Greek City-States INFO
... The city-state of Thebes was located on the eastern plain of Boeotia (pronounced bee-OH-sheh) in central Greece. Thebes was situated on wide farmlands, and it controlled northern and southern trade routes, sot he city was able to maintain a strong farming economy. An oligarchy governed Thebes’ large ...
... The city-state of Thebes was located on the eastern plain of Boeotia (pronounced bee-OH-sheh) in central Greece. Thebes was situated on wide farmlands, and it controlled northern and southern trade routes, sot he city was able to maintain a strong farming economy. An oligarchy governed Thebes’ large ...
File - Drama Class Spring 2013
... • Pericles had no other choice but to bring people into city walls • City safe from hunger as long as ships could come into ports • 2nd year of war PLAGUE outbreak in Athens, killing 1/3rd of population and PERICLES!!! • Athens still continued to fight for several years • 421 BC signed a truce (worn ...
... • Pericles had no other choice but to bring people into city walls • City safe from hunger as long as ships could come into ports • 2nd year of war PLAGUE outbreak in Athens, killing 1/3rd of population and PERICLES!!! • Athens still continued to fight for several years • 421 BC signed a truce (worn ...
The Greeks
... • The main flaw was citizenship. Old laws stated that foreigners that moved to Athens could not become citizens. This made many mad because they were under this category and the aristocracy would not change the law. • Really strong Navy and Army. ...
... • The main flaw was citizenship. Old laws stated that foreigners that moved to Athens could not become citizens. This made many mad because they were under this category and the aristocracy would not change the law. • Really strong Navy and Army. ...
Works Cited By: Aleena Manning "`Ancient Greek Girl Athlete
... website that included quotes from Spartan politicians. This website article has information on how the politicians saw the women. The agreed that women should have rights but also responsibilities (which are included in the article). J., O'Neal William. "The Status of Women in Ancient Athens." Ancie ...
... website that included quotes from Spartan politicians. This website article has information on how the politicians saw the women. The agreed that women should have rights but also responsibilities (which are included in the article). J., O'Neal William. "The Status of Women in Ancient Athens." Ancie ...
The Peloponnesian War
... After the Persian Wars one of Athens’ greatest leaders, Pericles, emerged. By 460 B.C., Pericles was the strongest leader in Athens. He remained the leader until his death 31 years later. He was so important that this time in Athens is often called the Age of Pericles. Pericles had three goals for A ...
... After the Persian Wars one of Athens’ greatest leaders, Pericles, emerged. By 460 B.C., Pericles was the strongest leader in Athens. He remained the leader until his death 31 years later. He was so important that this time in Athens is often called the Age of Pericles. Pericles had three goals for A ...
Life in Two City States Reading
... Desmosthenes, an Athenian leader, speaks to the Assembly. The Granger Collection, New York Athens became a democracy around 500 B.C.E. But unlike modern democracies, Athens allowed only free men to be citizens. All Athenian-born men over the age of 18 were considered Athenian citizens. Women and sla ...
... Desmosthenes, an Athenian leader, speaks to the Assembly. The Granger Collection, New York Athens became a democracy around 500 B.C.E. But unlike modern democracies, Athens allowed only free men to be citizens. All Athenian-born men over the age of 18 were considered Athenian citizens. Women and sla ...
File
... Greece, which made Athens one of the most democratic governments in history – *Direct Democracy is one in which citizens rule directly, not ...
... Greece, which made Athens one of the most democratic governments in history – *Direct Democracy is one in which citizens rule directly, not ...
Unit 4 Mediterranean Empires
... 29. Define Pericles. 30. Define Sparta. 31. (√) What details show that Sparta was governed differently than Athens? 32. Define helot. 33. At what age were Spartan boys sent to military camps to begin training for the army e. Women in Sparta (page 256) Main Idea: Spartan women had more rights and res ...
... 29. Define Pericles. 30. Define Sparta. 31. (√) What details show that Sparta was governed differently than Athens? 32. Define helot. 33. At what age were Spartan boys sent to military camps to begin training for the army e. Women in Sparta (page 256) Main Idea: Spartan women had more rights and res ...
Athens V Sparta - Primary Resources
... But, they did not take over Athens they said they would not burn it as long as Athens promised not to keep trying to take over. Athens was therefore left as it was and even now is one of the most famous cities in the world. ...
... But, they did not take over Athens they said they would not burn it as long as Athens promised not to keep trying to take over. Athens was therefore left as it was and even now is one of the most famous cities in the world. ...
