northern spotted owl draft
... generally have yellow eyes. Primary Habitat: As with its prey species the spotted owl is an old growth-mature forest specialist, and forages and roosts in late seral (older successional) stands that have >50% canopy closure. In wet forest areas, this species generally uses stands dominated by conife ...
... generally have yellow eyes. Primary Habitat: As with its prey species the spotted owl is an old growth-mature forest specialist, and forages and roosts in late seral (older successional) stands that have >50% canopy closure. In wet forest areas, this species generally uses stands dominated by conife ...
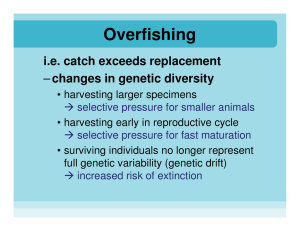
Controlling Overfishing
... • inefficient use of the catch (e.g. filleting, shark finning!!) • incidental catch (a.k.a. bycatch or “trash fish”) • habitat destruction (sea floor) ...
... • inefficient use of the catch (e.g. filleting, shark finning!!) • incidental catch (a.k.a. bycatch or “trash fish”) • habitat destruction (sea floor) ...
Ecology - pdecandia.com
... • About 10% of total energy consumed in one trophic level is incorporated into organisms of the next level - maintaining body temp, ability to move, and high reproductive rate require a lot of energy leaving less for higher levels - energy pyramids show the rate that each level stores energy as orga ...
... • About 10% of total energy consumed in one trophic level is incorporated into organisms of the next level - maintaining body temp, ability to move, and high reproductive rate require a lot of energy leaving less for higher levels - energy pyramids show the rate that each level stores energy as orga ...
Phosphorus and Nitrogen Cycles
... organisms, such as trees and then back to the nonliving environment. ...
... organisms, such as trees and then back to the nonliving environment. ...
Ecology - pdecandia.com
... • About 10% of total energy consumed in one trophic level is incorporated into organisms of the next level - maintaining body temp, ability to move, and high reproductive rate require a lot of energy leaving less for higher levels - energy pyramids show the rate that each level stores energy as orga ...
... • About 10% of total energy consumed in one trophic level is incorporated into organisms of the next level - maintaining body temp, ability to move, and high reproductive rate require a lot of energy leaving less for higher levels - energy pyramids show the rate that each level stores energy as orga ...
1/ Biodiversity and factors affecting it. a/ Human factors
... - How to measure it - Impact of light intensity on the distribution of plants in ecosystems- p174 - pH (air/soil/water) - How to measure it - Impact of water pH on the distribution of fish in aquatic ecosystems- p148-149 - Moisture levels (soil/air) - How to measure it - Impact of air/soil moisture ...
... - How to measure it - Impact of light intensity on the distribution of plants in ecosystems- p174 - pH (air/soil/water) - How to measure it - Impact of water pH on the distribution of fish in aquatic ecosystems- p148-149 - Moisture levels (soil/air) - How to measure it - Impact of air/soil moisture ...
Ecology - Greeley Schools
... Ecology is the study of interactions between organisms (biotic part) and their nonliving environment (abiotic factors) Biotic factors includes plants, animals, fungi, & microorganisms. They may be producers, consumers, or decomposers. Abiotic factors include climate, soil, temperature, water, air, s ...
... Ecology is the study of interactions between organisms (biotic part) and their nonliving environment (abiotic factors) Biotic factors includes plants, animals, fungi, & microorganisms. They may be producers, consumers, or decomposers. Abiotic factors include climate, soil, temperature, water, air, s ...
Slide 1 - South Bay Salt Pond Restoration Project
... for the occupation, utilization, operation, protection, enhancement, maintenance, and administration..” Section 1584: “..for the benefit of the general public to observe native flora an fauna and for scientific study or research.” Section 1585: “..department may construct facilities and conduct prog ...
... for the occupation, utilization, operation, protection, enhancement, maintenance, and administration..” Section 1584: “..for the benefit of the general public to observe native flora an fauna and for scientific study or research.” Section 1585: “..department may construct facilities and conduct prog ...
Community Composition and Predation • Predators selecting
... Community Composition and Predation ...
... Community Composition and Predation ...
CH 17 Section1 How Organisms Interact in
... – the process in which long term, interdependent changes take place in two species as a result of their interactions; some interactions among species are the result of a long evolutionary history in which many of the participants adjust to one another over time ...
... – the process in which long term, interdependent changes take place in two species as a result of their interactions; some interactions among species are the result of a long evolutionary history in which many of the participants adjust to one another over time ...
What have we done! - CastleSchoolBiology
... Deforestation: -Changes a forest into an area used for grazing land, logging, or urban purposes -Reduces biodiversity -Occurs even here on Long Island when a new model home or shopping center is built - Or can occur naturally ...
