Embryology Notes
... Cleavage Implantation Placenta Embryogenesis Basic organ plan and tissues laid out – most susceptible to damage or disorganization at this time ...
... Cleavage Implantation Placenta Embryogenesis Basic organ plan and tissues laid out – most susceptible to damage or disorganization at this time ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and between sensory inputs and motor outputs ...
... brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and between sensory inputs and motor outputs ...
Neural tube formation in the chick embryo - CSE IITK
... http://www.ibdm.univ-mrs.fr/equipe/axonguidance-in-the-mammalian-brain/ ...
... http://www.ibdm.univ-mrs.fr/equipe/axonguidance-in-the-mammalian-brain/ ...
36.1: The Nervous System
... 3 Types of neurons • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle ...
... 3 Types of neurons • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle ...
The Nervous System
... Amiotic (exceptions: olfactory and hippocampus) (become injured and do not regenerate) High metabolic rate: requires abundant oxygen and glucose ...
... Amiotic (exceptions: olfactory and hippocampus) (become injured and do not regenerate) High metabolic rate: requires abundant oxygen and glucose ...
Lecture 11a Nervous System
... • Form epithelium called ependyma • Line central canal of spinal cord and ventricles of brain: – secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – have cilia or microvilli that circulate CSF – monitor CSF – contain stem cells for repair ...
... • Form epithelium called ependyma • Line central canal of spinal cord and ventricles of brain: – secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – have cilia or microvilli that circulate CSF – monitor CSF – contain stem cells for repair ...
Assignment 2 - Gordon State College
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
The Biology of Mind
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... 2. The All – or – None Law says that action potentials will happen completely or not at all. 3. All action potentials are alike no matter the strength of the stimulus. 4. Frequency of impulse transmission is what separates strong from weak stimulus. 5. Stimuli not strong enough to trigger depolariza ...
... 2. The All – or – None Law says that action potentials will happen completely or not at all. 3. All action potentials are alike no matter the strength of the stimulus. 4. Frequency of impulse transmission is what separates strong from weak stimulus. 5. Stimuli not strong enough to trigger depolariza ...
Animal Development Lab terms
... the digestive tract of the animal. Blasocoel: The fluid-filled cavity that forms in the center of the blastula embryo. Blastopore: The external opening of the cavity (archenteron) of the gastrula. Blastula: A hollow ball of cells produced by cleavage of a fertilized ovum. Cleavage: The succession of ...
... the digestive tract of the animal. Blasocoel: The fluid-filled cavity that forms in the center of the blastula embryo. Blastopore: The external opening of the cavity (archenteron) of the gastrula. Blastula: A hollow ball of cells produced by cleavage of a fertilized ovum. Cleavage: The succession of ...
1. Receptor cells
... system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then ...
... system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then ...
HONR219D Due 3/08/16 Homework V More Vertebrate Anatomy
... learn to break them down into their most basic components, which are shown in the schematic below. These are usually covered by bones of the skull roof, so those are omitted here. There are three regions: • The neurocranum or braincase is a three-dimensional midline structure that houses the brain a ...
... learn to break them down into their most basic components, which are shown in the schematic below. These are usually covered by bones of the skull roof, so those are omitted here. There are three regions: • The neurocranum or braincase is a three-dimensional midline structure that houses the brain a ...
PR_161115_Inaktive_Gehirnzellen_E
... The researchers recorded from 190 GCs, only 27 of which they found to be active (ca. 14 percent). While this seems to give credibility to the ‘ten percent myth’, the team actually expected this outcome, as the DG is a brain structure where in any given task, only a very small percentage of neurons ...
... The researchers recorded from 190 GCs, only 27 of which they found to be active (ca. 14 percent). While this seems to give credibility to the ‘ten percent myth’, the team actually expected this outcome, as the DG is a brain structure where in any given task, only a very small percentage of neurons ...
Slide 1
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s ...
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s ...
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neu ...
... This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neu ...
Slide ()
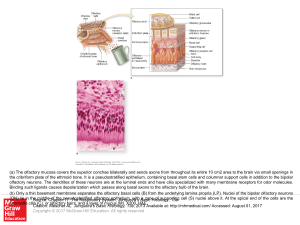
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
Modeling Synaptic Plasticity
... Synapses are the structures through which neurons communicate, and the loci of information storage in neural circuits. Synapses store information (‘learn’) thanks to synaptic plasticity: the efficacy of the communication between the two neurons connected by the synapse can change, as a function of t ...
... Synapses are the structures through which neurons communicate, and the loci of information storage in neural circuits. Synapses store information (‘learn’) thanks to synaptic plasticity: the efficacy of the communication between the two neurons connected by the synapse can change, as a function of t ...
The Nervous System Part I
... Nervous System – includes all neural tissue in the body Neural tissue – includes 2 types of cells: 1) Neurons – cells that send and receive electrical signals 2) Neuroglia (glial cells) – cells that support and protect neurons Organs of the Nervous System: 1) Brain and spinal cord 2) Sensory recept ...
... Nervous System – includes all neural tissue in the body Neural tissue – includes 2 types of cells: 1) Neurons – cells that send and receive electrical signals 2) Neuroglia (glial cells) – cells that support and protect neurons Organs of the Nervous System: 1) Brain and spinal cord 2) Sensory recept ...
SM 11.04.12 - Premio principe asturias
... for their significant neurobiological research into so-called «mirror neurons,» nerve cells found in the ventral premotor cortex of the brain which are activated not only when an individual performs a particular action, such as a hand movement, but also when the individual observes the same action b ...
... for their significant neurobiological research into so-called «mirror neurons,» nerve cells found in the ventral premotor cortex of the brain which are activated not only when an individual performs a particular action, such as a hand movement, but also when the individual observes the same action b ...
intraembryonic mesoderm胚內中胚層
... folds to form the neural tube. It is completed by the end of the 4th week. -The embryo is called neurula during neurulation. Neural Plate神經板 and Neural Tube神經管 -Neuroectoderm--neural plate induced by notochord and develops into CNS -Neural plate ( notochord) - neural folds and neural groove -End o ...
... folds to form the neural tube. It is completed by the end of the 4th week. -The embryo is called neurula during neurulation. Neural Plate神經板 and Neural Tube神經管 -Neuroectoderm--neural plate induced by notochord and develops into CNS -Neural plate ( notochord) - neural folds and neural groove -End o ...