North American Colonization
... Athens, only the men had political rights • Metics: born outside Athens, free and had to pay taxes but had no political rights and could not own land • Slaves: captured in war, together with metics made up more than half of Athenian society ...
... Athens, only the men had political rights • Metics: born outside Athens, free and had to pay taxes but had no political rights and could not own land • Slaves: captured in war, together with metics made up more than half of Athenian society ...
ancient greece powerpoint 1
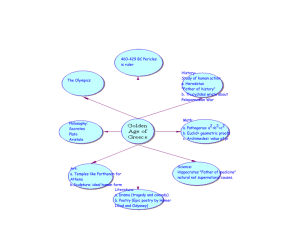
... How effective was Athenian Democracy? • Ancient Athens is often referred to as the cradle of democracy • Democracy flourished during the Golden Age of Athens (4th Century BCE) under Pericles Direct Democracy= All the male citizens would gather, discussed the issues, and then voted on them. • Howeve ...
... How effective was Athenian Democracy? • Ancient Athens is often referred to as the cradle of democracy • Democracy flourished during the Golden Age of Athens (4th Century BCE) under Pericles Direct Democracy= All the male citizens would gather, discussed the issues, and then voted on them. • Howeve ...
PowerPoint Overview of Ancient Greece
... How effective was Athenian Democracy? • Ancient Athens is often referred to as the cradle of democracy • Democracy flourished during the Golden Age of Athens (4th Century BCE) under Pericles Direct Democracy= All the male citizens would gather, discussed the issues, and then voted on them. • Howeve ...
... How effective was Athenian Democracy? • Ancient Athens is often referred to as the cradle of democracy • Democracy flourished during the Golden Age of Athens (4th Century BCE) under Pericles Direct Democracy= All the male citizens would gather, discussed the issues, and then voted on them. • Howeve ...
b. Thucydides wrote abou
... strategy was to avoid land battles among the Spartan army and wait for the right opportunity to strike against Sparta and its allies from sea. Spartans marched into Athenian territory by destroying everything and leaving nothing behind and restored. As time passed, a plague swept through the entire ...
... strategy was to avoid land battles among the Spartan army and wait for the right opportunity to strike against Sparta and its allies from sea. Spartans marched into Athenian territory by destroying everything and leaving nothing behind and restored. As time passed, a plague swept through the entire ...
Ancient_Greece - WordPress.com
... often as he pleased but also had the right to debate, offer amendments, and vote on proposals. Every man had a say in whether to declare war or stay in peace. Basically any thing that required a government decision, all male citizens were allowed to participate in. ...
... often as he pleased but also had the right to debate, offer amendments, and vote on proposals. Every man had a say in whether to declare war or stay in peace. Basically any thing that required a government decision, all male citizens were allowed to participate in. ...
Chapter 3 – Ancient Greece:100
... Athens: -‐ Government organizaEon – controlled by Archons (“first men”) –9 aristocrats who served for 1 year, & then became permanent members of the Areopagus (council of elders) who apptd. archons -‐ ...
... Athens: -‐ Government organizaEon – controlled by Archons (“first men”) –9 aristocrats who served for 1 year, & then became permanent members of the Areopagus (council of elders) who apptd. archons -‐ ...
Document A: Pericles (Modified) - mr. wright`s world geography class
... they dispersed and reassembled two months later. They brought with them their ostracon (a fragment of pottery), on which they had scratched the name of the person they thought represented a threat. The man with the most votes lost. He was exiled for 10 years, and this was thought to calm any anti-de ...
... they dispersed and reassembled two months later. They brought with them their ostracon (a fragment of pottery), on which they had scratched the name of the person they thought represented a threat. The man with the most votes lost. He was exiled for 10 years, and this was thought to calm any anti-de ...
Document A: Pericles (Modified)
... they dispersed and reassembled two months later. They brought with them their ostracon (a fragment of pottery), on which they had scratched the name of the person they thought represented a threat. The man with the most votes lost. He was exiled for 10 years, and this was thought to calm any anti-de ...
... they dispersed and reassembled two months later. They brought with them their ostracon (a fragment of pottery), on which they had scratched the name of the person they thought represented a threat. The man with the most votes lost. He was exiled for 10 years, and this was thought to calm any anti-de ...
