Biodiversity and Climate Change
... To use niche modeling as an example of how natural history collections are utilized by scientists. To show students the applications of niche modeling, such as climate change and urbanization. To familiarize students with the programs used to generate the models and the logic behind how those progra ...
... To use niche modeling as an example of how natural history collections are utilized by scientists. To show students the applications of niche modeling, such as climate change and urbanization. To familiarize students with the programs used to generate the models and the logic behind how those progra ...
Folder En - La biodiversité en Wallonie
... habitats, the EU suggested the implementation of a large ecological network ensuring the survival and dispersal of the species. This network of habitats, which is of great interest for the preservation of biodiversity, is called Natura 2000. Some of the habitats suggested by the Member States of the ...
... habitats, the EU suggested the implementation of a large ecological network ensuring the survival and dispersal of the species. This network of habitats, which is of great interest for the preservation of biodiversity, is called Natura 2000. Some of the habitats suggested by the Member States of the ...
Managing Uplands with Keystone Species
... greater than average change in other species populations or ecosystem processes; whose continued well-being is vital for the functioning of a whole community. ...
... greater than average change in other species populations or ecosystem processes; whose continued well-being is vital for the functioning of a whole community. ...
Out of the woods: how termites live inside and outside
... This student will examine the climatic factors that challenge termites outside wet forests, and their adaptations to it, using new data from individual termites and colonies. There will be an emphasis on genera (e.g. Macrotermes, Odontotermes) that are found abundantly in a range of habitats. Five s ...
... This student will examine the climatic factors that challenge termites outside wet forests, and their adaptations to it, using new data from individual termites and colonies. There will be an emphasis on genera (e.g. Macrotermes, Odontotermes) that are found abundantly in a range of habitats. Five s ...
BIO102-Ecology Part 2
... • Superior competitors become more numerous and attract predators • This allows other species to survive when they could have been out competed ...
... • Superior competitors become more numerous and attract predators • This allows other species to survive when they could have been out competed ...
BD 4.0 - Edquest
... the dodo bird, a flightless bird that lived on the island of Mautitius, in the Indian Ocean. The dodo became extinct when Portuguese explorers brought their domestic pets with them when they first landed on the island. The explorers used the dodo bird as food, but the reason the dodo became extinct ...
... the dodo bird, a flightless bird that lived on the island of Mautitius, in the Indian Ocean. The dodo became extinct when Portuguese explorers brought their domestic pets with them when they first landed on the island. The explorers used the dodo bird as food, but the reason the dodo became extinct ...
BIO102-Ecology Part 2
... • Superior competitors become more numerous and attract predators • This allows other species to survive when they could have been out competed ...
... • Superior competitors become more numerous and attract predators • This allows other species to survive when they could have been out competed ...
FRESHWATER ECOSYSTEM PPT
... and consumption. Human destruction of habitat through direct harvesting, pollution, atmospheric changes, and other factors is threatening current global stability, and if not addressed, ecosystems will be irreversibly affected. • Natural ecosystems provide an array of basic processes that affect hum ...
... and consumption. Human destruction of habitat through direct harvesting, pollution, atmospheric changes, and other factors is threatening current global stability, and if not addressed, ecosystems will be irreversibly affected. • Natural ecosystems provide an array of basic processes that affect hum ...
Chapter 4: The Human Body: From Food to Fuel
... Each species involved benefits b/c a predator that encounters an individual of 1 species will avoid similar individuals. Example: Bees & wasps have similar patterns of alternating yellow & black stripes. ...
... Each species involved benefits b/c a predator that encounters an individual of 1 species will avoid similar individuals. Example: Bees & wasps have similar patterns of alternating yellow & black stripes. ...
PLANET EARTH: Deserts
... adaptation - modification of an organism or its parts that makes it more fit for existence under the conditions of its environment desert - arid land with usually sparse vegetation; especially: such land having a very warm climate and receiving less than 25 centimeters (10 inches) of sporadic rainfa ...
... adaptation - modification of an organism or its parts that makes it more fit for existence under the conditions of its environment desert - arid land with usually sparse vegetation; especially: such land having a very warm climate and receiving less than 25 centimeters (10 inches) of sporadic rainfa ...
Chapter 3b - Department of Ecology and Evolution
... Trait-mediated indirect effect: Presence of a predator, causes prey to be active less and feed less on their own prey, so prey of second species increase in abundance, even though the second species did not decline (their feeding activity declined). ...
