Group 1 - Polk School District
... the outside world. -Two kings were primarily responsible for military affairs and served as leaders of the Spartan Army -A group of 5 men, known as ephors, were elected each year for the education of youth and the conduct of all citizens Pelopennesian War -At the beginning of the war, both sides bel ...
... the outside world. -Two kings were primarily responsible for military affairs and served as leaders of the Spartan Army -A group of 5 men, known as ephors, were elected each year for the education of youth and the conduct of all citizens Pelopennesian War -At the beginning of the war, both sides bel ...
File
... of Nicias. (421 BC) This peace was supposed to last 50 years but it only lasted about 6 years. Pericles nephew, Alcibiades was elected as general but he he was reckless and self-seeking. He later was removed from leadership for disrespecting religious items. Bitter about his demotion, he fled to the ...
... of Nicias. (421 BC) This peace was supposed to last 50 years but it only lasted about 6 years. Pericles nephew, Alcibiades was elected as general but he he was reckless and self-seeking. He later was removed from leadership for disrespecting religious items. Bitter about his demotion, he fled to the ...
Slide 1 - Images
... against the Persians. 2. Worked to drive the Persians out of Greek territories in Asia Minor. Because most of the chief officials and military leaders in the Delian League were Athenian, Athens gained control over all city-states, except Sparta. ...
... against the Persians. 2. Worked to drive the Persians out of Greek territories in Asia Minor. Because most of the chief officials and military leaders in the Delian League were Athenian, Athens gained control over all city-states, except Sparta. ...
Diodorus Siculus on The Battle of Chaeronea
... Both armies were now ready to engage; they were equal indeed in courage and personal valor, but in numbers and military experience a great advantage lay with the king. For he had fought many battles, gained most of them, and so learned much about war, but the best Athenian generals were now dead, an ...
... Both armies were now ready to engage; they were equal indeed in courage and personal valor, but in numbers and military experience a great advantage lay with the king. For he had fought many battles, gained most of them, and so learned much about war, but the best Athenian generals were now dead, an ...
City-State Dual Ancient Athens vs. Ancient Sparta
... 3. The lowest class was the thetes who were usually urban craftsmen or rowers. Metics – the people who lived outside the walls of Athens o Unable to own land o Could run industries and businesses Slaves constituted the lowest class in Ancient Athens. Slaves had no rights. They constituted one fo ...
... 3. The lowest class was the thetes who were usually urban craftsmen or rowers. Metics – the people who lived outside the walls of Athens o Unable to own land o Could run industries and businesses Slaves constituted the lowest class in Ancient Athens. Slaves had no rights. They constituted one fo ...
PersianWarChart key
... Below you will find a chart to help you organize your thoughts about the Persian Wars. Fill in the missing parts to help you study. The first one has been done for you. You do not need to use complete sentences. ...
... Below you will find a chart to help you organize your thoughts about the Persian Wars. Fill in the missing parts to help you study. The first one has been done for you. You do not need to use complete sentences. ...
PBS DVD - socialstudiesNCUHS
... 3. Helenes was a pennisula we know today as Greece / Macedonia. 4. Athens was built around the Acropolis / Olympia 5. The life of an Athenian: “Peaches and Cream” / “Nasty, Brutish and Short” 6. Athens common people: “They had no part or share in anything” – Aristotle / Hippocrates 7. Greece did not ...
... 3. Helenes was a pennisula we know today as Greece / Macedonia. 4. Athens was built around the Acropolis / Olympia 5. The life of an Athenian: “Peaches and Cream” / “Nasty, Brutish and Short” 6. Athens common people: “They had no part or share in anything” – Aristotle / Hippocrates 7. Greece did not ...
The Greeks: Crucible of Civilization
... 3. Helenes was a pennisula we know today as Greece / Macedonia. 4. Athens was built around the Acropolis / Olympia 5. The life of an Athenian: “Peaches and Cream” / “Nasty, Brutish and Short” 6. Athens common people: “They had no part or share in anything” – Aristotle / Hippocrates 7. Greece did not ...
... 3. Helenes was a pennisula we know today as Greece / Macedonia. 4. Athens was built around the Acropolis / Olympia 5. The life of an Athenian: “Peaches and Cream” / “Nasty, Brutish and Short” 6. Athens common people: “They had no part or share in anything” – Aristotle / Hippocrates 7. Greece did not ...
The Greeks
... • In response, Solon negotiated a compromise that cancelled all debts of poor farmers and outlawed the process of selling yourself into slavery, but he let the aristocracy keep their land • He also gave the lower class more political rights, setting examples for future peoples • He allowed any perso ...
... • In response, Solon negotiated a compromise that cancelled all debts of poor farmers and outlawed the process of selling yourself into slavery, but he let the aristocracy keep their land • He also gave the lower class more political rights, setting examples for future peoples • He allowed any perso ...
Alexander the Great
... Marathon. There, 10,000 Athenians defeated 25,000 Persians. The casualties reportedly numbered 6,400 Persians and only 192 Athenians. Though the Athenians were victorious, their city was now defenseless. They were fearful the Persians would sail down the coast and reach the city of Athens before the ...
... Marathon. There, 10,000 Athenians defeated 25,000 Persians. The casualties reportedly numbered 6,400 Persians and only 192 Athenians. Though the Athenians were victorious, their city was now defenseless. They were fearful the Persians would sail down the coast and reach the city of Athens before the ...
Station 1 Greek Money Barter
... city-states. Shortly after, an Athenian general by the name of Pericles insisted that all criminal trials be held in Athens. He also attempted to force the other city-states to adopt and use Athens money. Led by Sparta, the other city-states rebelled against the growing strength of Athens. This war ...
