Class X: Control and Coordination Some movements are in fact the
... Some movements, as in many animals and some plants, are not connected with growth.eg) cat running, children playing on swings. These visible movements are as a response to a change in the environment of the organism. Eg) The cat may be running because it has seen a mouse. Movement, in response to th ...
... Some movements, as in many animals and some plants, are not connected with growth.eg) cat running, children playing on swings. These visible movements are as a response to a change in the environment of the organism. Eg) The cat may be running because it has seen a mouse. Movement, in response to th ...
Science 6th primary. 1st term unit 4 lesson 1 Why does this
... 18 - …………………………… lies below the two cerebral hemispheres. 19 – the brain and spinal cord are connected by the ………………………………. 20 – the spinal cord extends inside a channel within the ……………………….. 21 – the ……………………… delivers the nerve messages from the body organs to the brain and vice ...
... 18 - …………………………… lies below the two cerebral hemispheres. 19 – the brain and spinal cord are connected by the ………………………………. 20 – the spinal cord extends inside a channel within the ……………………….. 21 – the ……………………… delivers the nerve messages from the body organs to the brain and vice ...
How and Why Brains Create Meaning from Sensory Information
... knowledge about their worlds by their own actions. Brains are exceedingly capable of grasping the salient features of complex situations and social relationships, which are captured in such words as 'value', 'significance', 'import', or 'bottom line', in a word, 'meaning'. It is my conclusion in thi ...
... knowledge about their worlds by their own actions. Brains are exceedingly capable of grasping the salient features of complex situations and social relationships, which are captured in such words as 'value', 'significance', 'import', or 'bottom line', in a word, 'meaning'. It is my conclusion in thi ...
myelin sheath
... emergence of cell assemblies in a small network of 69 neurons. They found that everything became active in their network. • They decided that they needed to include inhibitory synapses. This worked and cell assemblies did, indeed, form. • This was later confirmed in real brain circuitry. ...
... emergence of cell assemblies in a small network of 69 neurons. They found that everything became active in their network. • They decided that they needed to include inhibitory synapses. This worked and cell assemblies did, indeed, form. • This was later confirmed in real brain circuitry. ...
File
... They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better understanding of its parts and its respon ...
... They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better understanding of its parts and its respon ...
Nervous Systems
... Bird’s brain is large for its body size. Possess cerebrum, cerebellum and medulla oblongata ...
... Bird’s brain is large for its body size. Possess cerebrum, cerebellum and medulla oblongata ...
Document
... emergence of cell assemblies in a small network of 69 neurons. They found that everything became active in their network. • They decided that they needed to include inhibitory synapses. This worked and cell assemblies did, indeed, form. • This was later confirmed in real brain circuitry. ...
... emergence of cell assemblies in a small network of 69 neurons. They found that everything became active in their network. • They decided that they needed to include inhibitory synapses. This worked and cell assemblies did, indeed, form. • This was later confirmed in real brain circuitry. ...
An Exploration of the Brain
... with other bodily functions. Your cerebrum is divided into two parts called hemispheres. The left hemisphere controls the right side of your body and the right hemisphere controls the left side of your body. The two hemispheres are connected by something called the corpus callosum that allows the tw ...
... with other bodily functions. Your cerebrum is divided into two parts called hemispheres. The left hemisphere controls the right side of your body and the right hemisphere controls the left side of your body. The two hemispheres are connected by something called the corpus callosum that allows the tw ...
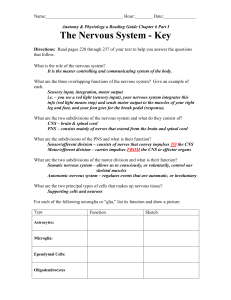
nervous system divisions cns, pns 1
... NERVOUS SYSTEM • Highly organized system of human body. • It is the organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. ...
... NERVOUS SYSTEM • Highly organized system of human body. • It is the organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. ...
New clues to the location of visual consciousness
... eyes can suffer from binocular rivalry. They generally cope with this condition in one of two ways. They either rely on the view from a single eye or they use each eye for a different purpose, such as close and far vision. The question of which neurons are responsible for this effect is a matter of ...
... eyes can suffer from binocular rivalry. They generally cope with this condition in one of two ways. They either rely on the view from a single eye or they use each eye for a different purpose, such as close and far vision. The question of which neurons are responsible for this effect is a matter of ...
A true science of consciousness explains
... when reported, access itself does not seem to be involved in generating the contents of experience, and therefore it has little power to explain phenomenology [10]. Now if it turns out that the neural mechanisms of perception established in our perfect experiment subside when their contents cannot b ...
... when reported, access itself does not seem to be involved in generating the contents of experience, and therefore it has little power to explain phenomenology [10]. Now if it turns out that the neural mechanisms of perception established in our perfect experiment subside when their contents cannot b ...
Durand and Barlow Chapter 2: An Integrative Approach to
... – Anger, hostility, emotional suppression, illness, and ...
... – Anger, hostility, emotional suppression, illness, and ...
Nerve cells - Dr Magrann
... receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. ...
... receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. ...