... Deforestation: -Changes a forest into an area used for grazing land, logging, or urban purposes -Reduces biodiversity -Occurs even here on Long Island when a new model home or shopping center is built - Or can occur naturally ...
Chapter 1
... Humans live within the world’s ecosystems and therefore change them as a result of population growth, technology, and consumption Problems: habitat destruction, pollution, atmospheric changes, over fishing the oceans, poaching, etc. ...
... Humans live within the world’s ecosystems and therefore change them as a result of population growth, technology, and consumption Problems: habitat destruction, pollution, atmospheric changes, over fishing the oceans, poaching, etc. ...
Complexity and Stability - Powerpoint for Nov. 2.
... • Disturbance agents: both physical and biological processes may cause disturbances, though we usually focus on physical processes • Physical - fires, ice storms, floods, drought, high winds, landslides, large waves • Biological - severe grazing, predation, disease, things that inadvertently kill or ...
... • Disturbance agents: both physical and biological processes may cause disturbances, though we usually focus on physical processes • Physical - fires, ice storms, floods, drought, high winds, landslides, large waves • Biological - severe grazing, predation, disease, things that inadvertently kill or ...
Living Resources Study Guide What was the size of Earth`s human
... The mating of animals in zoos or wildlife preserves is called captive breeding The ability of a plant species to fight disease is a result of its gene pool diversity Extinction: the disappearance from Earth of all members of a species Pollution: any change in the environment that has a negative effe ...
... The mating of animals in zoos or wildlife preserves is called captive breeding The ability of a plant species to fight disease is a result of its gene pool diversity Extinction: the disappearance from Earth of all members of a species Pollution: any change in the environment that has a negative effe ...
- Land for Wildlife
... habitat, tolerating fragmented ecosystems, and therefore is not a good species to use as an indicator of ecosystem health. It can be found in woodlands, shrublands, and rocky areas where conditions are dry for habitat, but are very common around the house and human habitation. They are arboreal and ...
... habitat, tolerating fragmented ecosystems, and therefore is not a good species to use as an indicator of ecosystem health. It can be found in woodlands, shrublands, and rocky areas where conditions are dry for habitat, but are very common around the house and human habitation. They are arboreal and ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... • Example: oxygen, sunlight, rocks, sand, and water. • Habitat – the place where an organism lives. ...
... • Example: oxygen, sunlight, rocks, sand, and water. • Habitat – the place where an organism lives. ...
Habitat loss - College of Forestry, University of Guangxi
... • As we move to talking about conservation biology and global ecology, we will talk more about how humans have altered ...
... • As we move to talking about conservation biology and global ecology, we will talk more about how humans have altered ...
Fishhook Waterflea *Detected in Michigan*
... Local Concern: Dietary preference put this species in direct competition with native planktivores. The long tail spine and barbs make this zooplankton less appealing to planktivorous fish, so population regulation from predation is unlikely to occur. This could have a serious effect on planktivore f ...
... Local Concern: Dietary preference put this species in direct competition with native planktivores. The long tail spine and barbs make this zooplankton less appealing to planktivorous fish, so population regulation from predation is unlikely to occur. This could have a serious effect on planktivore f ...
variation - Skinners` School Physics
... Variation in organisms characteristics are caused by the organisms having different alleles of genes. Some differences enable the organism to survive better (compete more successfully) The ones with beneficial alleles survive, breed and pass on their alleles to the next generation Those without bene ...
... Variation in organisms characteristics are caused by the organisms having different alleles of genes. Some differences enable the organism to survive better (compete more successfully) The ones with beneficial alleles survive, breed and pass on their alleles to the next generation Those without bene ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... Photic zone – well-lit upper layer of water where photosynthesis can take place Aphotic zone – permanently dark lower layer of water where producers use chemosynthesis to make food ...
... Photic zone – well-lit upper layer of water where photosynthesis can take place Aphotic zone – permanently dark lower layer of water where producers use chemosynthesis to make food ...
Gen Biology Exam 5 CH 30
... D.fairly long lifespan 43. Communities change over time, often in a known progression ending in a stable climax community. This is called ________. A.climax succession B.ecological progress C.ecological succession D.evolutionary progress 44. Human activity rarely affects the transfer rate of nutrien ...
... D.fairly long lifespan 43. Communities change over time, often in a known progression ending in a stable climax community. This is called ________. A.climax succession B.ecological progress C.ecological succession D.evolutionary progress 44. Human activity rarely affects the transfer rate of nutrien ...
REVIEW SHEET FOR ECOLOGY
... Ecology- the study of organisms and how they interact with their environment Ecosystem- consists of the living communities and the nonliving (abiotic) factors in an environment Eutrophication- the process where bodies of water are overloaded with nutrients- it is often the result of human activities ...
... Ecology- the study of organisms and how they interact with their environment Ecosystem- consists of the living communities and the nonliving (abiotic) factors in an environment Eutrophication- the process where bodies of water are overloaded with nutrients- it is often the result of human activities ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.