Computational and Experimental Study of the Mechanics of Heart
... Abstract : In the embryo, heart is initially a simple tubular structure that undergoes complex morphological changes as it transforms into a four-chambered pump. This work focuses on mechanisms that create heart tube (HT). The early embryo is composed of three relatively flat primary germ layers cal ...
... Abstract : In the embryo, heart is initially a simple tubular structure that undergoes complex morphological changes as it transforms into a four-chambered pump. This work focuses on mechanisms that create heart tube (HT). The early embryo is composed of three relatively flat primary germ layers cal ...
Pain - WordPress.com
... spinalthalamic tract). The above three fiber tracts are known also as the paleospinalthalamic tract. ...
... spinalthalamic tract). The above three fiber tracts are known also as the paleospinalthalamic tract. ...
Final review quiz
... In motor cortex, population firing rate vector refers to motor cortex neuron activations that result in pattern of muscle activations or ________________________ How do population firing rate vectors relate to the so-called “grandmother cell”? True or False: A single cell in the brain can be uniquel ...
... In motor cortex, population firing rate vector refers to motor cortex neuron activations that result in pattern of muscle activations or ________________________ How do population firing rate vectors relate to the so-called “grandmother cell”? True or False: A single cell in the brain can be uniquel ...
PhD Thesis - Laboratory of Cerebral Cortex Development
... place via lineage-restricted progenitors in a highly regulated way. This process is mastered by a large set of genes, among which some implicated in CNS pattern formation. Aim of this study was to disentangle the kinetic and histogenetic roles exerted by two of these genes, Emx2 and Foxg1, in cortic ...
... place via lineage-restricted progenitors in a highly regulated way. This process is mastered by a large set of genes, among which some implicated in CNS pattern formation. Aim of this study was to disentangle the kinetic and histogenetic roles exerted by two of these genes, Emx2 and Foxg1, in cortic ...
Test bank module 3 4 5 6 11 12
... 75. The best way to detect enlarged fluid-filled brain regions in some patients who have schizophrenia is to use a(n): A) EEG. B) MRI. C) PET scan. D) brain lesion. 76. To identify which specific brain areas are most active during a particular mental task, researchers would be most likely to make u ...
... 75. The best way to detect enlarged fluid-filled brain regions in some patients who have schizophrenia is to use a(n): A) EEG. B) MRI. C) PET scan. D) brain lesion. 76. To identify which specific brain areas are most active during a particular mental task, researchers would be most likely to make u ...
Basal Ganglia Subcircuits Distinctively Encode the
... ChR2-aided D1-/D2-MSNs identification. The striatum consists of two major subpopulations of MSNs, with one subtype expressing dopamine D1 receptors and another subtype expressing dopamine D2 receptors 18,22,48. The DIO constructs used to express ChR2–YFP do not permit expression in cells that do not ...
... ChR2-aided D1-/D2-MSNs identification. The striatum consists of two major subpopulations of MSNs, with one subtype expressing dopamine D1 receptors and another subtype expressing dopamine D2 receptors 18,22,48. The DIO constructs used to express ChR2–YFP do not permit expression in cells that do not ...
Cell Assemblies - CAAM @ Rice
... Behavior. Hebb asserts that a cell assembly is a group of neurons wired in a specific manner such that when a sufficient amount of neurons in this group are excited, the entire group becomes excited in a synchronized manner. Hebb went on to explain that these cell assemblies form via synaptic plasti ...
... Behavior. Hebb asserts that a cell assembly is a group of neurons wired in a specific manner such that when a sufficient amount of neurons in this group are excited, the entire group becomes excited in a synchronized manner. Hebb went on to explain that these cell assemblies form via synaptic plasti ...
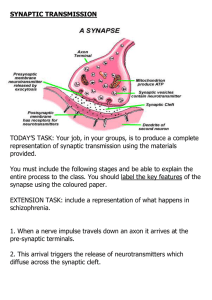
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... Neurotransmitter: a chemical substance released from a synaptic vesicle that affects the transfer of an impulse to another nerve or muscle. ...