Adaptive dynamical systems: A promising tool for embodied artificial
... In a “proof of principle” implementation in a simulation [2] we showed that we can extend a simple dynamical system (i.e. an oscillator) with an additional state variable and the corresponding evolution law (i.e. differential equation) in order to make it adaptive to a mechanical structure. The mech ...
... In a “proof of principle” implementation in a simulation [2] we showed that we can extend a simple dynamical system (i.e. an oscillator) with an additional state variable and the corresponding evolution law (i.e. differential equation) in order to make it adaptive to a mechanical structure. The mech ...
NEURONS AS BIOANTENNAS
... Although it was not possible to quantify the exact number of photons that hit the MEAs, the impossibility for the human eye to perceive them implies that their number was less than 10 units. The reactivity of neurons to very weak light pulses could be due to the presence of microtubules in their ce ...
... Although it was not possible to quantify the exact number of photons that hit the MEAs, the impossibility for the human eye to perceive them implies that their number was less than 10 units. The reactivity of neurons to very weak light pulses could be due to the presence of microtubules in their ce ...
NEURONS AS BIOANTENNAS
... Although it was not possible to quantify the exact number of photons that hit the MEAs, the impossibility for the human eye to perceive them implies that their number was less than 10 units. The reactivity of neurons to very weak light pulses could be due to the presence of microtubules in their ce ...
... Although it was not possible to quantify the exact number of photons that hit the MEAs, the impossibility for the human eye to perceive them implies that their number was less than 10 units. The reactivity of neurons to very weak light pulses could be due to the presence of microtubules in their ce ...
Itch neurons play a role in managing pain
... braking system for pain," says Sun. "This brake is not always triggered by the painful stimuli; it's only triggered by the strong pain stimuli. When the brake is on, the signal doesn't go through. But when you have a weak pain signal, it doesn't trigger the brake and the signal can go through." The ...
... braking system for pain," says Sun. "This brake is not always triggered by the painful stimuli; it's only triggered by the strong pain stimuli. When the brake is on, the signal doesn't go through. But when you have a weak pain signal, it doesn't trigger the brake and the signal can go through." The ...
nn2new-02
... To extract useful information, we have to average for a group of neurons in a local circuit where neuron codes the same information over a time window to obtain the firing rate r ...
... To extract useful information, we have to average for a group of neurons in a local circuit where neuron codes the same information over a time window to obtain the firing rate r ...
Unit XIV: Regulation
... - Cell body – contains all the normal cell parts nucleus, mitochondria, golgi, ER, cytoplasm, etc. - Dendrites – receptors on the cell body, receive impulses, used to pick up stimuli - Axon – long fiber that extends from the cell body, carries the impulse - Schwann’s Cells produce a Myelin sheath – ...
... - Cell body – contains all the normal cell parts nucleus, mitochondria, golgi, ER, cytoplasm, etc. - Dendrites – receptors on the cell body, receive impulses, used to pick up stimuli - Axon – long fiber that extends from the cell body, carries the impulse - Schwann’s Cells produce a Myelin sheath – ...
Neurons` Short-Term Plasticity Amplifies Signals
... this process: the short-term plasticity at hippocampal synapses that result from processing incoming signals resembling place-field responses. The researchers, Vitaly Klyachko and Charles Stevens, discovered a novel short-term plasticity mechanism by which excitatory and inhibitory synapses can selec ...
... this process: the short-term plasticity at hippocampal synapses that result from processing incoming signals resembling place-field responses. The researchers, Vitaly Klyachko and Charles Stevens, discovered a novel short-term plasticity mechanism by which excitatory and inhibitory synapses can selec ...
Week 14 The Memory Function of Sleep
... 13. What sort of oscillatory neural activity is connected with consolidation during REM? Pontogeniculo-occipital (PGO) waves and the EEG theta rhythm support REM sleep-dependent consolidation processes. In rats: • an increase in REM sleep PGO-wave density for 3–4 hours following training on an acti ...
... 13. What sort of oscillatory neural activity is connected with consolidation during REM? Pontogeniculo-occipital (PGO) waves and the EEG theta rhythm support REM sleep-dependent consolidation processes. In rats: • an increase in REM sleep PGO-wave density for 3–4 hours following training on an acti ...
Circuits, Circuits
... After learning, S will only fire when B & D are active (i.e. after a time interval of duration = t1). Details are unclear as to whether A & C develop inhibitory links to S. In future (e.g. when repeating the dance), the instructor still says ”Go”, which again resets the cortical oscillators, but now ...
... After learning, S will only fire when B & D are active (i.e. after a time interval of duration = t1). Details are unclear as to whether A & C develop inhibitory links to S. In future (e.g. when repeating the dance), the instructor still says ”Go”, which again resets the cortical oscillators, but now ...
Nervous System
... Dendrite: Extends from the cell body and receives nerve impulses from other neurons. Axon: An extension of the cell body that transmits nerve impulses to other cells. Myelin Sheath: Outer layer of the axon that serves as an insulator for the axon. There are gaps on the myelin sheath that allow the e ...
... Dendrite: Extends from the cell body and receives nerve impulses from other neurons. Axon: An extension of the cell body that transmits nerve impulses to other cells. Myelin Sheath: Outer layer of the axon that serves as an insulator for the axon. There are gaps on the myelin sheath that allow the e ...