Sea urchin Frog Chicken
... Cleavage: series of cell divisions by mitosis after fertilization that give rise to 2, 4, & 8 cell stages; Morula (16 cell stage) & Blatsula, which contains s single cell layer that surrounds a cavity called the BLASTOCOEL ...
... Cleavage: series of cell divisions by mitosis after fertilization that give rise to 2, 4, & 8 cell stages; Morula (16 cell stage) & Blatsula, which contains s single cell layer that surrounds a cavity called the BLASTOCOEL ...
BRAIN
... – Motor (efferent) — carry impulses away from the CNS – Interneurons (association neurons) — shuttle signals through CNS pathways; Responsible for integrating afferent information and formulating an efferent response to include higher cognitive functions ...
... – Motor (efferent) — carry impulses away from the CNS – Interneurons (association neurons) — shuttle signals through CNS pathways; Responsible for integrating afferent information and formulating an efferent response to include higher cognitive functions ...
The Nervous System
... pools in the CNS take in and put out impulses to other neuronal pools. Neurons or neuronal pools may receive excitatory or inhibitory input. If the input is excitatory, but subthreshold, then it will not create an action potential. The neuron/neuronal pool is, however, more suceptible to reach ...
... pools in the CNS take in and put out impulses to other neuronal pools. Neurons or neuronal pools may receive excitatory or inhibitory input. If the input is excitatory, but subthreshold, then it will not create an action potential. The neuron/neuronal pool is, however, more suceptible to reach ...
The Nervous System
... brain cells are damaged they are not replaced. • The brain and spinal cord are surrounded and protected by cerebrospinal fluid. ...
... brain cells are damaged they are not replaced. • The brain and spinal cord are surrounded and protected by cerebrospinal fluid. ...
Nervous System: Levels of Organization Review and
... this unit. Could you demonstrate each of these objectives? If so, you will be ready for the assessment below. If not, consider reviewing content related to these objectives before attempting the assessment. ...
... this unit. Could you demonstrate each of these objectives? If so, you will be ready for the assessment below. If not, consider reviewing content related to these objectives before attempting the assessment. ...
Chapter 24 Nervous Systems
... inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. A receiving neuron’s membrane may receive signals - that are both excitatory and inhibitory. - from many different sending neurons. The summation of excitation and inhibition determines if a neuron will t ...
... inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. A receiving neuron’s membrane may receive signals - that are both excitatory and inhibitory. - from many different sending neurons. The summation of excitation and inhibition determines if a neuron will t ...
Researchers find that neurons in the primary visual cortex listen to
... neurons in the primary visual cortex of mice listen begs the question of why have so many to just a small subset of the huge number of connections if most of them are going to be mostly synaptic inputs vying for attention. In their paper ignored. The researchers do not know yet, but published in the ...
... neurons in the primary visual cortex of mice listen begs the question of why have so many to just a small subset of the huge number of connections if most of them are going to be mostly synaptic inputs vying for attention. In their paper ignored. The researchers do not know yet, but published in the ...
Unit 9 - CoachClausi
... A Synapse is a point between a neuron that is sending a signal and the neuron or other cells that is receiving the signal. The ends of axons release chemicals called Neurotransmitters which move across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the surface of the next cell. When the chemicals bin ...
... A Synapse is a point between a neuron that is sending a signal and the neuron or other cells that is receiving the signal. The ends of axons release chemicals called Neurotransmitters which move across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the surface of the next cell. When the chemicals bin ...
Document
... mesoderm. Inactivation of BMP-4 in the hindbrain and spinal cord regions is effected by WNT3a and FGF. In the absence of inactivation, BMP-4 causes ectoderm to become epidermis and mesoderm to ventralize to form intermediate and lateral plate mesoderm. Important components of the mesodermal germ lay ...
... mesoderm. Inactivation of BMP-4 in the hindbrain and spinal cord regions is effected by WNT3a and FGF. In the absence of inactivation, BMP-4 causes ectoderm to become epidermis and mesoderm to ventralize to form intermediate and lateral plate mesoderm. Important components of the mesodermal germ lay ...
Nervous System powerpoint new
... not reached, the action potential will not occur at all. If the threshold is reached or exceeded a full action potential will result. ...
... not reached, the action potential will not occur at all. If the threshold is reached or exceeded a full action potential will result. ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... 1. Relay station for all synaptic input 2. Crude awareness of sensation 3. Some degree of consciousness 4. Role in motor control 1. Regulation of many homeostatic functions, such as temperature control, thirst, urine output, and food intake 2. Important link between nervous and endocrine systems 3. ...
... 1. Relay station for all synaptic input 2. Crude awareness of sensation 3. Some degree of consciousness 4. Role in motor control 1. Regulation of many homeostatic functions, such as temperature control, thirst, urine output, and food intake 2. Important link between nervous and endocrine systems 3. ...
Slide 1
... – a.k.a., association neurons – Lie between motor and sensory neurons in neural pathways – Shuttle signals through CNS pathways where integration occurs – > 99% of neurons in body – Most are multipolar – Most are confined within the CNS ...
... – a.k.a., association neurons – Lie between motor and sensory neurons in neural pathways – Shuttle signals through CNS pathways where integration occurs – > 99% of neurons in body – Most are multipolar – Most are confined within the CNS ...
