Multimodal imaging and the neural basis of EEG and fMRI
... noise caused by the MRI gradient system are all factors altering the experimental effects. Study of spontaneous (paradigm-free) brain activity, such as natural variations in EEG background (alpha rhythm), wakefulness, or activity during resting state EEG–fMRI is one strategy that can ascribe the tim ...
... noise caused by the MRI gradient system are all factors altering the experimental effects. Study of spontaneous (paradigm-free) brain activity, such as natural variations in EEG background (alpha rhythm), wakefulness, or activity during resting state EEG–fMRI is one strategy that can ascribe the tim ...
Document
... to sudden death during infancy Studies of SIDS victims reveal that many SIDS infants have abnormalities in the "arcuate nucleus," a portion of the brain that is likely to be involved in controlling breathing and waking during sleep Babies born with defects in other portions of the brain or body may ...
... to sudden death during infancy Studies of SIDS victims reveal that many SIDS infants have abnormalities in the "arcuate nucleus," a portion of the brain that is likely to be involved in controlling breathing and waking during sleep Babies born with defects in other portions of the brain or body may ...
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems
... each electrode is then amplified, stored and displayed on a monitor. We also measure several other physiological signals in conjunction with the EEG such as the ECG (heart function), respiration (lung function) and EMG (muscle function), as these recordings can influence the EEG. We then analyse the ...
... each electrode is then amplified, stored and displayed on a monitor. We also measure several other physiological signals in conjunction with the EEG such as the ECG (heart function), respiration (lung function) and EMG (muscle function), as these recordings can influence the EEG. We then analyse the ...
Slide 1
... eliminate seizures) (VIDEO) – It is as if you have two competing brains; and will follow their own instructions- “two separate minds” • Left- deliberating (rationalize) • Right- simple requests • Shirt unbutton/Grocery store items • “Walk” ...
... eliminate seizures) (VIDEO) – It is as if you have two competing brains; and will follow their own instructions- “two separate minds” • Left- deliberating (rationalize) • Right- simple requests • Shirt unbutton/Grocery store items • “Walk” ...
Visual categorization shapes feature selectivity in the primate
... Red circles : Neurons with statistically significant selectivity for diagnostic dimension only Blue circles : Neurons with significant selectivity for diagnostic and non-diagnostic feature Black triangles : Neurons with no significant selectivity Red star : Example neuron depicted in previous figure ...
... Red circles : Neurons with statistically significant selectivity for diagnostic dimension only Blue circles : Neurons with significant selectivity for diagnostic and non-diagnostic feature Black triangles : Neurons with no significant selectivity Red star : Example neuron depicted in previous figure ...
Ch. 11 Notes
... • Responsible for awareness of time, sequence, details, and order • Responsible for auditory receptive and verbal expressive strengths • Specializes in words, logic, analytical thinking, reading, and writing • Responsible for boundaries and knowing right from wrong • Knows and respects rules and dea ...
... • Responsible for awareness of time, sequence, details, and order • Responsible for auditory receptive and verbal expressive strengths • Specializes in words, logic, analytical thinking, reading, and writing • Responsible for boundaries and knowing right from wrong • Knows and respects rules and dea ...
Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VI. Growth Factors
... term survival of neurons are mediated by trophic factors that are secreted by the target nerve cells, bind to specific receptors, and signal to the nearby developing synapse. Within the nervous system, the most extensively studied of these factors is the family of neurotrophins. Almost 50 years ago, ...
... term survival of neurons are mediated by trophic factors that are secreted by the target nerve cells, bind to specific receptors, and signal to the nearby developing synapse. Within the nervous system, the most extensively studied of these factors is the family of neurotrophins. Almost 50 years ago, ...
1. What are some major differences between
... hypothalamus to PAG. The PANIC system is associated with the anterior cinculate, the BNST, and the preoptic area, as well as the dorsomedial thalamlus and PAG. 4. While there is still much work to be done to understand the brain bases of human emotion, what is the role of the amygdala in emotional p ...
... hypothalamus to PAG. The PANIC system is associated with the anterior cinculate, the BNST, and the preoptic area, as well as the dorsomedial thalamlus and PAG. 4. While there is still much work to be done to understand the brain bases of human emotion, what is the role of the amygdala in emotional p ...
Topic Option A Neurobio
... tissues in Xenopus, used as an animal model, Guidance: Terminology relating to embryonic during neurulation. brain areas or nervous system divisions is not required. 5. An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli. 6. Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other ...
... tissues in Xenopus, used as an animal model, Guidance: Terminology relating to embryonic during neurulation. brain areas or nervous system divisions is not required. 5. An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli. 6. Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) ISSN: , PP: 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org
... performed using functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). The field that has grown around the acquisition and analysis of fMRI data is intrinsically interdisciplinary in nature and involves contributions from researchers in neuroscience, psychology, physics and statistics, among others.Brain-map ...
... performed using functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). The field that has grown around the acquisition and analysis of fMRI data is intrinsically interdisciplinary in nature and involves contributions from researchers in neuroscience, psychology, physics and statistics, among others.Brain-map ...
dynamics and functional connectivity in barrel network
... experiments. Whisker deflections were done by giving the paired repetitive pulses of air-puffing (50 psi, 50 ms) through a tiny steel tube that was mounted on a micromanipulator and controlled with costume-made LabVIEW program. The stimulus patterns were paired bursts that constituted of frequency p ...
