similar cortical mechanisms for perceptual and motor learning
... the problem. Because sensory and motor systems use similar ‘hardware’ – neurons and synapses – they must have close analogies at the level of implementation. However, the issue is whether those similarities extend to the algorithmic level. Such similarities would simplify the interaction between sen ...
... the problem. Because sensory and motor systems use similar ‘hardware’ – neurons and synapses – they must have close analogies at the level of implementation. However, the issue is whether those similarities extend to the algorithmic level. Such similarities would simplify the interaction between sen ...
OriginalArticle
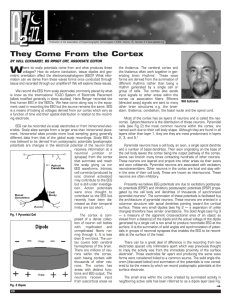
... For scanning electron microscopy, each chick embryo of each stage mentioned was processed as followed. After cutting the egg shell at the embryonic pole off, the embryos were seen floating on the yolk sac. The embryos were separated from the yolk by using a sharp tip scissors cutting around the bo ...
... For scanning electron microscopy, each chick embryo of each stage mentioned was processed as followed. After cutting the egg shell at the embryonic pole off, the embryos were seen floating on the yolk sac. The embryos were separated from the yolk by using a sharp tip scissors cutting around the bo ...
--The image of that apple is formed on your retina -
... 1)Parasol cells, aka M-cells synapse onto layers 1& 2 of the LGN. These layers are called the magnocellular layers. 2) midget cells, aka P-cells, synapse onto layers 3-6 of the LGN. These layers are called the parvocellular layers. 3) S-cells synapse onto the interlaminar layers of the LGN. The cell ...
... 1)Parasol cells, aka M-cells synapse onto layers 1& 2 of the LGN. These layers are called the magnocellular layers. 2) midget cells, aka P-cells, synapse onto layers 3-6 of the LGN. These layers are called the parvocellular layers. 3) S-cells synapse onto the interlaminar layers of the LGN. The cell ...
11.4: The Peripheral Nervous System
... injured region, and relays a message to the brain, causing our perception of pain. When the natural painkillers known as endorphins attach to SG cell receptor sites, they prevent or reduce the binding of the neurotransmitters that transmit the signal interpreted as pain. When the neurotransmitters d ...
... injured region, and relays a message to the brain, causing our perception of pain. When the natural painkillers known as endorphins attach to SG cell receptor sites, they prevent or reduce the binding of the neurotransmitters that transmit the signal interpreted as pain. When the neurotransmitters d ...
Black Box Methods – Neural Networks and Support Vector
... In engineering, these are referred to as black box processes because the mechanism that transforms the input into the output is obfuscated by a figurative box. The reasons for the opacity can vary; for instance, black box closed source software intentionally conceals proprietary algorithms, the blac ...
... In engineering, these are referred to as black box processes because the mechanism that transforms the input into the output is obfuscated by a figurative box. The reasons for the opacity can vary; for instance, black box closed source software intentionally conceals proprietary algorithms, the blac ...
Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
... Frontal eye field - located in frontal lobs just above the Broca’s area, to control muscles of the eye and eyelid. Auditory area - located in temporal lobe, to control hearing. Visual area - located in occipital lobe, to control visual recognition of objects and combine visual images. Sensory areas ...
... Frontal eye field - located in frontal lobs just above the Broca’s area, to control muscles of the eye and eyelid. Auditory area - located in temporal lobe, to control hearing. Visual area - located in occipital lobe, to control visual recognition of objects and combine visual images. Sensory areas ...
The Peripheral Nervous System The P.N.S.
... nervous system and how are the different? 2) What two types of nerves exist and what are 2 differences between them? 3) What 3 types of neurons are involved in reflex responses and in what order do nerve impulses travel through them? 4) What is the difference between a voluntary movement such as wal ...
... nervous system and how are the different? 2) What two types of nerves exist and what are 2 differences between them? 3) What 3 types of neurons are involved in reflex responses and in what order do nerve impulses travel through them? 4) What is the difference between a voluntary movement such as wal ...
Chocolate Chip Cookie Review
... 7. Down what part of the neuron does the impulse travel? 8. What is the name of the chemicals involved in neural transmission? 9. What is the gap between the neurons called? ...
... 7. Down what part of the neuron does the impulse travel? 8. What is the name of the chemicals involved in neural transmission? 9. What is the gap between the neurons called? ...
They Come From the Cortex - American Association of Sleep
... the thalamus. The cerebral cortex and the thalamus often work together in generating brain rhythms1. These wave forms are derived from the summation of different rhythms rather than being a rhythm generated by a single cell or group of cells. The cortex also sends input signals to other areas within ...
... the thalamus. The cerebral cortex and the thalamus often work together in generating brain rhythms1. These wave forms are derived from the summation of different rhythms rather than being a rhythm generated by a single cell or group of cells. The cortex also sends input signals to other areas within ...
SPHS 4050, Neurological Bases, PP 08b
... Pyramidal tracts originate in cortex and consist of upper motor neurons (1st order) and lower motor neurons (2nd order) During the descent, the axons of the upper motor neuron send off collaterals to the cerebellum (via the pons), as input for coordination of movement. In medulla, corticospinal UMN ...
