Microsoft Word 97
... pressures and stresses among the muscles and other connective tissues within bodies tend to escape nerve fatigue. Why is it important to organisms that they continue to receive impulses from these two types of receptors? ...
... pressures and stresses among the muscles and other connective tissues within bodies tend to escape nerve fatigue. Why is it important to organisms that they continue to receive impulses from these two types of receptors? ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... High speed (140 m/sec) Carry rapid information to/from CNS For example, position, balance, touch, and motor impulses ...
... High speed (140 m/sec) Carry rapid information to/from CNS For example, position, balance, touch, and motor impulses ...
Unit 2: Nervous System
... – Get message to CNS – Let CNS process and decide (NO need to have cell body right by dendrites) ...
... – Get message to CNS – Let CNS process and decide (NO need to have cell body right by dendrites) ...
Chemical Senses
... The 3-D model shown on the right (from Couto & Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, th ...
... The 3-D model shown on the right (from Couto & Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, th ...
Chapter 12: Nervous Tissue
... • dopamine -- regulating skeletal muscle tone • serotonin -- control of mood, temperature regulation & induction of sleep ...
... • dopamine -- regulating skeletal muscle tone • serotonin -- control of mood, temperature regulation & induction of sleep ...
Poster
... and the blue hydrophobic. When αsynuclein takes its helical form, it causes the hydrophobic amino acids to line up on one side of the molecule. This allows it to bind to the membranes. ...
... and the blue hydrophobic. When αsynuclein takes its helical form, it causes the hydrophobic amino acids to line up on one side of the molecule. This allows it to bind to the membranes. ...
Answer Key Chapter 28 - Scarsdale Public Schools
... fire an action potential in the receiving cell. The neuron will be able to fire an action potential as long as the incoming signals are collectively strong enough to bring the neuron’s membrane potential to threshold. 14. Epilepsy is sometimes referred to as an electrical storm of activity in t ...
... fire an action potential in the receiving cell. The neuron will be able to fire an action potential as long as the incoming signals are collectively strong enough to bring the neuron’s membrane potential to threshold. 14. Epilepsy is sometimes referred to as an electrical storm of activity in t ...
Lecture 7 – Synaptic Transmission II -
... NMDA receptor can conduct. Importantly, NMDA receptors are also permeable to Ca2+, which can act as second messenger. Triggers long-term changes in synaptic strength – long-term potentiation or long-term depression. These are potential mechanisms for learning and memory. Too much Ca2+ influx can kil ...
... NMDA receptor can conduct. Importantly, NMDA receptors are also permeable to Ca2+, which can act as second messenger. Triggers long-term changes in synaptic strength – long-term potentiation or long-term depression. These are potential mechanisms for learning and memory. Too much Ca2+ influx can kil ...
Ch. 10 Outline
... 3. Hyperpolarizes membrane of postsynaptic neuron 4. Action potential of postsynaptic neuron becomes less likely Summation of EPSPs and IPSPs A. EPSPs and IPSPs are added together in a process called summation B. More EPSPs lead to greater probability of an action potential Neurotransmitters Neurope ...
... 3. Hyperpolarizes membrane of postsynaptic neuron 4. Action potential of postsynaptic neuron becomes less likely Summation of EPSPs and IPSPs A. EPSPs and IPSPs are added together in a process called summation B. More EPSPs lead to greater probability of an action potential Neurotransmitters Neurope ...
The Nervous System
... 3. PNS is composed of nerves derived from the brain and spinal cord (12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves), which serve as linkage between the CNS and the body. 4. PNS can be subdivided into Sensory (afferent) nerves and Motor (efferent) nerves. Sensory nerves send nerve impulse ...
... 3. PNS is composed of nerves derived from the brain and spinal cord (12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves), which serve as linkage between the CNS and the body. 4. PNS can be subdivided into Sensory (afferent) nerves and Motor (efferent) nerves. Sensory nerves send nerve impulse ...
Class
... 97. The sympathetic nervous system operates (or is in primary control) during periods of a. stress b. circadian activity c. calm d. relaxation 98. Damage to the temporal lobe of the brain would probably be most harmful to the career of a. a painter b. an architect c. an actor d. a musician 99. An el ...
... 97. The sympathetic nervous system operates (or is in primary control) during periods of a. stress b. circadian activity c. calm d. relaxation 98. Damage to the temporal lobe of the brain would probably be most harmful to the career of a. a painter b. an architect c. an actor d. a musician 99. An el ...
Chapter 14
... 1. The three structural types of neurons are unipolar (one process extends from the cell body), bipolar (two processes extend from the cell body), and multipolar (three or more processes extend from the cell body). The three functional types of neurons are sensory neurons (afferent, unipolar, and bi ...