Athens and Sparta: Different, Yet the Same
... dealers. They were then put on sale in the slave market. ...
... dealers. They were then put on sale in the slave market. ...
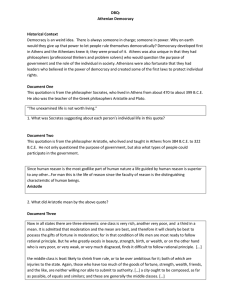
Athenian Democracy DBQ
... land, puts men to death without trial, and subjects women to violence. The rule of the many [...] is free from all those outrages which a king is wont to commit. There, places are given by lot, the magistrate is answerable for what he does, and measures rest with the commonalty. […] [Megabyzus says: ...
... land, puts men to death without trial, and subjects women to violence. The rule of the many [...] is free from all those outrages which a king is wont to commit. There, places are given by lot, the magistrate is answerable for what he does, and measures rest with the commonalty. […] [Megabyzus says: ...
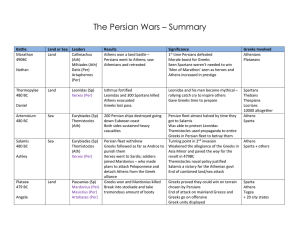
The Persian Wars – Summary Battle Land or Sea Leaders Results
... Was able to protect Leonidas Themistocles used propaganda to entire Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles naval policy justified Salamis a victory for the Athenia ...
... Was able to protect Leonidas Themistocles used propaganda to entire Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles naval policy justified Salamis a victory for the Athenia ...
Athenian Democracy - PHS
... land, puts men to death without trial, and subjects women to violence. The rule of the many [...] is free from all those outrages which a king is wont to commit. There, places are given by lot, the magistrate is answerable for what he does, and measures rest with the commonalty. […] [Megabyzus says: ...
... land, puts men to death without trial, and subjects women to violence. The rule of the many [...] is free from all those outrages which a king is wont to commit. There, places are given by lot, the magistrate is answerable for what he does, and measures rest with the commonalty. […] [Megabyzus says: ...
Development of Democracy in Ancient Greece
... All his laws were repealed by Solon apart from those dealing with homicide. ...
... All his laws were repealed by Solon apart from those dealing with homicide. ...
Athenian empire - bankstowntafehsc
... Over the next twenty years, Athens attempted to establish a land empire for itself by weakening the Peloponnesian League. It forged an alliance with Sparta’s enemies Argos and Megara, made war on Aegina and forced it to join the Delian League, and sent troops to Egypt to support a revolt against Per ...
... Over the next twenty years, Athens attempted to establish a land empire for itself by weakening the Peloponnesian League. It forged an alliance with Sparta’s enemies Argos and Megara, made war on Aegina and forced it to join the Delian League, and sent troops to Egypt to support a revolt against Per ...
File ancient greece
... Pericles, the leader of Athens, used part of the League’s treasury to rebuild Athens (the Parthenon and other major buildings on the Acropolis were constructed during this period). The Spartans feared the Athenians. War was inevitable when the Athenians started construction on a wall around the city ...
... Pericles, the leader of Athens, used part of the League’s treasury to rebuild Athens (the Parthenon and other major buildings on the Acropolis were constructed during this period). The Spartans feared the Athenians. War was inevitable when the Athenians started construction on a wall around the city ...
Document Booklet - SCSA - School Curriculum and Standards
... many days in Attica before the plague first broke out among the Athenians. Previously attacks of the plague had been reported from many other places … but there was no record of the disease being so virulent1 anywhere else or causing so many deaths as it did in Athens. At the beginning the doctors w ...
... many days in Attica before the plague first broke out among the Athenians. Previously attacks of the plague had been reported from many other places … but there was no record of the disease being so virulent1 anywhere else or causing so many deaths as it did in Athens. At the beginning the doctors w ...
Sculptures of the Sixth Century
... • Most depict women, but male figures also exist • Their function remains unknown, but some scholars suggest they were used for home worship and then buried with their owner ...
... • Most depict women, but male figures also exist • Their function remains unknown, but some scholars suggest they were used for home worship and then buried with their owner ...
GREEK WEDDINGS ATHENIAN MARRIAGE: The day before the
... the girls were taught wrestling, gymnastics and combat skills. Some historians believe the two schools were very similar, and that an attempt was made to train the girls as thoroughly as they trained the boys. In any case, the Spartans believed that strong young women would produce strong babies. At ...
