The Nervous System
... Events at the Synapse 1. Arriving action potential depolarizes the synaptic knob and presynaptic membrane 2. Calcium ions enter cytoplasm of knob 3. Neurotransmitter released through diffusion and exocytosis of neurotransmitter vesicles 4. Neurotransmitter goes across synapse and binds to receptor ...
... Events at the Synapse 1. Arriving action potential depolarizes the synaptic knob and presynaptic membrane 2. Calcium ions enter cytoplasm of knob 3. Neurotransmitter released through diffusion and exocytosis of neurotransmitter vesicles 4. Neurotransmitter goes across synapse and binds to receptor ...
Signal transmission at synapses
... 2. Hydrolysis: in the synaptict cleft (restores the resting potential in the postsynaptic membrane) ...
... 2. Hydrolysis: in the synaptict cleft (restores the resting potential in the postsynaptic membrane) ...
Chapter 12 Notes Part 3 File
... – The reversal in polarity causes electrical current to flow between the site of the action potential and the adjacent regions of membrane and triggers voltage-gated Na+ channels in the next segment to open; this next segment exhibits an action potential – This cycle continues to repeat – The action ...
... – The reversal in polarity causes electrical current to flow between the site of the action potential and the adjacent regions of membrane and triggers voltage-gated Na+ channels in the next segment to open; this next segment exhibits an action potential – This cycle continues to repeat – The action ...
Neuro-transmitters
... between brain and behaviour. Included among these areas are the physiological mechanisms associated with the central nervous system. An overall understanding of the anatomy of the brain structure reflects the diversity of the individual’s mental processes and behaviour. Some structures can highlight ...
... between brain and behaviour. Included among these areas are the physiological mechanisms associated with the central nervous system. An overall understanding of the anatomy of the brain structure reflects the diversity of the individual’s mental processes and behaviour. Some structures can highlight ...
1 Introduction to Neurobiology Rudolf Cardinal NST 1B
... is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any inhibition from IPSPs) they may sum and trigger an AP. In this way the postsynaptic neuron can integrate information from ...
... is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any inhibition from IPSPs) they may sum and trigger an AP. In this way the postsynaptic neuron can integrate information from ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
Document
... – Electrically charged particles (ions) – Neuron at rest – negative charge on inside compared to outside – -70 millivolts – resting potential ...
... – Electrically charged particles (ions) – Neuron at rest – negative charge on inside compared to outside – -70 millivolts – resting potential ...
Myers Module Four
... Each consists of a cell body and branching fibres. The dendrites are the bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. For the biology students: dendrites are complex microtubules, proof that neurons are specializations from ...
... Each consists of a cell body and branching fibres. The dendrites are the bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. For the biology students: dendrites are complex microtubules, proof that neurons are specializations from ...
Candy Neurons Activity
... Students work in pairs of two to create their candy neurons. They must be labeled and contain all key parts. Once they are done they must link of their diagram with another two groups. When you have a group of 6 come by for some direct instruction showing that neurons fire DAT way. Dendrites t ...
... Students work in pairs of two to create their candy neurons. They must be labeled and contain all key parts. Once they are done they must link of their diagram with another two groups. When you have a group of 6 come by for some direct instruction showing that neurons fire DAT way. Dendrites t ...
“The Physiology of Excitable Cells”
... we follow the trajectories of interacting ions in the potassium channel. With a fast supercomputer, we simulate the motion of 26 potassium ions and 26 chloride ions interacting through the intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive ...
... we follow the trajectories of interacting ions in the potassium channel. With a fast supercomputer, we simulate the motion of 26 potassium ions and 26 chloride ions interacting through the intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive ...
Slide ()
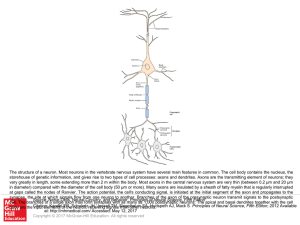
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
Neuron
... • Process continues down axon to the axon terminal. • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
... • Process continues down axon to the axon terminal. • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
... different neurons allowing the message from one to be multiplied very quickly by sending it to many other neurons. ...
... different neurons allowing the message from one to be multiplied very quickly by sending it to many other neurons. ...
Neurons - Jordan High School
... Action Potential (Nerve Impulse) All-or-none principle Action potential begins between -60 & -55 mV (threshold) Stimulus triggers action potential, or not at all if doesn’t meet threshold ...
... Action Potential (Nerve Impulse) All-or-none principle Action potential begins between -60 & -55 mV (threshold) Stimulus triggers action potential, or not at all if doesn’t meet threshold ...
Module 3
... contributes to various functions, such as regulating body temperature, sleep, mood, appetite, and pain. ...
... contributes to various functions, such as regulating body temperature, sleep, mood, appetite, and pain. ...
Psychology`s biological roots: neurons and neural communication
... There are dozens (at least 60) types and each activates many types of receptors Once they contact the postsynaptic neuron they can either: a) go through reuptake (reabsorbtion) b) be swept away through diffusion, c) or leave and then reexcite the neuron ...
... There are dozens (at least 60) types and each activates many types of receptors Once they contact the postsynaptic neuron they can either: a) go through reuptake (reabsorbtion) b) be swept away through diffusion, c) or leave and then reexcite the neuron ...
Design a Neuron
... Cell body – Contains all organelles including the nucleus. Attached to both dendrites and axon. ...
... Cell body – Contains all organelles including the nucleus. Attached to both dendrites and axon. ...
File
... • Presynaptic terminal: is the first part of the synapse & is usually (not always) the Axon terminal. The axon terminals are also called the bouton terminaux or synaptic knob. The synaptic knobs have synaptic vesicles that contain the NT (neurotransmitters). The NT are produced in the body & conduct ...
... • Presynaptic terminal: is the first part of the synapse & is usually (not always) the Axon terminal. The axon terminals are also called the bouton terminaux or synaptic knob. The synaptic knobs have synaptic vesicles that contain the NT (neurotransmitters). The NT are produced in the body & conduct ...
File
... when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
... when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
Neurons
... potential allows positive ions to flow in briefly, making the inside of the cell more positive. ...
... potential allows positive ions to flow in briefly, making the inside of the cell more positive. ...
L23-Neurotransmitter
... NEUROTRANSMITTERS DEFINITION: Are chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane . It then diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane, binds to and activates the receptors present leading to initiation of new electrical signals ...
... NEUROTRANSMITTERS DEFINITION: Are chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane . It then diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane, binds to and activates the receptors present leading to initiation of new electrical signals ...