... Neurotransmitter: a chemical substance released from a synaptic vesicle that affects the transfer of an impulse to another nerve or muscle. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... between neurons almost always occurs by chemical rather than electrical means. • Action potential causes release of specific chemical that are stored in synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic ending. • These chemicals are known as neurotransmitters and diffuse across the narrow gap between pre- and po ...
... between neurons almost always occurs by chemical rather than electrical means. • Action potential causes release of specific chemical that are stored in synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic ending. • These chemicals are known as neurotransmitters and diffuse across the narrow gap between pre- and po ...
The Nervous System
... spike initiation zone for the axon: in neurological terms it has the greatest hyperpolarized action potential threshold. While the axon and axon hillock are generally involved in information outflow, this region can also receive input from other neurons as well. The axon terminal is a specialized st ...
... spike initiation zone for the axon: in neurological terms it has the greatest hyperpolarized action potential threshold. While the axon and axon hillock are generally involved in information outflow, this region can also receive input from other neurons as well. The axon terminal is a specialized st ...
Biological Implementation of the Temporal Difference Algorithm for
... (cf. Houk, 2005). Synaptic inputs act immediately to produce bursting discharges in spiny neurons. These bursts function to embody a small focus of activity in the area of cerebral cortex to which they project. The loop between that area of cerebral cortex and the cerebellum then amplifies and refin ...
... (cf. Houk, 2005). Synaptic inputs act immediately to produce bursting discharges in spiny neurons. These bursts function to embody a small focus of activity in the area of cerebral cortex to which they project. The loop between that area of cerebral cortex and the cerebellum then amplifies and refin ...
DISC 23
... • The zygote divides first into two cells then four, eight etc until it forms a ball of cells, the morula. • The ball then develops a fluid filled core to form an early blastocyst. • As the blastocyst matures the inner cell mass expands at one end. • The blastocyst will attach itself to the endomet ...
... • The zygote divides first into two cells then four, eight etc until it forms a ball of cells, the morula. • The ball then develops a fluid filled core to form an early blastocyst. • As the blastocyst matures the inner cell mass expands at one end. • The blastocyst will attach itself to the endomet ...
Exam 4 Review Exercise 11
... Be able to identify the lobes, sulci, and fissures of the cerebrum. Fig. 13.8A Be able to identify the thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, corpus collosum, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, cerebellum, and arbor vitae. Fig. 13.9 Be able to identify Cranial Nerves I and II, and th ...
... Be able to identify the lobes, sulci, and fissures of the cerebrum. Fig. 13.8A Be able to identify the thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, corpus collosum, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, cerebellum, and arbor vitae. Fig. 13.9 Be able to identify Cranial Nerves I and II, and th ...
14.1-NervousMusculo-Skeletal-System
... The gap between the neurons is called the synapse. This is where an electrical signal is passed from an axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another neuron. The signals are passed via neurotransmitters (serotonin, for example), which once released into the synapse, they stimulate a new electrical sig ...
... The gap between the neurons is called the synapse. This is where an electrical signal is passed from an axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another neuron. The signals are passed via neurotransmitters (serotonin, for example), which once released into the synapse, they stimulate a new electrical sig ...
The Nervous System - Optum360Coding.com
... produce thick, fatty sheath, myelin, covering neurons; myelinated nerve fibers make up white matter; Schwann cells wrap around axons of motor and sensory neurons to form myelin sheath; neurolemma forms outermost layer of nerve fiber • Microglia (lower left): Specialized neuroglia protect nervous sys ...
... produce thick, fatty sheath, myelin, covering neurons; myelinated nerve fibers make up white matter; Schwann cells wrap around axons of motor and sensory neurons to form myelin sheath; neurolemma forms outermost layer of nerve fiber • Microglia (lower left): Specialized neuroglia protect nervous sys ...
