) freeze-thaw action and rocks broken apart by plant roots. ...
... (rocks and stones) freeze-thaw action and rocks broken apart by plant roots. ...
Science Study Guide What is the hot molten rock
... What is the vibration the spreads out away from a focus when an earthquake happens? ...
... What is the vibration the spreads out away from a focus when an earthquake happens? ...
Document
... 9. Melted and cooled magma or lava is a __________________________ rock. 10. ___________________________rocks are changed by heat and pressure. 11. The outermost layer of the Earth is called the __________________________. 12. The ___________________________ is solid nickel and iron; under extreme h ...
... 9. Melted and cooled magma or lava is a __________________________ rock. 10. ___________________________rocks are changed by heat and pressure. 11. The outermost layer of the Earth is called the __________________________. 12. The ___________________________ is solid nickel and iron; under extreme h ...
Geology Assessment Study Guide
... Geology Assessment Study Guide Test on ____________________ Part 1: History of the Earth ● How old is the earth? ____________________ ...
... Geology Assessment Study Guide Test on ____________________ Part 1: History of the Earth ● How old is the earth? ____________________ ...
Grade 6 Curriculum Map - Bibb County School District
... deposition S6E5f Effects of human activity on erosion S6E5i Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move S6E5e This movement can cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. S6E5e Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, g ...
... deposition S6E5f Effects of human activity on erosion S6E5i Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move S6E5e This movement can cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. S6E5e Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, g ...
Chapter 1 Review - Pattonville Heights Middle School
... What is the name given to one of the Earth’s natural resources that is made of non-living material found beneath the Earth’s surface? ...
... What is the name given to one of the Earth’s natural resources that is made of non-living material found beneath the Earth’s surface? ...
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Greek: γῆ, ge, ""earth""; μορφή, morfé, ""form""; and λόγος, logos, ""study"") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical or chemical processes operating at or near the earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphology is practiced within physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field.