... the girls were taught wrestling, gymnastics and combat skills. Some historians believe the two schools were very similar, and that an attempt was made to train the girls as thoroughly as they trained the boys. In any case, the Spartans believed that strong young women would produce strong babies. At ...
Test 4 - Upper Elementary
... a Renaissance. The Renaissance is the rebirth of Greek ideas. If Greece was conquered by Persia, there would have been no Athenian Golden Age and no great ideas to be reborn in the Renaissance. (3 pts: 2pts for discussion; 1 pt for spelling and grammar) 10. What did the Persian emperor Darius comman ...
... a Renaissance. The Renaissance is the rebirth of Greek ideas. If Greece was conquered by Persia, there would have been no Athenian Golden Age and no great ideas to be reborn in the Renaissance. (3 pts: 2pts for discussion; 1 pt for spelling and grammar) 10. What did the Persian emperor Darius comman ...
The Persian Wars - White Plains Public Schools
... in the other. This fearsome formation, or phalanx, became the most powerful fighting force in the ancient world. The Persian Wars, between Greece and the Persian Empire, began in Ionia on the coast of Anatolia. Greeks had long been settled there, but around 546 B.C., the Persians conquered the area. ...
... in the other. This fearsome formation, or phalanx, became the most powerful fighting force in the ancient world. The Persian Wars, between Greece and the Persian Empire, began in Ionia on the coast of Anatolia. Greeks had long been settled there, but around 546 B.C., the Persians conquered the area. ...
The Late Classical Period, 4th Century BCE
... Greek statues were bronzes, but few have survived. If this sculpture is a product of Praxiteles' workshop, it is the only large Greek bronze statue that can be attributed to a Greek sculptor. Praxiteles was widely popular in his day. His famous Aphrodite of Cnidus (late 360s bc) introduced the life- ...
... Greek statues were bronzes, but few have survived. If this sculpture is a product of Praxiteles' workshop, it is the only large Greek bronze statue that can be attributed to a Greek sculptor. Praxiteles was widely popular in his day. His famous Aphrodite of Cnidus (late 360s bc) introduced the life- ...
Document
... When they almost had a civil war, Solon was given authority to write new laws. He tried to balance power between rich and poor (it used to be if you couldn’t re-pay someone, you became their slave). He gave citizenship to some foreigners – to attract more business to Athens. He came up with an idea ...
... When they almost had a civil war, Solon was given authority to write new laws. He tried to balance power between rich and poor (it used to be if you couldn’t re-pay someone, you became their slave). He gave citizenship to some foreigners – to attract more business to Athens. He came up with an idea ...
Chapter Four
... BCE)--the Athenians won without Spartans’ help • The Battle of Salamis (480-479 BCE)– Athens rises to the forefront of Greek culture because of victory over Xerxes (Persia) ...
... BCE)--the Athenians won without Spartans’ help • The Battle of Salamis (480-479 BCE)– Athens rises to the forefront of Greek culture because of victory over Xerxes (Persia) ...
Chapter 27 Two City-States Athens and Sparta
... In Sparta, the purpose of education was to produce capable men and women who could fight to protect the city-state. Spartans were likely to abandon sickly infants who might not grow up to be strong soldiers. Spartans highly valued discipline and strength. From the age of 7, all Spartan children tra ...
... In Sparta, the purpose of education was to produce capable men and women who could fight to protect the city-state. Spartans were likely to abandon sickly infants who might not grow up to be strong soldiers. Spartans highly valued discipline and strength. From the age of 7, all Spartan children tra ...
Epikleros

An epikleros (ἐπίκληρος; plural epikleroi) was an heiress in ancient Athens and other ancient Greek city states, specifically a daughter of a man who had no male heirs. In Sparta, they were called patrouchoi (πατροῦχοι), as they were in Gortyn. Athenian women were not allowed to hold property in their own name; in order to keep her father's property in the family, an epikleros was required to marry her father's nearest male relative. Even if a woman was already married, evidence suggests that she was required to divorce her spouse to marry that relative. Spartan women were allowed to hold property in their own right, and so Spartan heiresses were subject to less restrictive rules. Evidence from other city-states is more fragmentary, mainly coming from the city-states of Gortyn and Rhegium.Plato wrote about epikleroi in his Laws, offering idealized laws to govern their marriages. In mythology and history, a number of Greek women appear to have been epikleroi, including Agariste of Sicyon and Agiatis, the widow of the Spartan king Agis IV. The status of epikleroi has often been used to explain the numbers of sons-in-law who inherited from their fathers-in-law in Greek mythology. The Third Sacred War originated in a dispute over epikleroi.