Population Factors
... Density-Independent Factors • Factors that affect the population regardless of its size may include… – Climate – rainfall and temperature – these are going to be plentiful or not – high or low – regardless of population numbers. – Pesticides/Toxins – man applies these and they will affect all organ ...
... Density-Independent Factors • Factors that affect the population regardless of its size may include… – Climate – rainfall and temperature – these are going to be plentiful or not – high or low – regardless of population numbers. – Pesticides/Toxins – man applies these and they will affect all organ ...
Slide 1 - PlattScience
... Brown anole eventually out-competed the green anole- reduced the green anole’s realized niche ...
... Brown anole eventually out-competed the green anole- reduced the green anole’s realized niche ...
Species and Populations
... A group of populations living and interacting with each other in a common habitat. Example: Tropical Rainforest- plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi. ...
... A group of populations living and interacting with each other in a common habitat. Example: Tropical Rainforest- plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi. ...
ORGANISMS AND POPULATIONS
... Biomes : Biome is a very large unit, constituting of a major vegetation type and associate fauna found in a specified zone. Annual variations in the intensity, duration of temperature and precipitation account for the formation of major biomes like desert, rain forest and tundra. Major Biomass of In ...
... Biomes : Biome is a very large unit, constituting of a major vegetation type and associate fauna found in a specified zone. Annual variations in the intensity, duration of temperature and precipitation account for the formation of major biomes like desert, rain forest and tundra. Major Biomass of In ...
Ecology Notes - Rochester Century High School
... given area that depend on each other) 10.Ecosystem All biotic and abiotic factors in the community 11.Biome: Areas of similar climatic conditions 12.Biosphere: All areas that sustain life ...
... given area that depend on each other) 10.Ecosystem All biotic and abiotic factors in the community 11.Biome: Areas of similar climatic conditions 12.Biosphere: All areas that sustain life ...
Competition - East Providence High School
... How does competition shape communities? By causing species to divide resources, competition helps determine the number and kinds of species in a community and the niche each species occupies. ...
... How does competition shape communities? By causing species to divide resources, competition helps determine the number and kinds of species in a community and the niche each species occupies. ...
APES Chapter 8 Vocabulary
... one example of each: interspecific competition, predation, and symbiosis. b. Distinguish between interference competition and exploitation competition. c. Summarize the competitive exclusion principle. ...
... one example of each: interspecific competition, predation, and symbiosis. b. Distinguish between interference competition and exploitation competition. c. Summarize the competitive exclusion principle. ...
File - Intervention
... What are the consequences of disruptions to the carbon cycle? Levels of carbon dioxide have increased through human activities with much of it not being removed by natural processes. This has caused a drastic increase in global climate change. These increase have also changed the oceans as they are ...
... What are the consequences of disruptions to the carbon cycle? Levels of carbon dioxide have increased through human activities with much of it not being removed by natural processes. This has caused a drastic increase in global climate change. These increase have also changed the oceans as they are ...
Biodiversity Dr.HSNiranjanaradhya Sree Siddaganga College
... Ecological benefits-: Biodiversity helps in the release of O2 by plants during photosynthesis. It also helps in soil conservation, recharge of underground water, Pollination and in maintaining Gaseous concentration ,air and water purification, climate regulation, generation of moisture and to recycl ...
... Ecological benefits-: Biodiversity helps in the release of O2 by plants during photosynthesis. It also helps in soil conservation, recharge of underground water, Pollination and in maintaining Gaseous concentration ,air and water purification, climate regulation, generation of moisture and to recycl ...
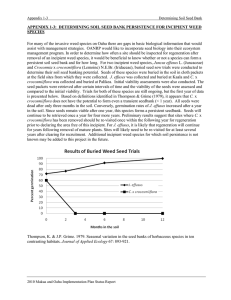
View or download Appendix 1-3: Determining Soil Seed Bank Persistence for Incipient Weed Species
... seed packets were retrieved after certain intervals of time and the viability of the seeds were assessed and compared to the initial viability. Trials for both of these species are still ongoing, but the first year of data is presented below. Based on definitions identified in Thompson & Grime (1979 ...
