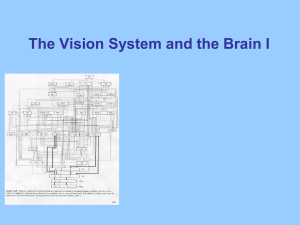
Lectures for 5th week: Visual System I
... Lateral geniculate nucleus Visual signals from the retina into the LGN are segregated according to (1) the type of ganglion cell and (2) the eye of origin. The LGN contains 6 layers of cells. The inner 2 contain large cells (magnocellular) and the outer 4 contain small cells (parvocellular). In bet ...
... Lateral geniculate nucleus Visual signals from the retina into the LGN are segregated according to (1) the type of ganglion cell and (2) the eye of origin. The LGN contains 6 layers of cells. The inner 2 contain large cells (magnocellular) and the outer 4 contain small cells (parvocellular). In bet ...
Learning - Dot Point 2.
... in structures of the brain that have a role in learning: – cerebellum: there is an increase in the number of neurons and synapses in the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for balance, muscle tone, and the performance of motor skills – amygdala: the amygdala becomes more active in adolesc ...
... in structures of the brain that have a role in learning: – cerebellum: there is an increase in the number of neurons and synapses in the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for balance, muscle tone, and the performance of motor skills – amygdala: the amygdala becomes more active in adolesc ...
Psychology
... The visual sensory information (watching the orchestra) would be detected in the retina by photoreceptors and sent to the occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) for processing also. Information would also be processed in the association areas and linked to other parts of the brain to allow Karina to ...
... The visual sensory information (watching the orchestra) would be detected in the retina by photoreceptors and sent to the occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) for processing also. Information would also be processed in the association areas and linked to other parts of the brain to allow Karina to ...
Synapse Formation
... Synapse formation is a complex process that requires appropriate projection of the axon to a specific target followed by the synthesis and targeting of multiple ion channels proteins to the synaptic site. The ability of the growth cone to navigate complex environments and recognize the target is cri ...
... Synapse formation is a complex process that requires appropriate projection of the axon to a specific target followed by the synthesis and targeting of multiple ion channels proteins to the synaptic site. The ability of the growth cone to navigate complex environments and recognize the target is cri ...
Summary of the Known Major Neurotransmitters
... Destruction of GABA-producing other neurons, helping to balance and offset neurons in Huntington’s disease excitatory messages. It is also involved in produces tremors and loss of allergies motor control, as well as personality changes. ...
... Destruction of GABA-producing other neurons, helping to balance and offset neurons in Huntington’s disease excitatory messages. It is also involved in produces tremors and loss of allergies motor control, as well as personality changes. ...
The Visual System: Periphery and Retina
... The initial detection of light is via photoreceptors- specialized cells that can transduce a small number of photons into an electrical signal. Light has to pass through the retinal neurons before it reaches the photoreceptors. The retinal circuitry leads from photoreceptors to bipolar cells to gang ...
... The initial detection of light is via photoreceptors- specialized cells that can transduce a small number of photons into an electrical signal. Light has to pass through the retinal neurons before it reaches the photoreceptors. The retinal circuitry leads from photoreceptors to bipolar cells to gang ...
NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS TEST PREVIEW
... 2. What’s the function of the nervous and endocrine systems? 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an ...
... 2. What’s the function of the nervous and endocrine systems? 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... • Presynaptic cell sends message along axon to axon terminal • Postsynaptic cell receives message as neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter = chemical, transmits signal from preto post- synaptic cell across synaptic cleft Synaptic knob = small, round, when postsynaptic cell is neuron, synapse on dendrite ...
... • Presynaptic cell sends message along axon to axon terminal • Postsynaptic cell receives message as neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter = chemical, transmits signal from preto post- synaptic cell across synaptic cleft Synaptic knob = small, round, when postsynaptic cell is neuron, synapse on dendrite ...
5-NeuralNetworks
... membrane exhibits spikes called action potentials. Spike originates in cell body, travels down axon, and causes synaptic terminals to release neurotransmitters. Chemical diffuses across synapse to dendrites of other neurons. Neurotransmitters can be excititory or inhibitory. If net input of neurotra ...
... membrane exhibits spikes called action potentials. Spike originates in cell body, travels down axon, and causes synaptic terminals to release neurotransmitters. Chemical diffuses across synapse to dendrites of other neurons. Neurotransmitters can be excititory or inhibitory. If net input of neurotra ...
Parasympathetic division
... arrangement of the neurons connecting the central nervous system to the effector organs. Visceral motor neurons in the CNS, known as preganglionic neurons, send their axons, called preganglionic fibers, to synapse on ganglionic neurons, whose cell bodies are located outside the CNS, in autonomic ga ...
... arrangement of the neurons connecting the central nervous system to the effector organs. Visceral motor neurons in the CNS, known as preganglionic neurons, send their axons, called preganglionic fibers, to synapse on ganglionic neurons, whose cell bodies are located outside the CNS, in autonomic ga ...
