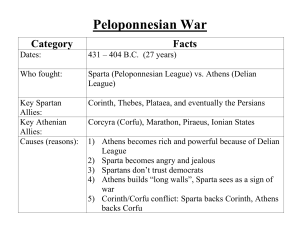
Peloponnesian War - Newton.k12.ma.us
... plague breaks out (430 B.C.) - last four years, 1/4 of Athenian populations dies 3) Athens suffers huge loss at Syracuse (many Athenians die and into slavery; 413 B.C.) 4) Delian League states flee and join Sparta 5) Persians give Sparta money to stop supporting Ionian states (hope Greek states kill ...
... plague breaks out (430 B.C.) - last four years, 1/4 of Athenian populations dies 3) Athens suffers huge loss at Syracuse (many Athenians die and into slavery; 413 B.C.) 4) Delian League states flee and join Sparta 5) Persians give Sparta money to stop supporting Ionian states (hope Greek states kill ...
Ancient Greece - Class Notes For Mr. Pantano
... working of the universe. In the 6th century BCE, the Greeks from Asia Minor began to question this belief. They based their knowledge on logic and ...
... working of the universe. In the 6th century BCE, the Greeks from Asia Minor began to question this belief. They based their knowledge on logic and ...
“Spartan” lifestyle is living without luxuries
... It included physical training, but also learned to read, write, and play musical instruments They served in the army from age 18 to 20, and then only in times of war after that ...
... It included physical training, but also learned to read, write, and play musical instruments They served in the army from age 18 to 20, and then only in times of war after that ...
The Greek “Polis”: Athens and Sparta I. The classical ______ (city
... 1. The homoloi (________) were adult male Spartan citizens over the age of eighteen. They had substantial rights of political participation which was unusual at a time so early in history 2. The periokoi (dwellers about) were what we would call “resident aliens”. These people were not citizens but e ...
... 1. The homoloi (________) were adult male Spartan citizens over the age of eighteen. They had substantial rights of political participation which was unusual at a time so early in history 2. The periokoi (dwellers about) were what we would call “resident aliens”. These people were not citizens but e ...
Chapter 7 Section 2 Guided Notes
... 2. Other city-states began to fear and resent _________________. 3. They looked to _______________________ which had not joined the alliance for ______________________. 4. Sparta formed the ____________________________ League, named after ________________________, the southern Greek ________________ ...
... 2. Other city-states began to fear and resent _________________. 3. They looked to _______________________ which had not joined the alliance for ______________________. 4. Sparta formed the ____________________________ League, named after ________________________, the southern Greek ________________ ...
Pericles - CarnoGold
... Athens Why did Spartans reject the aid of Athens in putting down a slave revolt? The public humiliation over the rejection later led to the 10-year banishment of Cimon, the leading politician in Athens. Solon, the Athenian lawgiver, introduced reforms including an important shift to wealth—which cou ...
... Athens Why did Spartans reject the aid of Athens in putting down a slave revolt? The public humiliation over the rejection later led to the 10-year banishment of Cimon, the leading politician in Athens. Solon, the Athenian lawgiver, introduced reforms including an important shift to wealth—which cou ...
Persian Wars (approx
... - Sickness killed many Athenians and they had no access to food because the Spartans surrounded their city - Athens surrendered - Sparta made Athens a part of the Spartan oligarchy - Athens began to recover - Greek city-states began to lose power as the Macedonian empire grew Macedonia Rises - King ...
... - Sickness killed many Athenians and they had no access to food because the Spartans surrounded their city - Athens surrendered - Sparta made Athens a part of the Spartan oligarchy - Athens began to recover - Greek city-states began to lose power as the Macedonian empire grew Macedonia Rises - King ...
Early Government
... where marble temples dedicated to gods and goddesses stood. The marketplace stood on flatter ground where free men spent much of their time debating. Early Government The earliest form of Government seen in city- states was a Monarchy . A government where the king or queen exercises central po ...
... where marble temples dedicated to gods and goddesses stood. The marketplace stood on flatter ground where free men spent much of their time debating. Early Government The earliest form of Government seen in city- states was a Monarchy . A government where the king or queen exercises central po ...
(Intro thru Spartan Women) (All Greece Notes are on
... •considered a citizen and could marry, but had to stay in barracks Age 30 ”_____________________________” •Considered a “____________________Citizen” •could vote in the _______________________________ •could live at home Age ______________ •Retire ...
... •considered a citizen and could marry, but had to stay in barracks Age 30 ”_____________________________” •Considered a “____________________Citizen” •could vote in the _______________________________ •could live at home Age ______________ •Retire ...
Sparta v. Athens
... and boxing • Women married at 19 • Women had considerable freedom, especially in running the family estates when their husbands were on active military service • Told husbands and sons going to war to “come back with your shield or on it” ...
... and boxing • Women married at 19 • Women had considerable freedom, especially in running the family estates when their husbands were on active military service • Told husbands and sons going to war to “come back with your shield or on it” ...
Panathenea - Education of Ancient Greece
... Reciting and musical performance of poetry. The teacher was called "Kytharistes"(Guitarist). Through letters, music and poetry, the pupils ...
... Reciting and musical performance of poetry. The teacher was called "Kytharistes"(Guitarist). Through letters, music and poetry, the pupils ...
Greek History
... 38. The ruler of Athens during the city's so-called Golden Age was_______. a. Solon b. Peisistratus c. Draco d. Pericles 39. The Greek mathematician that wrote a book called The Elements, which summarized all the knowledge of geometry up to his time, was _________. a. Euclid b. Eratosthenes c. Anaxa ...
