The Nervous System
... fibers that RECEIVE impulses • Axon: long fiber that SENDS the impulse on ...
... fibers that RECEIVE impulses • Axon: long fiber that SENDS the impulse on ...
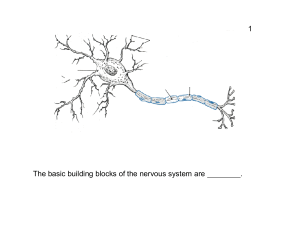
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
... The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
hebbRNN: A Reward-Modulated Hebbian Learning Rule for
... networks using a delayed and sparse reward signal (Miconi 2016). On individual trials, input is perturbed randomly at the synapses of individual neurons and these potential weight changes are accumulated in a Hebbian manner (multiplying pre- and post-synaptic weights) in an eligibility trace. At the ...
... networks using a delayed and sparse reward signal (Miconi 2016). On individual trials, input is perturbed randomly at the synapses of individual neurons and these potential weight changes are accumulated in a Hebbian manner (multiplying pre- and post-synaptic weights) in an eligibility trace. At the ...
20-NervousSystem
... Nerve impulses jump from node to node Multiple sclerosis and Tay-Sachs disease result from degeneration of the myelin sheath ...
... Nerve impulses jump from node to node Multiple sclerosis and Tay-Sachs disease result from degeneration of the myelin sheath ...
Microscopic Nervous System and Reflexes with answers
... lie within the brain and spinal cord; multipolar and link other neurons; transmit impulses from one part of the brain or spinal cord to another; direct incoming sensory impulses to appropriate parts for processing and interpreting; Motor Neurons (efferent neurons) – multipolar and carry impulses out ...
... lie within the brain and spinal cord; multipolar and link other neurons; transmit impulses from one part of the brain or spinal cord to another; direct incoming sensory impulses to appropriate parts for processing and interpreting; Motor Neurons (efferent neurons) – multipolar and carry impulses out ...
Spinal nerves
... structural support functions, but recently has emerged that this is just one of many functions. It has been demonstrated that the Glia can send signals to each other and to the neurons, altering the neural transmission mechanisms. ...
... structural support functions, but recently has emerged that this is just one of many functions. It has been demonstrated that the Glia can send signals to each other and to the neurons, altering the neural transmission mechanisms. ...
13.1- neurons
... Nerves within the brain that contain myelinated fibres are called white matter because the myelinated axons are whitish in colour. ...
... Nerves within the brain that contain myelinated fibres are called white matter because the myelinated axons are whitish in colour. ...
AP Psychology – Unit 3 – Biological Bases of Behavior
... 29. Raccoons have much more precise control of their paws than dogs. You would expect that raccoons have more cortical space dedicated to “paw control” in the ___________________ of their brains. a. frontal lobes b. parietal lobes c. temporal lobes d. occipital lobes 30. A person whose corpus callos ...
... 29. Raccoons have much more precise control of their paws than dogs. You would expect that raccoons have more cortical space dedicated to “paw control” in the ___________________ of their brains. a. frontal lobes b. parietal lobes c. temporal lobes d. occipital lobes 30. A person whose corpus callos ...
Slide ()
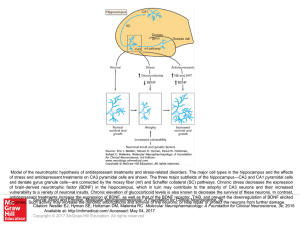
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
PHYLLUM CNIDARIA (11,000 spp, mostly marine) 4 Classes
... medusa, no velum Cubozoa (several spp) - cub-shaped jellyfish Anthozoa (6,000 spp) - no medusa, complex polyp Two body forms - POLYP (e.g. sea anemones) - MEDUSA (e.g., jellyfish) Radial symmetry, mouth surrounded by tentacles Blind Digestive Tract (no anus) Diploblastic (2 germ layers, ectoderm & e ...
... medusa, no velum Cubozoa (several spp) - cub-shaped jellyfish Anthozoa (6,000 spp) - no medusa, complex polyp Two body forms - POLYP (e.g. sea anemones) - MEDUSA (e.g., jellyfish) Radial symmetry, mouth surrounded by tentacles Blind Digestive Tract (no anus) Diploblastic (2 germ layers, ectoderm & e ...
Zika may cause brain damage in adults, too August 19, 2016 By
... In addition to causing the birth defect microcephaly, Zika can wreak havoc in our brains' stem cells, researchers from Rockefeller University and La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology found in a study published in the journal Cell Stem CellThursday. The stem cells, known as neural progen ...
... In addition to causing the birth defect microcephaly, Zika can wreak havoc in our brains' stem cells, researchers from Rockefeller University and La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology found in a study published in the journal Cell Stem CellThursday. The stem cells, known as neural progen ...
Document
... THIRD CLEAVAGE:-Is horizontal and 8 celled stage is formed having two tiers 4 lower macromeres and 4 upper micromeres i.e. DIFFERENTIAL CLEAVAGE. ...
... THIRD CLEAVAGE:-Is horizontal and 8 celled stage is formed having two tiers 4 lower macromeres and 4 upper micromeres i.e. DIFFERENTIAL CLEAVAGE. ...
The Nervous System
... | Also responsible for part of memory, planning, and learning of the brain. | The more complex the response to a given stimulus the greater number of interneurons. ...
... | Also responsible for part of memory, planning, and learning of the brain. | The more complex the response to a given stimulus the greater number of interneurons. ...
Nervous System
... cell would have, and a few specialized structures that set it apart. The main portion of the cell is called the soma or cell body. It contains the nucleus, which in turn contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes. ...
... cell would have, and a few specialized structures that set it apart. The main portion of the cell is called the soma or cell body. It contains the nucleus, which in turn contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes. ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam1_050117_final_solution
... Make a schematic drawing of the developing neural tube depicting the forming brain vesicles (derivatives of the three basic vesicles) (Label them by numbers (1-5)! Name these structures below! 5 points. ...
... Make a schematic drawing of the developing neural tube depicting the forming brain vesicles (derivatives of the three basic vesicles) (Label them by numbers (1-5)! Name these structures below! 5 points. ...
Motor Neuron
... – Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system – Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... – Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system – Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
Nerves Part 1 Powerpoint
... • Interneurons form the central nervous system (CNS) • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
... • Interneurons form the central nervous system (CNS) • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
KS4_nervous_models_Pupil_Sheets
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...