Name: Date: SECTION 1- THE POLIS = city
... What was the message Spartan women gave their men when they went into battle? “Come home with your shield, or on it!” = Win or die trying! Spartans tried to prevent change in their city. Provide two examples of this from the reading. 1. Spartans could not travel outside Sparta except for war 2. No c ...
... What was the message Spartan women gave their men when they went into battle? “Come home with your shield, or on it!” = Win or die trying! Spartans tried to prevent change in their city. Provide two examples of this from the reading. 1. Spartans could not travel outside Sparta except for war 2. No c ...
The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome: Cornell Notes
... solve its economic 1. Respected lawmaker made changes problems? a. outlawed slavery based on debt b. cancelled farmers’ debt What reforms did c. increased citizenship to four groups Solon make? d. three higher classes could vote e. all adult males were citizens How were Solon’s f. created Council of ...
... solve its economic 1. Respected lawmaker made changes problems? a. outlawed slavery based on debt b. cancelled farmers’ debt What reforms did c. increased citizenship to four groups Solon make? d. three higher classes could vote e. all adult males were citizens How were Solon’s f. created Council of ...
The Story of Ancient Greece Geography of Greece Greece is a small
... C. Greek city-states acted like their own ______________ III. Sparta A. Sparta was located in the ___________. B. Sparta was very _____________ and had its own _____________. C. Sparta conquered other city-states to gain ________________________________. D. There were ___________ classes of people i ...
... C. Greek city-states acted like their own ______________ III. Sparta A. Sparta was located in the ___________. B. Sparta was very _____________ and had its own _____________. C. Sparta conquered other city-states to gain ________________________________. D. There were ___________ classes of people i ...
Review of Cambridge Companion to the Age of Pericles
... many trends that dominated Athenian history for much of the fifth century' (18). It is clear by the introduction, which acquaints the reader with the ancient sources for the period and provides a general overview of 'Athenian History and Society in the Age of Pericles,' that the target readership is ...
... many trends that dominated Athenian history for much of the fifth century' (18). It is clear by the introduction, which acquaints the reader with the ancient sources for the period and provides a general overview of 'Athenian History and Society in the Age of Pericles,' that the target readership is ...
Hebrews, Persians and Greeks, 1100
... • Control of helots through terror • Valued courage, blind obedience, personal simplicity and contempt for fear and pain • Military bonds outweighed family ...
... • Control of helots through terror • Valued courage, blind obedience, personal simplicity and contempt for fear and pain • Military bonds outweighed family ...
The Athenian Globe tribune
... The end of the long and bitter Peloponnesian War finally came today when the city of Athens surrendered to two Spartan kings, Agis and Pausanias. With a reported 100,000 citizens starving in the besieged city, officials felt they had no choice but to accept defeat. As one devastated elderly man repo ...
... The end of the long and bitter Peloponnesian War finally came today when the city of Athens surrendered to two Spartan kings, Agis and Pausanias. With a reported 100,000 citizens starving in the besieged city, officials felt they had no choice but to accept defeat. As one devastated elderly man repo ...
Rise of the Greeks - Mr. Banks` AP World History Page
... THE EMERGENCE OF THE POLIS Farmers as soldiers: no special training Exception: Sparta ...
... THE EMERGENCE OF THE POLIS Farmers as soldiers: no special training Exception: Sparta ...
The Melian Dialogue
... "My answer is bring them on." —on Iraqi insurgents attacking U.S. forces, Washington, D.C., July 3, 2003 "Our enemies are innovative and resourceful, and so are we. They never stop thinking about new ways to harm our country and our people, and neither do we." —Washington, D.C., Aug. 5, 2004 (Watch ...
... "My answer is bring them on." —on Iraqi insurgents attacking U.S. forces, Washington, D.C., July 3, 2003 "Our enemies are innovative and resourceful, and so are we. They never stop thinking about new ways to harm our country and our people, and neither do we." —Washington, D.C., Aug. 5, 2004 (Watch ...
Athens VS Sparta
... training at age of 7 (Boys AND girls) • At 20, boys had to pass a rigorous physical test that determined • They then served until; they were 60 • whether they would be Spartan warriors or not • Boys learned to read and write, but these were not seen as important skills ...
... training at age of 7 (Boys AND girls) • At 20, boys had to pass a rigorous physical test that determined • They then served until; they were 60 • whether they would be Spartan warriors or not • Boys learned to read and write, but these were not seen as important skills ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Alexandria an ancient Hellenistic city in
... Athens has the Delian League, Sparta has the Peloponnesian League Athens – navy Sparta – army What events happen during the war? o Sparta surrounds Athens (Athens tried to avoid fighting on land) o Under siege from Sparta, Athens retreats within city walls Plague strikes because of the close quart ...