... 38. The ruler of Athens during the city's so-called Golden Age was_______. a. Solon b. Peisistratus c. Draco d. Pericles 39. The Greek mathematician that wrote a book called The Elements, which summarized all the knowledge of geometry up to his time, was _________. a. Euclid b. Eratosthenes c. Anaxa ...
The Golded Age of Greece Guided Notes
... o __________________ Sought truths about broad concepts such as truth, justice, and virtue o Plato Most famous work is, the ________________. Timaeus and Critias (speak of Atlantis) o Aristotle Used logic and reason to study the natural world. ____________- is clear and ordered thinking ...
... o __________________ Sought truths about broad concepts such as truth, justice, and virtue o Plato Most famous work is, the ________________. Timaeus and Critias (speak of Atlantis) o Aristotle Used logic and reason to study the natural world. ____________- is clear and ordered thinking ...
greekgovernment
... (polis) had its own personality, goals, laws and customs. Ancient Greeks were very loyal to their city-state. If you asked an ancient Greek where he was from, he would not say, "I live in Greece." If he was from Sparta, he would say, "I am a Spartan." If he lived in Athens, he would say, "I am Athen ...
... (polis) had its own personality, goals, laws and customs. Ancient Greeks were very loyal to their city-state. If you asked an ancient Greek where he was from, he would not say, "I live in Greece." If he was from Sparta, he would say, "I am a Spartan." If he lived in Athens, he would say, "I am Athen ...
Athenian Vs. American Democracy
... • Each group will get a scenario, a problem to be solved by a government. • Decide in your group which government would do a better job: Athens or the US. • Create a multi-step action plan for the government to solve that particular problem. • Show your response on chart paper. ...
... • Each group will get a scenario, a problem to be solved by a government. • Decide in your group which government would do a better job: Athens or the US. • Create a multi-step action plan for the government to solve that particular problem. • Show your response on chart paper. ...
Greece II (Review and Assessment Questions p. 224)
... b. Why was the Athenian victory in the Battle at Marathon significant? The Athenians victory saved the peninsula (Greece) from Persian rule. The battle is also a symbol of the bravery of the few over the many. The victory increased their sense of importance because they believed the gods favored the ...
... b. Why was the Athenian victory in the Battle at Marathon significant? The Athenians victory saved the peninsula (Greece) from Persian rule. The battle is also a symbol of the bravery of the few over the many. The victory increased their sense of importance because they believed the gods favored the ...
The Rise of Greek Democracy
... To understand the rise of Greek democracy, we have to look at the differences between our modern nation-state, which is a large collection of people, cities, and states, and the city-states like ancient Athens, which occupied the urban center of Athens and the surrounding countryside of Attica. The ...
... To understand the rise of Greek democracy, we have to look at the differences between our modern nation-state, which is a large collection of people, cities, and states, and the city-states like ancient Athens, which occupied the urban center of Athens and the surrounding countryside of Attica. The ...
Ancient Greece and You
... Be Golden Like the Greeks (Or at Least Athens) 480-404 BCE • Pericles (445 BCE) – Non-wealthy could hold public office, paid jury duty, interest in public life ...
... Be Golden Like the Greeks (Or at Least Athens) 480-404 BCE • Pericles (445 BCE) – Non-wealthy could hold public office, paid jury duty, interest in public life ...
Governments
... the military. These men used a variety of means to gain control, from political tactics to violence. • After removing the oligarchs from power, many of these men established themselves as the absolute rulers of their respective city-states. This meant they had complete control of all aspects of gove ...
... the military. These men used a variety of means to gain control, from political tactics to violence. • After removing the oligarchs from power, many of these men established themselves as the absolute rulers of their respective city-states. This meant they had complete control of all aspects of gove ...
warring city-states
... The Council members were chosen by lot, or at random. These reforms allowed Athenian citizens to participate in a ...
... The Council members were chosen by lot, or at random. These reforms allowed Athenian citizens to participate in a ...
Classical Greece Test Review Name: #______ Date: Classical
... Athenian General Pericles consolidated his own power by using all the tribute money to serve rich and poor citizens. Generals were among the only public officials in Athens who were elected. They could not keep their job for more than one year. Pericles paid wages to jurors and members of th ...
... Athenian General Pericles consolidated his own power by using all the tribute money to serve rich and poor citizens. Generals were among the only public officials in Athens who were elected. They could not keep their job for more than one year. Pericles paid wages to jurors and members of th ...
Epikleros

An epikleros (ἐπίκληρος; plural epikleroi) was an heiress in ancient Athens and other ancient Greek city states, specifically a daughter of a man who had no male heirs. In Sparta, they were called patrouchoi (πατροῦχοι), as they were in Gortyn. Athenian women were not allowed to hold property in their own name; in order to keep her father's property in the family, an epikleros was required to marry her father's nearest male relative. Even if a woman was already married, evidence suggests that she was required to divorce her spouse to marry that relative. Spartan women were allowed to hold property in their own right, and so Spartan heiresses were subject to less restrictive rules. Evidence from other city-states is more fragmentary, mainly coming from the city-states of Gortyn and Rhegium.Plato wrote about epikleroi in his Laws, offering idealized laws to govern their marriages. In mythology and history, a number of Greek women appear to have been epikleroi, including Agariste of Sicyon and Agiatis, the widow of the Spartan king Agis IV. The status of epikleroi has often been used to explain the numbers of sons-in-law who inherited from their fathers-in-law in Greek mythology. The Third Sacred War originated in a dispute over epikleroi.























