Lecture 3 Birth of the Renaissance and the Italian City States
... Center of the Renaissance during the 14th and 15th centuries. A republic, ruled by the signora (council of rich guild leaders) Faced social crisis in late 14th century, Chiompi Revolt by lower classes Eventually dominated by the Medici family: ...
... Center of the Renaissance during the 14th and 15th centuries. A republic, ruled by the signora (council of rich guild leaders) Faced social crisis in late 14th century, Chiompi Revolt by lower classes Eventually dominated by the Medici family: ...
The Renaissance in Italy
... • The intellectual and economic changes that occurred in Europe from the fourteenth through the sixteenth centuries. • An age in which artistic, social, scientific, cultural and political thought turned in new directions. • Concerned with civic and moral questions, not science or theology. • Emphasi ...
... • The intellectual and economic changes that occurred in Europe from the fourteenth through the sixteenth centuries. • An age in which artistic, social, scientific, cultural and political thought turned in new directions. • Concerned with civic and moral questions, not science or theology. • Emphasi ...
The Renaissance (1350
... The Medici Family Controlled Florence, they made their Fortune in Banking Lorenzo “The Magnificent” was the most Famous of the Medici Family 1. Rule Florence as a Dictator 2. Was a Patron of the Arts ...
... The Medici Family Controlled Florence, they made their Fortune in Banking Lorenzo “The Magnificent” was the most Famous of the Medici Family 1. Rule Florence as a Dictator 2. Was a Patron of the Arts ...
6) Renaissance & Reformation Beginnings
... • Vote for another pope- establishes two popes called The Western Schism – Pope in Rome and Anti-pope in Avignon • @ one point there would be 3 people claiming to be pope. ...
... • Vote for another pope- establishes two popes called The Western Schism – Pope in Rome and Anti-pope in Avignon • @ one point there would be 3 people claiming to be pope. ...
5 Themes of the Renaissance
... the liberty to determine the form and value our lives shall acquire….man is the master of his own destiny! ...
... the liberty to determine the form and value our lives shall acquire….man is the master of his own destiny! ...
File
... The new political leaders of Florence had hired Michelangelo, the most skilled sculptor of his time, to create a work that would symbolize the city. He decided on the young biblical hero, David, who defeated the giant Goliath with a simple slingshot and stone. Michelangelo wanted his work to encoura ...
... The new political leaders of Florence had hired Michelangelo, the most skilled sculptor of his time, to create a work that would symbolize the city. He decided on the young biblical hero, David, who defeated the giant Goliath with a simple slingshot and stone. Michelangelo wanted his work to encoura ...
New Patterns of Renaissance Thought Secularism
... political opportunities opening up for Western Europe in the Late Middle Ages encouraged more people to take an interest in this world. During the Renaissance, people saw life on Earth as worth living for its own sake, not just as an ordeal to endure before going to heaven. The art of the period in ...
... political opportunities opening up for Western Europe in the Late Middle Ages encouraged more people to take an interest in this world. During the Renaissance, people saw life on Earth as worth living for its own sake, not just as an ordeal to endure before going to heaven. The art of the period in ...
WHII: SOL 2b
... • Artists (daVinci, Michelangelo, Raphael) • Author (Castiglione: The Book of the Courtier and Machiavelli: The Prince) • Wealth: Medici family of Florence ...
... • Artists (daVinci, Michelangelo, Raphael) • Author (Castiglione: The Book of the Courtier and Machiavelli: The Prince) • Wealth: Medici family of Florence ...
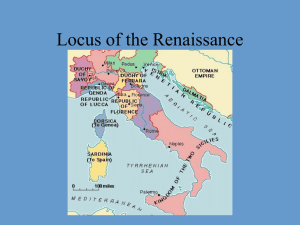
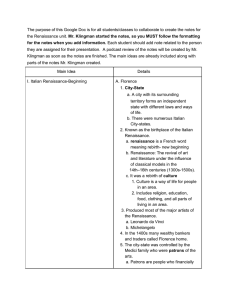
The purpose of this Google Doc is for all students/classes to
... 3. Was a reason for the late start of Renaissance in the rest of Europe compared to Italy. ...
... 3. Was a reason for the late start of Renaissance in the rest of Europe compared to Italy. ...
Renaissance Part 2
... Characteristics of Renaissance Literature • Author uses Vernacular (the everyday language of their homeland, NOT LATIN) • Writing is about self-expression, or concerns of the everyday life, or entertaining and is usually secular (not religious) • May be religious if the author is pointing out what ...