... seed packets were retrieved after certain intervals of time and the viability of the seeds were assessed and compared to the initial viability. Trials for both of these species are still ongoing, but the first year of data is presented below. Based on definitions identified in Thompson & Grime (1979 ...
The Biosphere
... that belong to the same species and live in the same area – Example: the alligator population of Greenfield Lake ...
... that belong to the same species and live in the same area – Example: the alligator population of Greenfield Lake ...
Planet in Peril Part I Key
... 3. What law in the United States protects wild species? (not in movie – Endangered Species Act) 4. What is the science of protecting species? (conservation biology) 5. What countries are the top importers of illegal wildlife (United States, China) 6. For what reasons are endangered species sold arou ...
... 3. What law in the United States protects wild species? (not in movie – Endangered Species Act) 4. What is the science of protecting species? (conservation biology) 5. What countries are the top importers of illegal wildlife (United States, China) 6. For what reasons are endangered species sold arou ...
Stephen Matthews(6 MB, Updated: Dec
... Class 7: new entry-high and low emissions (11 species) Class 8: new entry-high emissions (16 species) ...
... Class 7: new entry-high and low emissions (11 species) Class 8: new entry-high emissions (16 species) ...
Conservation Biology and Restoration Ecology
... Many species that are threatened could potentially provide crops, fibers, and medicines for human use, making biodiversity a crucial natural resource. The loss of these species would mean the loss of any possible medicinal benefits they might offer. The loss of species also means the loss of genes. ...
... Many species that are threatened could potentially provide crops, fibers, and medicines for human use, making biodiversity a crucial natural resource. The loss of these species would mean the loss of any possible medicinal benefits they might offer. The loss of species also means the loss of genes. ...
Name: Characteristics of Life and Ecology Guided Notes (PAP) What
... life. In an area that contains no Soil examples: bare rock, lava flow or glaciers. ...
... life. In an area that contains no Soil examples: bare rock, lava flow or glaciers. ...
Seashore Ecosystem
... used to estimate population sizeldensity, frequency or biomass of species in a fairly uniform habitat (e.g. a grassland) a square quadrat frame(of known area, such as 0.25m2 or 1m2)is placed randomly on the ground and organisms inside it are identified and counted the sampling is repeated many times ...
... used to estimate population sizeldensity, frequency or biomass of species in a fairly uniform habitat (e.g. a grassland) a square quadrat frame(of known area, such as 0.25m2 or 1m2)is placed randomly on the ground and organisms inside it are identified and counted the sampling is repeated many times ...
How Ecosystems Change A. 1. 2.
... spores are carried by the wind and settle on the rock. Lichens release ...
... spores are carried by the wind and settle on the rock. Lichens release ...
UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE AT MARTIN STUDENT CHAPTER
... Exotic and Invasive Plants and Animals The campus at the University of Tennessee at Martin consists of approximately 900 acres, which are used to enhance educational experiences and provide research opportunities. Many native species of plants and animals are present, but there are also numerous non ...
... Exotic and Invasive Plants and Animals The campus at the University of Tennessee at Martin consists of approximately 900 acres, which are used to enhance educational experiences and provide research opportunities. Many native species of plants and animals are present, but there are also numerous non ...
Jeopardy
... one species eats mature bamboo stalks, one species eats bamboo shoots, and one species eats leaves. This is an example of ...
... one species eats mature bamboo stalks, one species eats bamboo shoots, and one species eats leaves. This is an example of ...
Jeopardy
... one species eats mature bamboo stalks, one species eats bamboo shoots, and one species eats leaves. This is an example of ...
... one species eats mature bamboo stalks, one species eats bamboo shoots, and one species eats leaves. This is an example of ...
The Pattern of Evolution
... Natural selection • All organisms have the ability to out reproduce their natural resources. Thus, there is competition for limited resources • There is variation among individuals in every population. Thus, some individuals within the population will compete better for natural resources than other ...
... Natural selection • All organisms have the ability to out reproduce their natural resources. Thus, there is competition for limited resources • There is variation among individuals in every population. Thus, some individuals within the population will compete better for natural resources than other ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.