... experiments. Whisker deflections were done by giving the paired repetitive pulses of air-puffing (50 psi, 50 ms) through a tiny steel tube that was mounted on a micromanipulator and controlled with costume-made LabVIEW program. The stimulus patterns were paired bursts that constituted of frequency p ...
Chapter 04-06
... a passive maturation process that occurs over time. Child as a computational system Children undergo continuous (quantitative) cognitive change Development through increasingly sophisticated hardware and software ...
... a passive maturation process that occurs over time. Child as a computational system Children undergo continuous (quantitative) cognitive change Development through increasingly sophisticated hardware and software ...
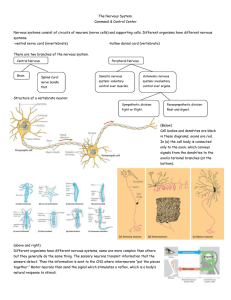
The Human Body Systems
... 1. Receive information about what’s happening to the body (both inside & out) 2. Responds to those internal and environmental stimuli 3. Maintains homeostasis B. The Neuron – the basic unit of structure & function 1. Cells that carry information to, from & through the brain by way of nerve impulses. ...
... 1. Receive information about what’s happening to the body (both inside & out) 2. Responds to those internal and environmental stimuli 3. Maintains homeostasis B. The Neuron – the basic unit of structure & function 1. Cells that carry information to, from & through the brain by way of nerve impulses. ...
Slide 1 - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... 4. Recurrent networks of spiking neurons. This is a field that is advancing rapidly! There were two absolutely seminal papers about a decade ago: van Vreeswijk and Sompolinsky (Science, 1996) van Vreeswijk and Sompolinsky (Neural Comp., 1998) We now understand very well randomly connected networks ...
... 4. Recurrent networks of spiking neurons. This is a field that is advancing rapidly! There were two absolutely seminal papers about a decade ago: van Vreeswijk and Sompolinsky (Science, 1996) van Vreeswijk and Sompolinsky (Neural Comp., 1998) We now understand very well randomly connected networks ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane This process is due to stimulation from either heat, chemicals, pressure or light ...
... a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane This process is due to stimulation from either heat, chemicals, pressure or light ...
ChapTer 3 - Physicians for Social Responsibility
... The tissue of the outer layer of the cerebral cortex consists mainly of neural cell bodies and is known as gray matter. Just beneath run neural projections that relay signals between cortical cells and virtually every other area of the brain. This tissue is known as white matter, owing to the myelin ...
... The tissue of the outer layer of the cerebral cortex consists mainly of neural cell bodies and is known as gray matter. Just beneath run neural projections that relay signals between cortical cells and virtually every other area of the brain. This tissue is known as white matter, owing to the myelin ...
2-3 nervous sys Sp13
... Electrical currents involve movement of charged (+ or -) particles Analogy: Power Plant Creates Charge Power Lines Move that Charge (electrical current) ...
... Electrical currents involve movement of charged (+ or -) particles Analogy: Power Plant Creates Charge Power Lines Move that Charge (electrical current) ...
Template for designing a research poster
... Figure 2: Memristor crossbar array. In the context of technology. neuromorphic hardware, vertical electrodes represent o Requires less power during dynamic operation. [5] input to an array of neurons, while horizontal electrodes represent output from a separate array of neurons. At each intersection ...
... Figure 2: Memristor crossbar array. In the context of technology. neuromorphic hardware, vertical electrodes represent o Requires less power during dynamic operation. [5] input to an array of neurons, while horizontal electrodes represent output from a separate array of neurons. At each intersection ...
CH 3 Practice Test
... the amount of serotonin that can cross the axon’s membrane b. the +3 to +7 volt capacity of a typical motor neuron c. the ability of a motor neuron to either contract or relax a muscle group d. a brief electrical impulse that transmits information along the axon of a ...
... the amount of serotonin that can cross the axon’s membrane b. the +3 to +7 volt capacity of a typical motor neuron c. the ability of a motor neuron to either contract or relax a muscle group d. a brief electrical impulse that transmits information along the axon of a ...
Nervous
... The limbic system, a ring of cortical and noncortical centers around the brainstem, mediates primary emotions and attaches emotional “feelings” to survival–related functions. The association of primary emotions with different situations during human development requires parts of the neocortex, espec ...
... The limbic system, a ring of cortical and noncortical centers around the brainstem, mediates primary emotions and attaches emotional “feelings” to survival–related functions. The association of primary emotions with different situations during human development requires parts of the neocortex, espec ...
Neuroplasticity - University of Michigan–Flint
... • Occurs when neurons lose input from another brain region, e.g. postsynaptic neurons in the striatum become supersensitive to dopamine in patient with Parkinson ...
... • Occurs when neurons lose input from another brain region, e.g. postsynaptic neurons in the striatum become supersensitive to dopamine in patient with Parkinson ...
Document
... • The nearer to the front of the brain we go, the ‘newer’ it is. • The hindbrain controls more primitive functions- - heart rate and breathing- - where as the forebrain controls more thought and logical patterns – - -planning and behavior. ...
... • The nearer to the front of the brain we go, the ‘newer’ it is. • The hindbrain controls more primitive functions- - heart rate and breathing- - where as the forebrain controls more thought and logical patterns – - -planning and behavior. ...