THERIGHTBRAINPOWERPOINT
... The cells in the nervous system are composed of Neurons and glia cells. Neurons are individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. Glia cells are found throughout the nervous system . They provide nourishment to the neurons, help remove waste products a ...
... The cells in the nervous system are composed of Neurons and glia cells. Neurons are individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. Glia cells are found throughout the nervous system . They provide nourishment to the neurons, help remove waste products a ...
Nets vs. Symbols
... depending on whether the result is excitatory or inhibitory, an output pulse may or may not be generated. In artificial nets, each node continually updates its state by generating an internal activation value which is a function of its inputs and internal parameters. This is then used to generate an ...
... depending on whether the result is excitatory or inhibitory, an output pulse may or may not be generated. In artificial nets, each node continually updates its state by generating an internal activation value which is a function of its inputs and internal parameters. This is then used to generate an ...
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
... Deteriorates with Alzheimers. • Dopamine – bodily movements – lack of causes Parkinson’s disease. Too much may cause schizophrenic episodes. • Endorphins: relieve pain and increase our sense of well-being. • Serotonin: our feel good NT ...
... Deteriorates with Alzheimers. • Dopamine – bodily movements – lack of causes Parkinson’s disease. Too much may cause schizophrenic episodes. • Endorphins: relieve pain and increase our sense of well-being. • Serotonin: our feel good NT ...
NeuralNets273ASpring09
... Neurons • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt ( ...
... Neurons • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt ( ...
Neurophysiology
... • More frequently it is spastic, that is, the affected muscles are rigid and the reflexes accentuated. • Paralysis originating in a motor nerve (UMN) of the spinal cord is always spastic • Paralysis originating in peripheral nerves (LMN) is ...
... • More frequently it is spastic, that is, the affected muscles are rigid and the reflexes accentuated. • Paralysis originating in a motor nerve (UMN) of the spinal cord is always spastic • Paralysis originating in peripheral nerves (LMN) is ...
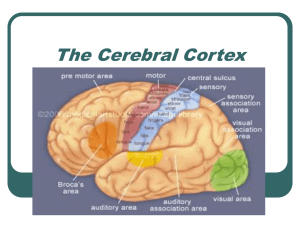
The Cerebral Cortex
... older more primitive limbic system & brainstem. -Gyri are the grooves in the brain & Sulci are the humps in between the grooves. Newer neural networks within the cerebrum form specialized work teams that enable our perception, thinking and speaking. Covering our cerebral hemispheres is the thin cap ...
... older more primitive limbic system & brainstem. -Gyri are the grooves in the brain & Sulci are the humps in between the grooves. Newer neural networks within the cerebrum form specialized work teams that enable our perception, thinking and speaking. Covering our cerebral hemispheres is the thin cap ...
Current Research Areas
... – Combination of motor neurons from embryonic stem cells, neurotrophic factor to promote axonal growth and other factors produced functioning motor neurons innervating muscle ...
... – Combination of motor neurons from embryonic stem cells, neurotrophic factor to promote axonal growth and other factors produced functioning motor neurons innervating muscle ...
to Psychology 3
... - nervous system tissue is composed of two types: gila and neurons 1. Glia: The Supporting System - glia cells exist throughout the nervous system and provide structural support and insulation for neurons - glia cells may supply nutrients, remove wastes, repair damage, or perform other non neural ta ...
... - nervous system tissue is composed of two types: gila and neurons 1. Glia: The Supporting System - glia cells exist throughout the nervous system and provide structural support and insulation for neurons - glia cells may supply nutrients, remove wastes, repair damage, or perform other non neural ta ...
Axial vs. Appendicular Skeleton
... Cervical spinal nerves (C1 to C8) control signals to the back of the head, the neck and shoulders, the arms and hands, and the diaphragm. Thoracic spinal nerves (T1 to T12) control signals to the chest muscles, some muscles of the back, and parts of the abdomen. Lumbar spinal nerves (L1 to L5) contr ...
... Cervical spinal nerves (C1 to C8) control signals to the back of the head, the neck and shoulders, the arms and hands, and the diaphragm. Thoracic spinal nerves (T1 to T12) control signals to the chest muscles, some muscles of the back, and parts of the abdomen. Lumbar spinal nerves (L1 to L5) contr ...
Neurons - E-Learning/An-Najah National University
... thousands of axon terminals. These terminals contain hundreds of tiny vesicles, or membranous sacs, that contain chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
... thousands of axon terminals. These terminals contain hundreds of tiny vesicles, or membranous sacs, that contain chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
05 - Nervous Tissue
... proximal part of the dendrites, but not in the axon hillock or axon. When there’s neuronal damage, these bodies move towards the periphery of the soma giving the impression that they have disappeared – this is called Chromatolysis. ...
... proximal part of the dendrites, but not in the axon hillock or axon. When there’s neuronal damage, these bodies move towards the periphery of the soma giving the impression that they have disappeared – this is called Chromatolysis. ...
Nature 411, 189 - 193 (2001)
... of similarity data in support of different hypotheses of putative homology. A phylogenetic analysis based on parsimony cannot discriminate between such alternative hypotheses of putative homology, because sauropsids and mammals are sister groups. One solution to this dilemma is to include embryologi ...
... of similarity data in support of different hypotheses of putative homology. A phylogenetic analysis based on parsimony cannot discriminate between such alternative hypotheses of putative homology, because sauropsids and mammals are sister groups. One solution to this dilemma is to include embryologi ...