... Trait-mediated indirect effect: Presence of a predator, causes prey to be active less and feed less on their own prey, so prey of second species increase in abundance, even though the second species did not decline (their feeding activity declined). ...
TERRESTRIAL ECOLOGY STUDY GUIDE
... 3. What is a trophic level? 4. What happens to biological production and biomass as energy flows up a food chain? 5. What does it mean to “eat lower in the food chain?” 6. What is ecological succession? 7. List examples of ecological disturbances both natural and human caused. 8. What is primary suc ...
... 3. What is a trophic level? 4. What happens to biological production and biomass as energy flows up a food chain? 5. What does it mean to “eat lower in the food chain?” 6. What is ecological succession? 7. List examples of ecological disturbances both natural and human caused. 8. What is primary suc ...
Community Ecology
... Species in a community that have the highest abundance or highest biomass These species have a powerful effect on the distribution and eating patterns of all other species in a community Possible reasons for a dominant species • Dominant species is most competitive in acquiring limited resourc ...
... Species in a community that have the highest abundance or highest biomass These species have a powerful effect on the distribution and eating patterns of all other species in a community Possible reasons for a dominant species • Dominant species is most competitive in acquiring limited resourc ...
File
... Plant Adaptations What resource is limited at the bottom of a forest? ____________________________________ What adaptation allows plants to absorb more light? __________________________________ What allows plants to absorb more water in dry climates? ______________________________ What root design h ...
... Plant Adaptations What resource is limited at the bottom of a forest? ____________________________________ What adaptation allows plants to absorb more light? __________________________________ What allows plants to absorb more water in dry climates? ______________________________ What root design h ...
Jeopardy
... D. studying the internal organs of a seal to learn how it survives in its environment ...
... D. studying the internal organs of a seal to learn how it survives in its environment ...
Science Notebook Chapter 2 - Answer Key
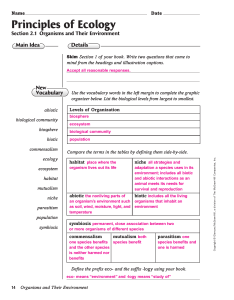
... organizer below. List the biological levels from largest to smallest. Levels of Organization ...
... organizer below. List the biological levels from largest to smallest. Levels of Organization ...
20:38 min - s3.amazonaws.com
... Across Belle Isle Park, a tall grass is quickly invading. Phragmites australis, or the common reed, is a perennial grass found all around the world. The grass grows an impressive 613 feet tall with upright stems and long flat smooth leaves. Its preferred habitat is wetlands, ditches, streams and pon ...
... Across Belle Isle Park, a tall grass is quickly invading. Phragmites australis, or the common reed, is a perennial grass found all around the world. The grass grows an impressive 613 feet tall with upright stems and long flat smooth leaves. Its preferred habitat is wetlands, ditches, streams and pon ...
Habitats PPT
... • Shelter: physical structures that a species lives near, around, on top of, or inside of. • It could be a specific structure as specific as a log, nest, or burrow. • It could also refer to cover, or the assortment of plants, rocks, water, decomposing matter, in which an organism can remain protecte ...
... • Shelter: physical structures that a species lives near, around, on top of, or inside of. • It could be a specific structure as specific as a log, nest, or burrow. • It could also refer to cover, or the assortment of plants, rocks, water, decomposing matter, in which an organism can remain protecte ...
MS - LS2 - 2 Construct an explanation that predicts
... Construct an explanation that predicts patterns of interactions among organisms across multiple ecosystems. A. I understand prey and predator interactions Directions: Read the following facts and answer 1-3 The Couch’s spadefoot frog has these characteristics. • Adults eat insects and spiders. • ...
... Construct an explanation that predicts patterns of interactions among organisms across multiple ecosystems. A. I understand prey and predator interactions Directions: Read the following facts and answer 1-3 The Couch’s spadefoot frog has these characteristics. • Adults eat insects and spiders. • ...
Why we do what we do
... The resulting conflict between these predators and farmers protecting their livelihood reduces the natural habitat areas where the animals can safely exist. GAME FARMERS: - With a shift in focus from cattle farming to a livelihood dependent on game for tourism and/or hunting, there has been an incre ...
... The resulting conflict between these predators and farmers protecting their livelihood reduces the natural habitat areas where the animals can safely exist. GAME FARMERS: - With a shift in focus from cattle farming to a livelihood dependent on game for tourism and/or hunting, there has been an incre ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.