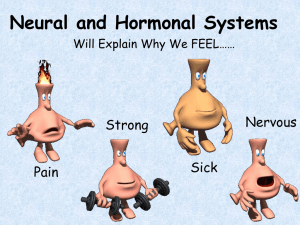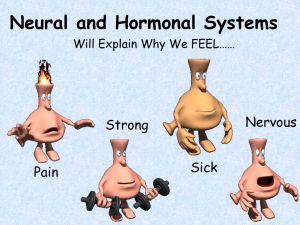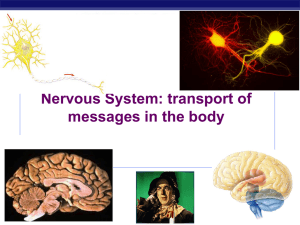
Synapse
... neurotransmitters in the brain affecting motor skills, memory, concentration Long-term effects: loss of memory, inability to concentrate, lowered ...
... neurotransmitters in the brain affecting motor skills, memory, concentration Long-term effects: loss of memory, inability to concentrate, lowered ...
Module 3
... • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more K) ...
... • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more K) ...
Nueron - AP Psychology Community
... • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more K) ...
... • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more K) ...
eating spaghetti!
... neurotransmitter that is synthesized in neurons of central nervous system & in cells in intestinal walls. This modulates anger, mood, sleep, sexuality, and appetite. Increases with the consumption of carbohydrates (pasta). http://www.faqs.org/nutrition/MetObe/Mood-Food-Relationships.html ...
... neurotransmitter that is synthesized in neurons of central nervous system & in cells in intestinal walls. This modulates anger, mood, sleep, sexuality, and appetite. Increases with the consumption of carbohydrates (pasta). http://www.faqs.org/nutrition/MetObe/Mood-Food-Relationships.html ...
AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 48 Neurons synapses and
... vertebrates and invertebrates, and it is released by the neurons that synapse with muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction. If you look ahead to Chapter 50, Figure 50.29, you will see a synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell, resulting in depolarization of the muscle cell and its contraction. ...
... vertebrates and invertebrates, and it is released by the neurons that synapse with muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction. If you look ahead to Chapter 50, Figure 50.29, you will see a synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell, resulting in depolarization of the muscle cell and its contraction. ...
SVHS ADV BIOLOGY NAME: 9th ed. Tortora PERIOD: 1 2 3 4 5 6
... The two main subdivisions of the nervous system are _________________________________ and __________________________________ ...
... The two main subdivisions of the nervous system are _________________________________ and __________________________________ ...
Document
... • Neural networks – Patterns of neural activity – Interconnected neurons that fire together or sequentially ...
... • Neural networks – Patterns of neural activity – Interconnected neurons that fire together or sequentially ...
3-8_NeuronDiversity_SalmaA
... Glutamatergic neurons: Glutamate is one of two primary excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter, the other being Aspartate. Glutamate receptors are one of four categories, three of which are ligand-gated ion channels and one of which is a G-protein coupled receptor (often referred to as GPCR).Glutamat ...
... Glutamatergic neurons: Glutamate is one of two primary excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter, the other being Aspartate. Glutamate receptors are one of four categories, three of which are ligand-gated ion channels and one of which is a G-protein coupled receptor (often referred to as GPCR).Glutamat ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... accumbens acts up more in adolescence is due to the different ways the younger brains deal with the neurotransmitter dopamine. • Dopamine, the brain chemical involved in motivation and in reinforcing behavior, is particularly abundant and active in the teen years (Wallis, 2004, para 21) • In additio ...
... accumbens acts up more in adolescence is due to the different ways the younger brains deal with the neurotransmitter dopamine. • Dopamine, the brain chemical involved in motivation and in reinforcing behavior, is particularly abundant and active in the teen years (Wallis, 2004, para 21) • In additio ...