All about human eyes and ears - St Ignatius RC Primary School
... An audiometer hearing test is usually administered to a person sitting in a soundproof booth wearing a set of headphones which is connected to an audiometer. Small foam insert earphones placed in the ears may also be used. The audiometer produces tones at specific frequencies and set volume levels t ...
... An audiometer hearing test is usually administered to a person sitting in a soundproof booth wearing a set of headphones which is connected to an audiometer. Small foam insert earphones placed in the ears may also be used. The audiometer produces tones at specific frequencies and set volume levels t ...
Linking reward expectation to behavior in the basal ganglia
... movement to the rewarded location, evident as shorter response times (the amount of time elapsed between the appearance of the target and the initiation of the eye movement) to that location. To find the neural signals that might be responsible for generating these reward-related changes in response ...
... movement to the rewarded location, evident as shorter response times (the amount of time elapsed between the appearance of the target and the initiation of the eye movement) to that location. To find the neural signals that might be responsible for generating these reward-related changes in response ...
Embryology of Myelomeningocele and Anencephaly
... caudal end as the primitive streak regresses; true cranial growth of the notochord is minimal. The notochordal process consists of a cord of cells radially arranged around a central lumen called the notochordal canal (Fig. 5). The notochordal canal is continuous dorsally with the amnionic cavity thr ...
... caudal end as the primitive streak regresses; true cranial growth of the notochord is minimal. The notochordal process consists of a cord of cells radially arranged around a central lumen called the notochordal canal (Fig. 5). The notochordal canal is continuous dorsally with the amnionic cavity thr ...
Nervous System
... – Includes nerves that carry sensory information from receptors to the CNS and nerves that carry motor responses back to periphery – Many actions are reflex activities – Reflex • A programmed response to a stimulus that is automatic • Can be conscious or unconscious but not mentally willed • Protect ...
... – Includes nerves that carry sensory information from receptors to the CNS and nerves that carry motor responses back to periphery – Many actions are reflex activities – Reflex • A programmed response to a stimulus that is automatic • Can be conscious or unconscious but not mentally willed • Protect ...
ecture 23- special senses
... They contain receptors called odorant-binding proteins that match specific odorant particles. They can only be stimulated by water-soluble and lipid-soluble particles that can diffuse through the overlaying mucus. Depolarization is produced the G protein-second messenger mechanism. ...
... They contain receptors called odorant-binding proteins that match specific odorant particles. They can only be stimulated by water-soluble and lipid-soluble particles that can diffuse through the overlaying mucus. Depolarization is produced the G protein-second messenger mechanism. ...
The triple origin of skull in higher vertebrates: a study
... expressed in the XIXth century by Goethe (1791) and Oken (1807) (see Jeffs and Keynes (1990) and references therein) and was formulated in an extreme form in the vertebrate theory of the skull, according to which the skull is made up of one (or three) somehow modified vertebrae. Progress in embryolo ...
... expressed in the XIXth century by Goethe (1791) and Oken (1807) (see Jeffs and Keynes (1990) and references therein) and was formulated in an extreme form in the vertebrate theory of the skull, according to which the skull is made up of one (or three) somehow modified vertebrae. Progress in embryolo ...
Reactivation of Latent Herpes Simplex Virus from Dissociated
... immunoglobulin (Cappel Laboratories, Cochranville, Pa., U.S.A.) diluted 1/20 in complete medium for 30 min at room temperature. The coverslips were then washed in PBS and fixed in 95 ~ ethanol/5 ~ glacial acetic acid for 10 min at - 2 0 °C. They were then incubated for 30 min with 40 ~tl rabbit anti ...
... immunoglobulin (Cappel Laboratories, Cochranville, Pa., U.S.A.) diluted 1/20 in complete medium for 30 min at room temperature. The coverslips were then washed in PBS and fixed in 95 ~ ethanol/5 ~ glacial acetic acid for 10 min at - 2 0 °C. They were then incubated for 30 min with 40 ~tl rabbit anti ...