Poster
... In the mammalian central nervous system, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the primary inhibitory signaling molecule. One receptor for this molecule, GABAB, has been linked to feelings of calmness, as well as mental disorders such as alcoholism and depression. Pharmaceutical compounds that bind the ...
... In the mammalian central nervous system, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the primary inhibitory signaling molecule. One receptor for this molecule, GABAB, has been linked to feelings of calmness, as well as mental disorders such as alcoholism and depression. Pharmaceutical compounds that bind the ...
Document
... Types of Neurons Unipolar: o One single process extending from cell body. o one side of axon is the peripheral process associated with body part, other side is the central process that enters brain or spinal cord. o Cell bodies create a tissue mass called ganglia. ...
... Types of Neurons Unipolar: o One single process extending from cell body. o one side of axon is the peripheral process associated with body part, other side is the central process that enters brain or spinal cord. o Cell bodies create a tissue mass called ganglia. ...
AP Psychology Test Review
... Jeremy was born with several brain abnormalities. One of these, decreased his ability to coordinate his movements. Which of the following parts of the brain may be damaged? ...
... Jeremy was born with several brain abnormalities. One of these, decreased his ability to coordinate his movements. Which of the following parts of the brain may be damaged? ...
The Great Brain Drain Review
... When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory b ...
... When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory b ...
brain drain answers
... When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory b ...
... When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory b ...
Biology Cells unit: LT8 Review
... Put the images in the correct order to represent the sodiumpotassium pump. The first one is already labeled #1. ...
... Put the images in the correct order to represent the sodiumpotassium pump. The first one is already labeled #1. ...
Nervous System Chapter 11 Answers
... 15. What is the all-or-nothing phenomenon? An action potential occurs completely, or not at all (THRESHOLD must be reached to open up sodium channels) 16. What variables influence the conduction velocity of a neuron? Axon diameter (Larger diameter results in faster conduction of impulse) Degr ...
... 15. What is the all-or-nothing phenomenon? An action potential occurs completely, or not at all (THRESHOLD must be reached to open up sodium channels) 16. What variables influence the conduction velocity of a neuron? Axon diameter (Larger diameter results in faster conduction of impulse) Degr ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... Similar in spirit to Fourier decomposition. Bumps = radial basis ...
... Similar in spirit to Fourier decomposition. Bumps = radial basis ...
Endocrine System
... Results from loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra Symptoms include: difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements ...
... Results from loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra Symptoms include: difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... The Brain and Neural Networks Interconnected neurons form networks in the brain. Theses networks are complex and modify with growth and experience. ...
... The Brain and Neural Networks Interconnected neurons form networks in the brain. Theses networks are complex and modify with growth and experience. ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... neurons run in two directions, forming two-directional pathways and networks, in which activity at point A triggers activity at point B, and vice versa. This is often called reentrant connectivity (Edelman, 1989). (p. 65) From Section 2.1 Re-entrant loops are equivalent to neural networks with two o ...
... neurons run in two directions, forming two-directional pathways and networks, in which activity at point A triggers activity at point B, and vice versa. This is often called reentrant connectivity (Edelman, 1989). (p. 65) From Section 2.1 Re-entrant loops are equivalent to neural networks with two o ...
Students know
... What are stimulants? • Drugs change how the brain works, by changing the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that are generated. • Stimulants-drugs that increase the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that neurons generate by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the syna ...
... What are stimulants? • Drugs change how the brain works, by changing the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that are generated. • Stimulants-drugs that increase the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that neurons generate by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the syna ...
Unit 13 Autonomic Nervous System
... Figure 8.4 Norepinephrine (NE) receptors are adrenergic receptors (α and β) in the sympathetic pathway. Acetylcholine (Ach) receptors in the ganglia and skeletal muscles (not shown here) are called ...
... Figure 8.4 Norepinephrine (NE) receptors are adrenergic receptors (α and β) in the sympathetic pathway. Acetylcholine (Ach) receptors in the ganglia and skeletal muscles (not shown here) are called ...
C2 - The Biological Perspective
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
The Nervous System
... • A neuron has a large cell body that contains the nucleus. • Dendrites - threadlike extensions on the cell body that carry impulses toward the neuron’s cell body. • Axon - carries impulses away from the cell body. ...
... • A neuron has a large cell body that contains the nucleus. • Dendrites - threadlike extensions on the cell body that carry impulses toward the neuron’s cell body. • Axon - carries impulses away from the cell body. ...
Quiz Answers
... d) The neuron would integrate the information based upon the summed depolarization that occurs. e) The neuron would short circuit. ...
... d) The neuron would integrate the information based upon the summed depolarization that occurs. e) The neuron would short circuit. ...
The Biological Perspective
... enough to fit into the receptor site without actually stimulating the cell This blocks acetylcholine from its receptor sites causing ...
... enough to fit into the receptor site without actually stimulating the cell This blocks acetylcholine from its receptor sites causing ...
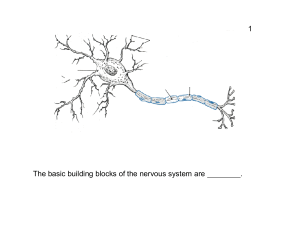
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as ...
Lab 9 Nervous histology post lab answer key 2010
... terminal, nucleus of Schwann cell (neurilemma ok too), Schwann cell (myelin sheath ok), axon hillock, nucleus 2. Match the term with the description: a. b. c. ...
... terminal, nucleus of Schwann cell (neurilemma ok too), Schwann cell (myelin sheath ok), axon hillock, nucleus 2. Match the term with the description: a. b. c. ...
LABORATORY 9
... terminal, nucleus of Schwann cell (neurilemma ok too), Schwann cell (myelin sheath ok), axon hillock, nucleus 2. Match the term with the description: a. b. c. ...
... terminal, nucleus of Schwann cell (neurilemma ok too), Schwann cell (myelin sheath ok), axon hillock, nucleus 2. Match the term with the description: a. b. c. ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... effectors (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands and adipose tissue). - signals from CNS motor neurons to visceral effectors pass through synapses at autonomic ganglia, dividing efferent axons into 2 groups: 1. preganglionic fibers 2. postganglionic fibers 3. Interneurons or association neurons: - l ...
... effectors (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands and adipose tissue). - signals from CNS motor neurons to visceral effectors pass through synapses at autonomic ganglia, dividing efferent axons into 2 groups: 1. preganglionic fibers 2. postganglionic fibers 3. Interneurons or association neurons: - l ...
Physiology 1B
... Interneurons- CNS neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and the motor outputs Motor Neurons- Carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscle glands. ...
... Interneurons- CNS neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and the motor outputs Motor Neurons- Carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscle glands. ...