Nervous System
... 2. The structural unit of the nervous system is the ________________ or _______________. 3. There are two types of nerve fibers. _________________ connect with other neurons to receive information and a single ________________ conducts impulses away from the cell body. 4. Impulses are passed from on ...
... 2. The structural unit of the nervous system is the ________________ or _______________. 3. There are two types of nerve fibers. _________________ connect with other neurons to receive information and a single ________________ conducts impulses away from the cell body. 4. Impulses are passed from on ...
Brain Bark
... The basic cell making up the brain and nervous system, consisting of a long fiber called an axon, which transmits impulses, and many short fibers called dendrites, which receive them ...
... The basic cell making up the brain and nervous system, consisting of a long fiber called an axon, which transmits impulses, and many short fibers called dendrites, which receive them ...
A Type of Basket Cell in Superficial Layers of the Cat Visual Cortex
... and 20). These synapses show a very thin postsynaptic density and are similar in m o r p h o l o g y to those formed by the axon o f other types of smooth stellate cells4,7,12,17,18,25,26. DISCUSSION This paper presents, for the first time, evidence for a type of interneuron whose axon terminals for ...
... and 20). These synapses show a very thin postsynaptic density and are similar in m o r p h o l o g y to those formed by the axon o f other types of smooth stellate cells4,7,12,17,18,25,26. DISCUSSION This paper presents, for the first time, evidence for a type of interneuron whose axon terminals for ...
Spiking Neurons with Boltzmann-like Properties to
... below. WB is the target post-synaptic weight and Wj is the incoming synaptic weight to the post-synaptic neuron. In these simulations, WB was set to 4. ∆+ wij = (1 − wij ) ∗ R ∗ 10(WB −Wj ) ...
... below. WB is the target post-synaptic weight and Wj is the incoming synaptic weight to the post-synaptic neuron. In these simulations, WB was set to 4. ∆+ wij = (1 − wij ) ∗ R ∗ 10(WB −Wj ) ...
Myers AP - Unit 03B
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) = a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computergenerated images of soft tissue. MRI scans show brain anatomy. ...
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) = a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computergenerated images of soft tissue. MRI scans show brain anatomy. ...
Sound frequency (pitch, tone) measured in hertz (cycles per sec)
... Motion causes ion gates of hair cells open to K+, leading to graded depolarization of the hair cell ...
... Motion causes ion gates of hair cells open to K+, leading to graded depolarization of the hair cell ...
Zebrafish primary neurons initiate expression of the
... of nucleus of posterior commissure. In E the solid lines represent segment borders. Bars, 50 µm. ...
... of nucleus of posterior commissure. In E the solid lines represent segment borders. Bars, 50 µm. ...
9e_CH_02 - Biloxi Public Schools
... contain sacs of chemicals called neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft, where many of them bind to receptor sites on the dendrite of the receiving neuron. Dozens of neurotransmitters have been identified. ...
... contain sacs of chemicals called neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft, where many of them bind to receptor sites on the dendrite of the receiving neuron. Dozens of neurotransmitters have been identified. ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... ___ 24. Contrary to early belief, the brains of adult mammals have neural stem cells, located next to the ventricles (cavities), that are able to differentiate into new neurons and glial (supporting) cells. ___ 25. The elevated folds of the cerebral surface are sulci, and the depressed grooves are c ...
... ___ 24. Contrary to early belief, the brains of adult mammals have neural stem cells, located next to the ventricles (cavities), that are able to differentiate into new neurons and glial (supporting) cells. ___ 25. The elevated folds of the cerebral surface are sulci, and the depressed grooves are c ...
(SCI) patients in the United States
... cells. Another type called commissure association column cells send their axons across midline to terminate in gray matter close to their origin. The last are called intrasegemntal association column cells, and their axons terminate within the segment in which they originate from. Propriospinal spin ...
... cells. Another type called commissure association column cells send their axons across midline to terminate in gray matter close to their origin. The last are called intrasegemntal association column cells, and their axons terminate within the segment in which they originate from. Propriospinal spin ...
Photo Album
... Figure 1.12 Radial glia perform support and guidance functions for migrating neurons. In early development, radial glia span the thickness of the expanding brain parenchyma between the ventricle and outer surface depicted on the left. (Inset) Defined layers of the neural tube from the ventricular t ...
... Figure 1.12 Radial glia perform support and guidance functions for migrating neurons. In early development, radial glia span the thickness of the expanding brain parenchyma between the ventricle and outer surface depicted on the left. (Inset) Defined layers of the neural tube from the ventricular t ...
Brain
... Central area of gray matter shaped like a butterfly and surrounded by white matter in 3 columns Gray matter = neuron cell bodies with little myelin White matter = myelinated axons ...
... Central area of gray matter shaped like a butterfly and surrounded by white matter in 3 columns Gray matter = neuron cell bodies with little myelin White matter = myelinated axons ...



















![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009531099_1-530d7c194a24d89985e18840d7e0199e-300x300.png)


