MATH 409, Fall 2013 [3mm] Advanced Calculus I
... interval [a, b] is also uniformly continuous on [a, b]. Proof: Assume that a function f : [a, b] → R is not uniformly continuous on [a, b]. We have to show that f is not continuous on [a, b]. By assumption, there exists ε > 0 such that for any δ > 0 we can find two points x, y ∈ [a, b] satisfying |x ...
... interval [a, b] is also uniformly continuous on [a, b]. Proof: Assume that a function f : [a, b] → R is not uniformly continuous on [a, b]. We have to show that f is not continuous on [a, b]. By assumption, there exists ε > 0 such that for any δ > 0 we can find two points x, y ∈ [a, b] satisfying |x ...
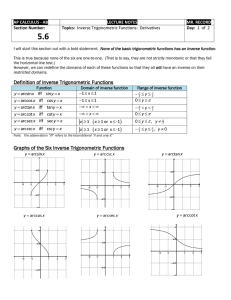
5.6: Inverse Trigonometric Functions: Differentiation
... LECTURE NOTES Topics: Inverse Trigonometric Functions: Derivatives - Inverse Trig Function Analyisis ...
... LECTURE NOTES Topics: Inverse Trigonometric Functions: Derivatives - Inverse Trig Function Analyisis ...
Trig Final Exam Review
... Solve the problem. 26) The grade resistance F of a car traveling up or down a hill is modeled by the equation F = W sin θ, where W is the weight of the car and θ is the angle of the hill's grade (θ > 0 for uphill travel, θ < 0 for downhill travel). What is the grade resistance (to the nearest pound) ...
... Solve the problem. 26) The grade resistance F of a car traveling up or down a hill is modeled by the equation F = W sin θ, where W is the weight of the car and θ is the angle of the hill's grade (θ > 0 for uphill travel, θ < 0 for downhill travel). What is the grade resistance (to the nearest pound) ...





![MATH 409, Fall 2013 [3mm] Advanced Calculus I](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/019184906_1-2ea198de2d20e978c4b1d91fadeb6dab-300x300.png)