The NERVOUS System
... E. Characteristics of Nerves • Nerves (Neurons) • amitotic: they do not divide (cannot be replaced if destroyed) -high metabolic rate-require constant O2 and glucose, die within a few minutes without O2 ...
... E. Characteristics of Nerves • Nerves (Neurons) • amitotic: they do not divide (cannot be replaced if destroyed) -high metabolic rate-require constant O2 and glucose, die within a few minutes without O2 ...
Neurons
... • Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. • Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between schwann cells. – Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping’ the gaps in an axon). ...
... • Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. • Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between schwann cells. – Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping’ the gaps in an axon). ...
The Autonomic Nervous System - Ashland Independent Schools
... Sympathetic Division of the ANS • Axons of motor nerves (from T1-L2) exit through ventral root of spinal nerves, branch and enter sympathetic ganglia (trunks) located in chains along vertebral column – Sympathetic preganglionic neurons exit the spinal cord only between levels T1-L2 • Short pre-gan ...
... Sympathetic Division of the ANS • Axons of motor nerves (from T1-L2) exit through ventral root of spinal nerves, branch and enter sympathetic ganglia (trunks) located in chains along vertebral column – Sympathetic preganglionic neurons exit the spinal cord only between levels T1-L2 • Short pre-gan ...
Psychology Chapter 19: Group Interaction
... i. There are different types of neurotransmitters a. Norepinephrine – involved in memory or learning b. Endorphin – inhibits pain c. Acetylocholine – involved in movement and memory (associated with paralysis and Alzheimer’s) d. Dopamine – involved in learning, emotional arousal and movement (too mu ...
... i. There are different types of neurotransmitters a. Norepinephrine – involved in memory or learning b. Endorphin – inhibits pain c. Acetylocholine – involved in movement and memory (associated with paralysis and Alzheimer’s) d. Dopamine – involved in learning, emotional arousal and movement (too mu ...
RetinaCircuts
... Figure 3.10 Circuit to explain the Mach band effect based on lateral inhibition. The circuit works like the one for the Hermann grid in Figure 3.6, with each bipolar cell sending inhibition to its neighbors. If we know the initial output of each receptor and the amount of lateral inhibition, we can ...
... Figure 3.10 Circuit to explain the Mach band effect based on lateral inhibition. The circuit works like the one for the Hermann grid in Figure 3.6, with each bipolar cell sending inhibition to its neighbors. If we know the initial output of each receptor and the amount of lateral inhibition, we can ...
Lecture3
... over long distances to other cells. • Sensory neurons carry information from sense organs to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons carry information from the CNS to muscles ...
... over long distances to other cells. • Sensory neurons carry information from sense organs to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons carry information from the CNS to muscles ...
MBBC Junior Neuroscience E-Book v1
... triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. This occurs when a neuron is activated and temporarily reverses the electrical state of its interior membrane from negative to positive. ACETYLCHOLINE - A neurotransmitter active both in the brain, where it regulates memory, and in the peripheral nervous s ...
... triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. This occurs when a neuron is activated and temporarily reverses the electrical state of its interior membrane from negative to positive. ACETYLCHOLINE - A neurotransmitter active both in the brain, where it regulates memory, and in the peripheral nervous s ...
Introduction to Psychology
... GABA Inhibitory neurotransmitter. Low amounts present in seizures and insomnia. Many sedative/tranquilizing drugs act by enhancing the effects of GABA. Alcohol and increases GABA. Anti-anxiety meds Epilepsy and GABA Substance P Responsible for transmission of pain from certain sensory neurons to ...
... GABA Inhibitory neurotransmitter. Low amounts present in seizures and insomnia. Many sedative/tranquilizing drugs act by enhancing the effects of GABA. Alcohol and increases GABA. Anti-anxiety meds Epilepsy and GABA Substance P Responsible for transmission of pain from certain sensory neurons to ...
Neurons
... ● The synapse is the gap between the axon terminals and the next cell ● A neurotransmitter is a chemical that is used to transmit an impulse to another cell ...
... ● The synapse is the gap between the axon terminals and the next cell ● A neurotransmitter is a chemical that is used to transmit an impulse to another cell ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... The synapse is the gap between the axon terminals and the next cell A neurotransmitter is a chemical that is used to transmit an impulse to another cell ...
... The synapse is the gap between the axon terminals and the next cell A neurotransmitter is a chemical that is used to transmit an impulse to another cell ...
Practice questions 1. How are functionalism and behaviourism
... a) axons, graded, dendrites, action, neurotransmitters b) cell body, action, axon, graded, ions c) dendrites, graded, axon, action, neurotransmitters d) dendrites, graded, axon, action, ions e) synaptic buttons, all-or-none, cell body, graded, neurotransmitters ...