... Pyramidal tracts originate in cortex and consist of upper motor neurons (1st order) and lower motor neurons (2nd order) During the descent, the axons of the upper motor neuron send off collaterals to the cerebellum (via the pons), as input for coordination of movement. In medulla, corticospinal UMN ...
The Nervous System - INAYA Medical College
... • Line the central cavities of the brain and spinal column ...
... • Line the central cavities of the brain and spinal column ...
File
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
Single-trial decoding of intended eye movement goals from lateral
... analyzing neurons with low firing rates and short epochs. The quantile indexes were used as r in Eq. 1. MI was compared against a null distribution obtained by shuffling target locations and calculating MI for 1,000 different shuffles. We labeled neurons as having significant target location informa ...
... analyzing neurons with low firing rates and short epochs. The quantile indexes were used as r in Eq. 1. MI was compared against a null distribution obtained by shuffling target locations and calculating MI for 1,000 different shuffles. We labeled neurons as having significant target location informa ...
Worksheet: Planning an experimental approach to answer - Bio-Link
... al., 2002. Circulation Research). 5) Why do you think cardiomyocytes beat at different rates in the dish? Justify your answer based on your readings or research (10 points) ...
... al., 2002. Circulation Research). 5) Why do you think cardiomyocytes beat at different rates in the dish? Justify your answer based on your readings or research (10 points) ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers - AP Psychology
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
kn35l1SvSY1SkTqq
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems
... • Plasticity - changes in the nervous system that are reflected in behavioral changes to stimuli (i.e. learning and memory) – Changes may include altered cell synthesis of protein molecules, dendrites and their connections, synaptic activity – Areas known for memory - cortex, limbic system (hippocam ...
... • Plasticity - changes in the nervous system that are reflected in behavioral changes to stimuli (i.e. learning and memory) – Changes may include altered cell synthesis of protein molecules, dendrites and their connections, synaptic activity – Areas known for memory - cortex, limbic system (hippocam ...
Anthozoan Cnidarian Development
... Pax family transcription factors are homeodomain transcription factors that contain both a homeodomain and a paired domain, both of which bind DNA and influence transcription as well as an octapeptide domain. As in bilaterian animals, there are four classes of Pax genes in cnidarians. Pax genes are ...
... Pax family transcription factors are homeodomain transcription factors that contain both a homeodomain and a paired domain, both of which bind DNA and influence transcription as well as an octapeptide domain. As in bilaterian animals, there are four classes of Pax genes in cnidarians. Pax genes are ...
Chemical Senses
... The 3-D model shown on the right (from Couto & Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, th ...
... The 3-D model shown on the right (from Couto & Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, th ...
Commentary on slides Lecture 16
... Commentary on slides Lecture 16 1. Central pattern generators can, in turn, be accessed by higher levels of motor control. These higher levels include the cerebellum, a large structure at the junction of the pons and medulla, the basal ganglia in the forebrain and the motor cortex. Let’s begin by co ...
... Commentary on slides Lecture 16 1. Central pattern generators can, in turn, be accessed by higher levels of motor control. These higher levels include the cerebellum, a large structure at the junction of the pons and medulla, the basal ganglia in the forebrain and the motor cortex. Let’s begin by co ...
Fact sheet (PDF, 63.03 KB) (opens in a new window)
... which traditionally have been some of the most challenging cases for surgeons. Nervous injury, from trauma, disease or otherwise, is a major medical problem. Mature neurons do not undergo cell division and therefore it is very difficult to achieve successful rehabilitation after nerve injuries. It i ...
... which traditionally have been some of the most challenging cases for surgeons. Nervous injury, from trauma, disease or otherwise, is a major medical problem. Mature neurons do not undergo cell division and therefore it is very difficult to achieve successful rehabilitation after nerve injuries. It i ...
W7 Lecture
... Axons: undergo action potentials to deliver information, typically neurotransmitters, from the axon terminals. ...
... Axons: undergo action potentials to deliver information, typically neurotransmitters, from the axon terminals. ...
Ch 3 Biological Bases of Behavior
... – Neurotransmitters: the chemical signal that transmits across the synapse – Dendrites: receive messages from other neurons – Glial Cells: Supports neuron structure; cleans up unused neurotransmitters ...
... – Neurotransmitters: the chemical signal that transmits across the synapse – Dendrites: receive messages from other neurons – Glial Cells: Supports neuron structure; cleans up unused neurotransmitters ...
Unit 3D Worksheet 1) In the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS
... heavily ________________axon. This would be an afferent/efferent sensory/motor neuron. 4) Effectors of the ANS innervate ___________muscle, __________muscle and ________via a ______neuron __________made up of _______and ________ganglionic neurons with a synaptic____________. These would be visceral ...
... heavily ________________axon. This would be an afferent/efferent sensory/motor neuron. 4) Effectors of the ANS innervate ___________muscle, __________muscle and ________via a ______neuron __________made up of _______and ________ganglionic neurons with a synaptic____________. These would be visceral ...