... 1. The three structural types of neurons are unipolar (one process extends from the cell body), bipolar (two processes extend from the cell body), and multipolar (three or more processes extend from the cell body). The three functional types of neurons are sensory neurons (afferent, unipolar, and bi ...
Sensory Systems
... The number of ommatidia per eye varies from species to species with only a few in ants, to 800 in fruit flies, to as many as 10,000 ommatidia in the compound eye of the horsefly. The compound eye provides information about patterns in the environment and is very good at detecting movement. The worl ...
... The number of ommatidia per eye varies from species to species with only a few in ants, to 800 in fruit flies, to as many as 10,000 ommatidia in the compound eye of the horsefly. The compound eye provides information about patterns in the environment and is very good at detecting movement. The worl ...
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... Motor regulation of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands & adipose tissue (“visceral effectors”) through stimulation of “visceral efferent fibers” Sympathetic (Σ) division – “fight or flight” response Parasympathetic (PΣ) division – rest & repose (“conserve & restore”) response “dual innervatio ...
... Motor regulation of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands & adipose tissue (“visceral effectors”) through stimulation of “visceral efferent fibers” Sympathetic (Σ) division – “fight or flight” response Parasympathetic (PΣ) division – rest & repose (“conserve & restore”) response “dual innervatio ...
Motivation
... arise from the brain stem. Each neuron has an axon that can influence more than 100,000 postsynaptic neurons spread widely across the brain. Their synapses release neurotransmitter into the extracellular fluid, not into a confined synaptic cleft. ...
... arise from the brain stem. Each neuron has an axon that can influence more than 100,000 postsynaptic neurons spread widely across the brain. Their synapses release neurotransmitter into the extracellular fluid, not into a confined synaptic cleft. ...
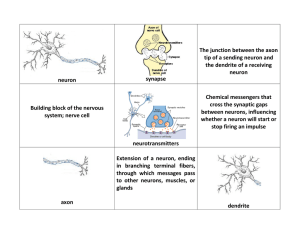
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons, influencing whether a neuron will start or stop firing an impulse ...
... Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons, influencing whether a neuron will start or stop firing an impulse ...
Ch.02 - Neuroscience
... Nerve cells Basic building blocks of the body’s information processing system. Made up of Dendrites Axons ...
... Nerve cells Basic building blocks of the body’s information processing system. Made up of Dendrites Axons ...
Neuron is the basic working unit of the nervous system, specialized
... triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. This occurs when a neuron is activated and temporarily reverses the electrical state of its interior membrane from negative to positive. ACETYLCHOLINE ‐ A neurotransmitter active both in the brain, where it regulates memory, and in the peripheral nervo ...
... triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. This occurs when a neuron is activated and temporarily reverses the electrical state of its interior membrane from negative to positive. ACETYLCHOLINE ‐ A neurotransmitter active both in the brain, where it regulates memory, and in the peripheral nervo ...
Chapter 15
... Postganglionic axons (unmyelinated)- relatively short - neurotransmitter is acetylcholine Distribution is more specific and less diffuse than sympathetic ...
... Postganglionic axons (unmyelinated)- relatively short - neurotransmitter is acetylcholine Distribution is more specific and less diffuse than sympathetic ...
PERSPECTIVES
... Making connections. Dependence of presynaptic terminal prop- expect from such an experiment is The strength of a synaptic connec- erties on the type of postsynaptic target cell. Presynaptic boutons that all of the presynaptic boutons tion depends on several key factors: formed by the axons of layer ...
... Making connections. Dependence of presynaptic terminal prop- expect from such an experiment is The strength of a synaptic connec- erties on the type of postsynaptic target cell. Presynaptic boutons that all of the presynaptic boutons tion depends on several key factors: formed by the axons of layer ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... • Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft • At the postsynaptic mb. The neurotransmitter merges with receptor sites • AP starts at the postsynaptic mb • Neurotransmitters may be broken down by enzymes, washed away, or recycles ...
... • Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft • At the postsynaptic mb. The neurotransmitter merges with receptor sites • AP starts at the postsynaptic mb • Neurotransmitters may be broken down by enzymes, washed away, or recycles ...
Biology 3201
... Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between schwann cells. Function: Saltatory Conduction (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping’ the gaps in an axon). ...
... Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between schwann cells. Function: Saltatory Conduction (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping’ the gaps in an axon). ...
Lecture 3
... Complexity of Neural Processing Things to bear in mind: •One neuron may connect to 1000 post-synaptic neurons. •One neuron may receive 10,000 inputs from other cells. ...
... Complexity of Neural Processing Things to bear in mind: •One neuron may connect to 1000 post-synaptic neurons. •One neuron may receive 10,000 inputs from other cells. ...