... a) axons, graded, dendrites, action, neurotransmitters b) cell body, action, axon, graded, ions c) dendrites, graded, axon, action, neurotransmitters d) dendrites, graded, axon, action, ions e) synaptic buttons, all-or-none, cell body, graded, neurotransmitters ...
Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
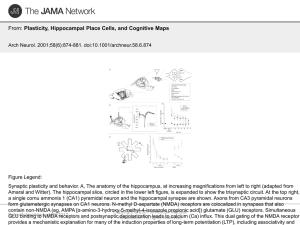
... Synaptic plasticity and behavior. A, The anatomy of the hippocampus, at increasing magnifications from left to right (adapted from Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1 ...
... Synaptic plasticity and behavior. A, The anatomy of the hippocampus, at increasing magnifications from left to right (adapted from Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1 ...
Drugs - IVCC
... • Continued use of some drugs (opiates) causes neurons to shrink or otherwise work less effectively, forcing the user to rely on the drug for pleasure ...
... • Continued use of some drugs (opiates) causes neurons to shrink or otherwise work less effectively, forcing the user to rely on the drug for pleasure ...
Information Processing SG
... The nervous system is like an information highway. It is responsible for controlling and coordinating all the functions and movements in the body and allows you to respond to changes in your environment The nervous system is made up of _____________ that are strings of long thin cells called _______ ...
... The nervous system is like an information highway. It is responsible for controlling and coordinating all the functions and movements in the body and allows you to respond to changes in your environment The nervous system is made up of _____________ that are strings of long thin cells called _______ ...
Neural Conduction
... Theories of Addiction • There are two problems with this theory: (1) Many of the conditioned effects elicited by drugtaking environments are similar to the effects of the drug, not to the drug’s withdrawal effects (2) Addicts and experimental animals often find drug-related cues rewarding, even in t ...
... Theories of Addiction • There are two problems with this theory: (1) Many of the conditioned effects elicited by drugtaking environments are similar to the effects of the drug, not to the drug’s withdrawal effects (2) Addicts and experimental animals often find drug-related cues rewarding, even in t ...
in the central nervous system
... Impulses flow from synaptic knobs to dendrites (one direction) Excitatory transmitters • acetylcholine, norepinephrine, histamine, glutamic acid ...
... Impulses flow from synaptic knobs to dendrites (one direction) Excitatory transmitters • acetylcholine, norepinephrine, histamine, glutamic acid ...
Title Nerve cell or neuron Learning outcome At the end of the lesson
... • At the end of the lesson Ss will be able to • Say about nerve cell. • Describe the different parts a nerve cell. • Compare between a cell body and a cell • Draw a picture of a neuron. ...
... • At the end of the lesson Ss will be able to • Say about nerve cell. • Describe the different parts a nerve cell. • Compare between a cell body and a cell • Draw a picture of a neuron. ...
Nervous Tissue - Fisiokinesiterapia
... Epinephrine and norepinephrine. Can have excitatory or inhibitory effects. Secreted by the CNS and PNS. Secreted by the adrenal glands. ...
... Epinephrine and norepinephrine. Can have excitatory or inhibitory effects. Secreted by the CNS and PNS. Secreted by the adrenal glands. ...
Exam 3B key
... Pertussin toxin, a stimulator of G-protein function, mimics the hormone's action ...
... Pertussin toxin, a stimulator of G-protein function, mimics the hormone's action ...
Untitled 2
... - In the brain finer dendrites are highly specialised for collecting information, bristling with dendrites spines which represent points of close contact - synapses - with other neurons ...
... - In the brain finer dendrites are highly specialised for collecting information, bristling with dendrites spines which represent points of close contact - synapses - with other neurons ...
Nervous System
... A. synapse is a functional junction between one neuron and another or between a neuron and an effector organ such as muscle or gland. B.Chemical Synapse: At a chemical synapse, there is only one-way information transfer from a presynaptic neuron to a post-synaptic neuron ...
... A. synapse is a functional junction between one neuron and another or between a neuron and an effector organ such as muscle or gland. B.Chemical Synapse: At a chemical synapse, there is only one-way information transfer from a presynaptic neuron to a post-synaptic neuron ...
Nervous System
... 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another. Once the impulse reaches the end of the axon, it is able to jump the gap by ...
... 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another. Once the impulse reaches the end of the axon, it is able to jump the gap by ...
Chapter 12 - Nervous Tissue
... glands) in response to the sensory input 2. The endocrine system reacts more slowly via ___________. 3. ____________ is the study of nervous system function and disorders. B. Divisions of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (____) - consists of ______ & spinal cord. Most impulses that stimu ...
... glands) in response to the sensory input 2. The endocrine system reacts more slowly via ___________. 3. ____________ is the study of nervous system function and disorders. B. Divisions of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (____) - consists of ______ & spinal cord. Most impulses that stimu ...