Lecture 2 (Neurons)
... Fill the space between neurons Envelope synapses to limit the spread of neurotransmitters Regulate chemical content of extracellular fluid Remove neurotransmitters from synapse ...
... Fill the space between neurons Envelope synapses to limit the spread of neurotransmitters Regulate chemical content of extracellular fluid Remove neurotransmitters from synapse ...
The Brain and Its Disorders
... • Axon terminal releases neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters cross the synapse and bind to receptors on another neuron • Neurotransmitters released, taken up again by first neuron ...
... • Axon terminal releases neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters cross the synapse and bind to receptors on another neuron • Neurotransmitters released, taken up again by first neuron ...
Stochastic fluctuations of the synaptic function
... The response of single excitatory synapses in hippocampal neurons to a quantal release of neurotransmitters shows a large variability. In a recent paper, Liu et al., 1999, reported that the stimulation of putative single synaptic boutons of hippocampal neurons at excitatory synapses produced quantal ...
... The response of single excitatory synapses in hippocampal neurons to a quantal release of neurotransmitters shows a large variability. In a recent paper, Liu et al., 1999, reported that the stimulation of putative single synaptic boutons of hippocampal neurons at excitatory synapses produced quantal ...
Answers to Questions — neurons
... A threshold ensures that action potentials are not produced unless the neuron has received enough stimulation. 2. What might happen if a drug blocked neurotransmitter receptors? Neurotransmitters would not be able to bind with the receptors and initiate impulses in the neuron. 3. Hyponatremia occurs ...
... A threshold ensures that action potentials are not produced unless the neuron has received enough stimulation. 2. What might happen if a drug blocked neurotransmitter receptors? Neurotransmitters would not be able to bind with the receptors and initiate impulses in the neuron. 3. Hyponatremia occurs ...
Nervous System I
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... – Not all-or-none – Changes the probability of the postsynaptic neuron firing • Positive voltage shift – excitatory PSP • Negative voltage shift – inhibitory PSP ...
... – Not all-or-none – Changes the probability of the postsynaptic neuron firing • Positive voltage shift – excitatory PSP • Negative voltage shift – inhibitory PSP ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
ACh - Perkins Science
... between a neuron and the cell it is signaling a.In the CNS, this second cell will be another neuron. b.In the PNS, the second cell will be in a muscle or gland; often called myoneural or neuromuscular junctions ...
... between a neuron and the cell it is signaling a.In the CNS, this second cell will be another neuron. b.In the PNS, the second cell will be in a muscle or gland; often called myoneural or neuromuscular junctions ...
A2.2.2.SecretSignals - jj-sct
... We have learned that chemical and electrical factors work together to send signals. We know that the brain and spinal cord team up to deal with all the messages that are sent around the body on a minute to minute and often a second to second basis. We also know that all body functions depend on thes ...
... We have learned that chemical and electrical factors work together to send signals. We know that the brain and spinal cord team up to deal with all the messages that are sent around the body on a minute to minute and often a second to second basis. We also know that all body functions depend on thes ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - How Neurons Communicate - Neurons are communication specialists in our brain and spinal cord; they use an electrochemical communication process. - An electrical impulse (called the action potential) travels down to the bottom of the axon where synaptic vesicles open and release chemicals called ne ...
... - How Neurons Communicate - Neurons are communication specialists in our brain and spinal cord; they use an electrochemical communication process. - An electrical impulse (called the action potential) travels down to the bottom of the axon where synaptic vesicles open and release chemicals called ne ...
File
... Neurotransmitter Mobilization and Release (Cont’d) • The vesicle membrane will fuse with the presynaptic membrane releasing the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft • Neurons can contain and release more than one kind of neurotransmitter • The neurotransmitter molecules then diffuse across the ...
... Neurotransmitter Mobilization and Release (Cont’d) • The vesicle membrane will fuse with the presynaptic membrane releasing the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft • Neurons can contain and release more than one kind of neurotransmitter • The neurotransmitter molecules then diffuse across the ...