
Presynaptic Modulation of the Retinogeniculate Synapse
... stimulation (Chen et al., 2002). In some cases, synaptic responses consisted of a large input and a small input that contributed ⬍10% of the synaptic current. Series resistance (3– 6 M⍀) was monitored to ensure constancy throughout the experiment. Constant bath perfusion (⬃3 ml/ min) was provided wi ...
... stimulation (Chen et al., 2002). In some cases, synaptic responses consisted of a large input and a small input that contributed ⬍10% of the synaptic current. Series resistance (3– 6 M⍀) was monitored to ensure constancy throughout the experiment. Constant bath perfusion (⬃3 ml/ min) was provided wi ...
Targeting Axonal Protein Synthesis in Neuroregeneration and Degeneration REVIEW Jimena Baleriola
... sclerosis (ALS) and spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). For example, ALS-causing mutations in the RNA-binding protein TDP-43 impairs axonal trafficking of mRNA granules to distal axons [41]. Similarly, reduced levels of survival of motor neuron (SMN) decrease axonal mRNA localization and human SMN1 mutat ...
... sclerosis (ALS) and spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). For example, ALS-causing mutations in the RNA-binding protein TDP-43 impairs axonal trafficking of mRNA granules to distal axons [41]. Similarly, reduced levels of survival of motor neuron (SMN) decrease axonal mRNA localization and human SMN1 mutat ...
tracts - Anatomický ústav 1. LF UK
... Spinal cord is supplied by spinal arteries coming from the branches of the subclavian artery and the descending aorta (aa. intercostales posteriores , aa . lumbales , a iliolumbalis , aa . sacrales laterales). They enter into the spinal canal through the foramen intervertebralia . Another source in ...
... Spinal cord is supplied by spinal arteries coming from the branches of the subclavian artery and the descending aorta (aa. intercostales posteriores , aa . lumbales , a iliolumbalis , aa . sacrales laterales). They enter into the spinal canal through the foramen intervertebralia . Another source in ...
pain impulses
... Pain Perceptions – based on expectations, past experience, anxiety, suggestions ◦ Affective – one’s emotional factors that can affect pain experience ◦ Behavioral – how one expresses or controls pain ◦ Cognitive – one’s beliefs (attitudes) about pain ...
... Pain Perceptions – based on expectations, past experience, anxiety, suggestions ◦ Affective – one’s emotional factors that can affect pain experience ◦ Behavioral – how one expresses or controls pain ◦ Cognitive – one’s beliefs (attitudes) about pain ...
a scaling cross platform tool for the analysis of neurophysiological data
... 1. Introduction The study of neurons as the functional component of the nervous system began in 1873 when Camillo Golgi developed a staining technique that made them visible to researchers using microscopes [1]. Combined with the work of Santiago Ramón y Cajal these scientists laid the foundation fo ...
... 1. Introduction The study of neurons as the functional component of the nervous system began in 1873 when Camillo Golgi developed a staining technique that made them visible to researchers using microscopes [1]. Combined with the work of Santiago Ramón y Cajal these scientists laid the foundation fo ...
Context Dependency in the Globus Pallidus Internal Segment
... delivery, the animal usually returned the handle to the center target with a self-paced movement prior to the lighting of five LEDs at the onset of the next trial. Comparison of the two behavioral contexts in which movements were generated shows that cued movements were triggered by an auditory tone ...
... delivery, the animal usually returned the handle to the center target with a self-paced movement prior to the lighting of five LEDs at the onset of the next trial. Comparison of the two behavioral contexts in which movements were generated shows that cued movements were triggered by an auditory tone ...
Glial heterogeneity: the increasing complexity of the brain
... to 400 µm. Their morphological heterogeneity has already been described by RioHortega, who distinguished four types. In white matter fiber tracts such as the optic nerve or the corpus callosum, axons are mainly oriented in parallel, and so are the processes of the oligodendrocytes. In contrast, in g ...
... to 400 µm. Their morphological heterogeneity has already been described by RioHortega, who distinguished four types. In white matter fiber tracts such as the optic nerve or the corpus callosum, axons are mainly oriented in parallel, and so are the processes of the oligodendrocytes. In contrast, in g ...