... Athens has the Delian League, Sparta has the Peloponnesian League Athens – navy Sparta – army What events happen during the war? o Sparta surrounds Athens (Athens tried to avoid fighting on land) o Under siege from Sparta, Athens retreats within city walls Plague strikes because of the close quart ...
Chapter 11 Study Guide
... 24) Athens moved into a democracy. What kind of democracy do they have and who are allowed to participate in their government? How does that compare to United States democracy? Athenian style of ...
... 24) Athens moved into a democracy. What kind of democracy do they have and who are allowed to participate in their government? How does that compare to United States democracy? Athenian style of ...
Sparta
... – Spent their days marching, exercising, and fighting – Slept without blankets on hard benches – Daily diet: bowl of coarse black porridge • Spartan girls – Some military training – Ran, wrestled, and played sports – Considerable freedom – ran the family estates when their husbands were on active mi ...
... – Spent their days marching, exercising, and fighting – Slept without blankets on hard benches – Daily diet: bowl of coarse black porridge • Spartan girls – Some military training – Ran, wrestled, and played sports – Considerable freedom – ran the family estates when their husbands were on active mi ...
SWBAT compare and contrast the lives of individuals in Athens and
... number of Athenian citizens to participate in their government at a high level. Laws were passed by a majority vote in the assembly. ...
... number of Athenian citizens to participate in their government at a high level. Laws were passed by a majority vote in the assembly. ...
What is the definition of Citizenship: Courtesy of Grolier`s New Book
... Political inequality persisted nevertheless. In the case of Athens, some of the solutions to the most critical issues about citizenship were attributed to lawgivers. For example, Solon, a poor aristocrat, was elected archon (a chief magistrate of the polis) in 594 B.C. and set about reforming the co ...
... Political inequality persisted nevertheless. In the case of Athens, some of the solutions to the most critical issues about citizenship were attributed to lawgivers. For example, Solon, a poor aristocrat, was elected archon (a chief magistrate of the polis) in 594 B.C. and set about reforming the co ...
Comparing the Government of
... Brutus Magnamus, Roman Senator (397 BCE). Excerpt from a speech on the Senate floor. “I say to you my fellow Senators; let not the wary opinions of the common deter you in what is best for Rome. It is we that have the power, nay the responsibility, to our forefathers who founded this great land befo ...
... Brutus Magnamus, Roman Senator (397 BCE). Excerpt from a speech on the Senate floor. “I say to you my fellow Senators; let not the wary opinions of the common deter you in what is best for Rome. It is we that have the power, nay the responsibility, to our forefathers who founded this great land befo ...
Aristotle: On Greek Governance
... “the people” are to be defined and how their views are to be taken into account. In ancient Athens – where Western-style democratic practices first emerged – Aristotle saw that no political system is ideal. But he believed that, when large numbers of citizens share in decision making, there are fewe ...
... “the people” are to be defined and how their views are to be taken into account. In ancient Athens – where Western-style democratic practices first emerged – Aristotle saw that no political system is ideal. But he believed that, when large numbers of citizens share in decision making, there are fewe ...
Athenian democracy

Athenian democracy developed around the fifth century BC in the Greek city-state (known as a polis) of Athens, comprising the city of Athens and the surrounding territory of Attica and is the first known democracy in the world. Other Greek cities set up democracies, most following the Athenian model, but none are as well documented as Athens.It was a system of direct democracy, in which participating citizens voted directly on legislation and executive bills. Participation was not open to all residents: to vote one had to be an adult, male citizen, and the number of these ""varied between 30,000 and 50,000 out of a total population of around 250,000 to 300,000.""The longest-lasting democratic leader was Pericles. After his death, Athenian democracy was twice briefly interrupted by oligarchic revolutions towards the end of the Peloponnesian War. It was modified somewhat after it was restored under Eucleides; and the most detailed accounts of the system are of this fourth-century modification rather than the Periclean system. Democracy was suppressed by the Macedonians in 322 BC. The Athenian institutions were later revived, but how close they were to a real democracy is debatable. Solon (594 BC), Cleisthenes (508/7 BC), an aristocrat, and Ephialtes (462 BC) contributed to the development of Athenian democracy.