... Characteristics of Renaissance Literature • Author uses Vernacular (the everyday language of their homeland, NOT LATIN) • Writing is about self-expression, or concerns of the everyday life, or entertaining and is usually secular (not religious) • May be religious if the author is pointing out what ...
Renaissance
... you their blood, their goods, their life, and their children , as I have before said, when the necessity is remote; but when it approaches, they revolt. And the prince who has relied solely on their words, without making preparations is ruined” ...
... you their blood, their goods, their life, and their children , as I have before said, when the necessity is remote; but when it approaches, they revolt. And the prince who has relied solely on their words, without making preparations is ruined” ...
Renaissance Period + Sonnets NOTES
... and the “divine right of kings” becomes the new rule of England. There is much civil unrest and thus, fictional literature dissipates and _____________________________ and ________________________become the new trend in writing. ...
... and the “divine right of kings” becomes the new rule of England. There is much civil unrest and thus, fictional literature dissipates and _____________________________ and ________________________become the new trend in writing. ...
Jeopardy on Renaissance and Reformation
... 2. Began Reformation in 1517 with 95 theses (Martin Luther) 3. 2 ideas basic to all types of Protestantism (inner faith, Bible as true authority) 4. Small sect which rejected infant baptism (Anabaptists) 5. 2 ideas basic ONLY to Calvinism (theocracy and predestination) Wild Card 1. Kept notebooks wi ...
... 2. Began Reformation in 1517 with 95 theses (Martin Luther) 3. 2 ideas basic to all types of Protestantism (inner faith, Bible as true authority) 4. Small sect which rejected infant baptism (Anabaptists) 5. 2 ideas basic ONLY to Calvinism (theocracy and predestination) Wild Card 1. Kept notebooks wi ...
Chapter 1 The Renaissance and Reformation
... 4) What artists brought the Renaissance to northern Europe? 5) What themes did humanist thinkers and other writers explore? 6) What impact did printing have on Europe? 7) How did church abuses spark criticism in Europe? 8) Describe how Martin Luther challenged Catholic Church teachings. 9) How did J ...
... 4) What artists brought the Renaissance to northern Europe? 5) What themes did humanist thinkers and other writers explore? 6) What impact did printing have on Europe? 7) How did church abuses spark criticism in Europe? 8) Describe how Martin Luther challenged Catholic Church teachings. 9) How did J ...
Renaissance
... Italian cities such as Florence, Milan, Naples, Rome, and Venice became patrons of the arts. Examples include Lorenzo de Medici and Isabella d'Este. ...
... Italian cities such as Florence, Milan, Naples, Rome, and Venice became patrons of the arts. Examples include Lorenzo de Medici and Isabella d'Este. ...
7th grade Chapter 20 review
... Europeans developed a new way of understanding the world called humanism that was based on ancient Greek and Roman ideas. Humanists want to gain knowledge through reason and gave importance to the individual and human society. One famous humanist is Petrarch who traveled around monasteries to find a ...
... Europeans developed a new way of understanding the world called humanism that was based on ancient Greek and Roman ideas. Humanists want to gain knowledge through reason and gave importance to the individual and human society. One famous humanist is Petrarch who traveled around monasteries to find a ...
Renaissance Powerpoint
... THE RENAISSANCE MOVES NORTH Why? • Italian artists flee Italy and move north because Italy gets invaded • Wealthy merchants in the north begin to be patrons of the arts How was it different? • Northern artists focused on religion and social reform ...
... THE RENAISSANCE MOVES NORTH Why? • Italian artists flee Italy and move north because Italy gets invaded • Wealthy merchants in the north begin to be patrons of the arts How was it different? • Northern artists focused on religion and social reform ...
How did Medieval people tell the time?
... Northern Renaissance? Erasmus and the northern humanists were interested in the early Christian period as well in Roman & Greek culture Erasmus believed that in its early years Christianity had existed in harmony with classical civilization He applied the critical method developed by the Italian ...
... Northern Renaissance? Erasmus and the northern humanists were interested in the early Christian period as well in Roman & Greek culture Erasmus believed that in its early years Christianity had existed in harmony with classical civilization He applied the critical method developed by the Italian ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... mathematics, science, technology a. word means rebirth (revival) 1) revival of learning about classical (Greek and Roman) ideas and achievements 2. time period (1300 – 1600 A.D.) ...
... mathematics, science, technology a. word means rebirth (revival) 1) revival of learning about classical (Greek and Roman) ideas and achievements 2. time period (1300 – 1600 A.D.) ...