The Effect of Environmental Factors on the
... the gut. When the sacs were everted and grown on a firm clot the endoderm developed into high columnar or cylindrical epithelium which usually was almost or completely devoid of goblet aells, although these were present wherever the epithelium had invaginated into the underlying connective tissue. S ...
... the gut. When the sacs were everted and grown on a firm clot the endoderm developed into high columnar or cylindrical epithelium which usually was almost or completely devoid of goblet aells, although these were present wherever the epithelium had invaginated into the underlying connective tissue. S ...
189084_189084 - espace@Curtin
... A9, and A10 dopamine cell groups should be considered different from each other, and that there are notable differences in the neurons within the A9 cell group. These aspects have not been previously studied in mice in any detail. ...
... A9, and A10 dopamine cell groups should be considered different from each other, and that there are notable differences in the neurons within the A9 cell group. These aspects have not been previously studied in mice in any detail. ...
PAIN CONTROL THEORIES
... Pain Perceptions – based on expectations, past experience, anxiety, suggestions Affective – one’s emotional factors that can affect pain experience Behavioral – how one expresses or controls pain Cognitive – one’s beliefs (attitudes) about pain ...
... Pain Perceptions – based on expectations, past experience, anxiety, suggestions Affective – one’s emotional factors that can affect pain experience Behavioral – how one expresses or controls pain Cognitive – one’s beliefs (attitudes) about pain ...
13 Nervous System
... communication with sensory neurons. Association areas are located in all the lobes; the prefrontal area of the frontal lobe is especially necessary to higher mental functions. A visual association area occurs in the occipital lobe, and an auditory association area occurs in the temporal lobe. In the ...
... communication with sensory neurons. Association areas are located in all the lobes; the prefrontal area of the frontal lobe is especially necessary to higher mental functions. A visual association area occurs in the occipital lobe, and an auditory association area occurs in the temporal lobe. In the ...
PART IV INTEGRATION AND COORDINATION IN HUMANS
... communication with sensory neurons. Association areas are located in all the lobes; the prefrontal area of the frontal lobe is especially necessary to higher mental functions. A visual association area occurs in the occipital lobe, and an auditory association area occurs in the temporal lobe. In the ...
... communication with sensory neurons. Association areas are located in all the lobes; the prefrontal area of the frontal lobe is especially necessary to higher mental functions. A visual association area occurs in the occipital lobe, and an auditory association area occurs in the temporal lobe. In the ...
Sleep and sleep states: Thalamic regulation
... more regular than delta waves in vivo. The latter studies demonstrated that this form of delta-wave activity is generated intrinsically by the interplay of IT and Ih currents in thalamocortical (TC) neurons. Slow oscillations (<1 Hz) can be generated by the cortex; they were observed in cortical sli ...
... more regular than delta waves in vivo. The latter studies demonstrated that this form of delta-wave activity is generated intrinsically by the interplay of IT and Ih currents in thalamocortical (TC) neurons. Slow oscillations (<1 Hz) can be generated by the cortex; they were observed in cortical sli ...
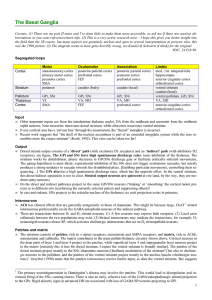
The Basal Ganglia
... • Do the direct and indirect pathways project to the same GPi/SNr neurons (‘braking’ or ‘smoothing’ the cortical motor pattern) or to different sets (reinforcing the currently selected pattern and suppressing others)? • In cats and rodents, GPe projects to the reticular nucleus of the thalamus; no s ...
... • Do the direct and indirect pathways project to the same GPi/SNr neurons (‘braking’ or ‘smoothing’ the cortical motor pattern) or to different sets (reinforcing the currently selected pattern and suppressing others)? • In cats and rodents, GPe projects to the reticular nucleus of the thalamus; no s ...
The Human Mirror Neuron System and Embodied
... (action production); on others, the animal would observe the experimenter manipulate the object (action observation) or view the object passively as a visual control (Gallese et al., 1996). These studies revealed two distinct classes of neurons: canonical neurons and mirror neurons. Canonical neuron ...