... city-states. Shortly after, an Athenian general by the name of Pericles insisted that all criminal trials be held in Athens. He also attempted to force the other city-states to adopt and use Athens money. Led by Sparta, the other city-states rebelled against the growing strength of Athens. This war ...
Honor Code
... _______ and the ________________ for support. ii) Some city-states passed rule from one tyrant to another, while others reorganized. 2) Sparta Builds a Military State - located in the southern part of Greece, known as the _____________________. - unlike other city-states, Sparta built a ____________ ...
... _______ and the ________________ for support. ii) Some city-states passed rule from one tyrant to another, while others reorganized. 2) Sparta Builds a Military State - located in the southern part of Greece, known as the _____________________. - unlike other city-states, Sparta built a ____________ ...
WWII- The Home front
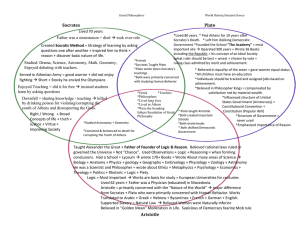
... ____________________________________________, even the best of men, but ________ is ____________without desire. -Aristotle Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome • Greece set lasting standards in ________________ and ________________ • Developed ________ ________________in order for their citizens to act ...
... ____________________________________________, even the best of men, but ________ is ____________without desire. -Aristotle Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome • Greece set lasting standards in ________________ and ________________ • Developed ________ ________________in order for their citizens to act ...
Classical Greece and the Hellenistic Period
... Lysistrata: women withhold sex until peace is negotiated; play ends with Athenians and Spartans dancing together in peace ...
... Lysistrata: women withhold sex until peace is negotiated; play ends with Athenians and Spartans dancing together in peace ...
Rivals: Athens vs. Sparta - Harrison Humanities
... • City-states shared a common culture, many other systems were different. • Civilization was spread throughout the world due to diversity and travels around the Med. • Left physical structures like the Parthenon, much of the legacy is non- tangible- ideas represented in writings and art. • Higher st ...
... • City-states shared a common culture, many other systems were different. • Civilization was spread throughout the world due to diversity and travels around the Med. • Left physical structures like the Parthenon, much of the legacy is non- tangible- ideas represented in writings and art. • Higher st ...
The Spartans and Women in Ancient Greece
... the only ones who rule your men?’, she replied ‘Because we are the only women too who give birth to men.’ -- From Plutarch, Sayings of Spartan Women, quoted in Cartledge, The Spartans (125) Statue of a winner of the Heraia (footrace every four years to honor Hera) ...
... the only ones who rule your men?’, she replied ‘Because we are the only women too who give birth to men.’ -- From Plutarch, Sayings of Spartan Women, quoted in Cartledge, The Spartans (125) Statue of a winner of the Heraia (footrace every four years to honor Hera) ...
11: Athens System Action Patterns: Making Decisions
... “Our way of governing is not copied from other states. Instead, it is an example for them to copy. Our government is called a democracy because it is run by all our citizens instead of a small group at the top. In private disputes between people, our laws treat everyone equally, no matter their stat ...
... “Our way of governing is not copied from other states. Instead, it is an example for them to copy. Our government is called a democracy because it is run by all our citizens instead of a small group at the top. In private disputes between people, our laws treat everyone equally, no matter their stat ...
World History Greece pt1
... 5 sections in red ◦ Pericles’ Plan for Athens Direct democracy, glorifying Athens, Athenian Empire ...
... 5 sections in red ◦ Pericles’ Plan for Athens Direct democracy, glorifying Athens, Athenian Empire ...
Script: Slide 1: The three ancient cities of Greece were Sparta
... society, so women, slaves, and foreigners did not have many of the same rights as men. Slide 5: Thebes was an ancient city-state in Greece that is not as prominent as the other two city-states, Sparta and Athens. During the Persian Wars, Thebes fought for the Persian side, against the Spartans and A ...
... society, so women, slaves, and foreigners did not have many of the same rights as men. Slide 5: Thebes was an ancient city-state in Greece that is not as prominent as the other two city-states, Sparta and Athens. During the Persian Wars, Thebes fought for the Persian side, against the Spartans and A ...
The Golden Age of Athens!
... Athena called Parthenonruins still there today •By 460 B.C. Athens is the leading city-state in Greece ...
... Athena called Parthenonruins still there today •By 460 B.C. Athens is the leading city-state in Greece ...
Epikleros

An epikleros (ἐπίκληρος; plural epikleroi) was an heiress in ancient Athens and other ancient Greek city states, specifically a daughter of a man who had no male heirs. In Sparta, they were called patrouchoi (πατροῦχοι), as they were in Gortyn. Athenian women were not allowed to hold property in their own name; in order to keep her father's property in the family, an epikleros was required to marry her father's nearest male relative. Even if a woman was already married, evidence suggests that she was required to divorce her spouse to marry that relative. Spartan women were allowed to hold property in their own right, and so Spartan heiresses were subject to less restrictive rules. Evidence from other city-states is more fragmentary, mainly coming from the city-states of Gortyn and Rhegium.Plato wrote about epikleroi in his Laws, offering idealized laws to govern their marriages. In mythology and history, a number of Greek women appear to have been epikleroi, including Agariste of Sicyon and Agiatis, the widow of the Spartan king Agis IV. The status of epikleroi has often been used to explain the numbers of sons-in-law who inherited from their fathers-in-law in Greek mythology. The Third Sacred War originated in a dispute over epikleroi.