... (action production); on others, the animal would observe the experimenter manipulate the object (action observation) or view the object passively as a visual control (Gallese et al., 1996). These studies revealed two distinct classes of neurons: canonical neurons and mirror neurons. Canonical neuron ...
PDF
... Theme: Sensory systems Topic: Auditory systems: central anatomy Keywords: Auditory; Hearing; Corticobulbar projection; Granule cell domain; Cochlear nucleus ...
... Theme: Sensory systems Topic: Auditory systems: central anatomy Keywords: Auditory; Hearing; Corticobulbar projection; Granule cell domain; Cochlear nucleus ...
Neuronal Interaction Dynamics in Cat Primary Visual Cortex
... (compare Fig. 1). The construction was based on the activity of 178 neurons. DPAs were computed in the time interval between 40 and 65 msec after stimulus onset corresponding to the peak responses in the PSTHs. The activation level is shown in a color scale normalized to maximal activation separatel ...
... (compare Fig. 1). The construction was based on the activity of 178 neurons. DPAs were computed in the time interval between 40 and 65 msec after stimulus onset corresponding to the peak responses in the PSTHs. The activation level is shown in a color scale normalized to maximal activation separatel ...
Morphological Studies of Wobbler Mouse Dorsal Root Ganglia
... animal models have been suggested to cause these symptoms, such as oxidative stress due to mitochondrial dysfunction, protein aggregation, neuroinflammation in different parts of the central nervous system and impaired axonal transport [26]. Up till now, none of the cellular defects found have led t ...
... animal models have been suggested to cause these symptoms, such as oxidative stress due to mitochondrial dysfunction, protein aggregation, neuroinflammation in different parts of the central nervous system and impaired axonal transport [26]. Up till now, none of the cellular defects found have led t ...
Extra-Classical Tuning Predicts Stimulus
... nonlinear response properties, different classes of stimuli drive a neuron along different regions of a nonlinear stimulus–response curve. Determining the degree to which RF nonlinearities influence stimulus-dependent STRFs and experimentally characterizing such nonlinearities are important for unde ...
... nonlinear response properties, different classes of stimuli drive a neuron along different regions of a nonlinear stimulus–response curve. Determining the degree to which RF nonlinearities influence stimulus-dependent STRFs and experimentally characterizing such nonlinearities are important for unde ...
Acetylcholine Acetylcholine IUPAC name[hide] 2-Acetoxy
... potentiation in many regions, including the dentate gyrus, CA1, piriform cortex, and neocortex. This effect most likely occurs either through enhancing currents through NMDA receptors or indirectly by suppressing adaptation. The suppression of adaptation has been shown in brain slices of regions CA1 ...
... potentiation in many regions, including the dentate gyrus, CA1, piriform cortex, and neocortex. This effect most likely occurs either through enhancing currents through NMDA receptors or indirectly by suppressing adaptation. The suppression of adaptation has been shown in brain slices of regions CA1 ...
A computational account for the ontogeny of mirror neurons via
... In the early 1990s, mirror neurons were discovered in the ventral premotor cortex of the macaque monkey (Di Pellegrino et al., 1992). These neurons fired both when the monkeys grabbed an object and when they watched another primate grab that same object. Mirror neuron-like activity has been observed ...
... In the early 1990s, mirror neurons were discovered in the ventral premotor cortex of the macaque monkey (Di Pellegrino et al., 1992). These neurons fired both when the monkeys grabbed an object and when they watched another primate grab that same object. Mirror neuron-like activity has been observed ...
Encoding of Movement Fragments in the Motor Cortex
... Almost 100 years ago, it was postulated that the motor cortex should be viewed as a synthetic organ for complex motor actions (Leyton and Sherrington, 1917). According to this view, individual motor cortical neurons encode elementary, time-dependent movement fragments, which are combined via the ana ...
... Almost 100 years ago, it was postulated that the motor cortex should be viewed as a synthetic organ for complex motor actions (Leyton and Sherrington, 1917). According to this view, individual motor cortical neurons encode elementary, time-dependent movement fragments, which are combined via the ana ...




















![Acetylcholine Acetylcholine IUPAC name[hide] 2-Acetoxy](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001757659_1-dd3a11ed2d1408ee2f9aa2f256cd3204-300x300.png)

