DOPAMINE RECEPTORS
... Dopamine Receptors • There are five types of dopamine receptors.D1,D2,D3,D4,D5. • We can catogorize dopamine receptors in two two main subtypes: • D1 like receptor family: the Gs protein is involved and adenylyl cyclase would be activated. The action of the enzyme causes the conversion of adenosine ...
... Dopamine Receptors • There are five types of dopamine receptors.D1,D2,D3,D4,D5. • We can catogorize dopamine receptors in two two main subtypes: • D1 like receptor family: the Gs protein is involved and adenylyl cyclase would be activated. The action of the enzyme causes the conversion of adenosine ...
Print › AP Psych Unit 5 | Quizlet | Quizlet
... a sleep disorder characterized by high arousal and an appearance of being terrified; unlike nightmares, night terrors occur during Stage 4 sleep, within two or three hours of falling asleep and are seldom remembered ...
... a sleep disorder characterized by high arousal and an appearance of being terrified; unlike nightmares, night terrors occur during Stage 4 sleep, within two or three hours of falling asleep and are seldom remembered ...
Drug induced coma & Party drugs by Dr ML Tse
... • Toxidrome: cyclical coma:deep coma/agitated episodes, resp depression, rigidity, myoclonus face limbs, bradycardia • Typically pull out the ET tube and fully awake in 6 hrs • Flumazenil not consistent • Withdrawal? ...
... • Toxidrome: cyclical coma:deep coma/agitated episodes, resp depression, rigidity, myoclonus face limbs, bradycardia • Typically pull out the ET tube and fully awake in 6 hrs • Flumazenil not consistent • Withdrawal? ...
Opioids General - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... coupled to G proteins. Each opioid receptor has a unique distribution in the brain, spinal cord, and periphery. Opioids combine reversibly with these receptors and alter the transmission and perception of pain. Other effects: In addition to analgesia, opioids can induce other CNS effects that includ ...
... coupled to G proteins. Each opioid receptor has a unique distribution in the brain, spinal cord, and periphery. Opioids combine reversibly with these receptors and alter the transmission and perception of pain. Other effects: In addition to analgesia, opioids can induce other CNS effects that includ ...
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... ORGANISATION FOR THE PROHIBITION OF CHEMICAL WEAPONS Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons ...
... ORGANISATION FOR THE PROHIBITION OF CHEMICAL WEAPONS Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons ...
Summary of the Known Major Neurotransmitters
... Effect of Deficit Paralysis; A factor associated with Alzheimer’s disease: levels of acetylcholine are severely reduced associated with memory impairment. Excitatory: involved in voluntary muscle Muscle rigidity; movements, attention, learning, memory, A factor associated with and emotional arousal ...
... Effect of Deficit Paralysis; A factor associated with Alzheimer’s disease: levels of acetylcholine are severely reduced associated with memory impairment. Excitatory: involved in voluntary muscle Muscle rigidity; movements, attention, learning, memory, A factor associated with and emotional arousal ...
multiple choice
... 30) The protein that dictates the conversion of the undifferentiated gonads into the testes is controlled by the A) X chromosome. B) ob/ob protein. C) gene D) gene E) leptin protein. ...
... 30) The protein that dictates the conversion of the undifferentiated gonads into the testes is controlled by the A) X chromosome. B) ob/ob protein. C) gene D) gene E) leptin protein. ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. ...
... Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. ...
glutamate - Dental Decks
... on the postsynaptic membrane of the dendrite accept only certain neurotransmitters. In the brain, 30 different neurotransmitters have been classified as amino acids, amines, and neuropeptides. • Amino acid neurotransmitters: - Glutamate, GABA, and glycine. Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter ...
... on the postsynaptic membrane of the dendrite accept only certain neurotransmitters. In the brain, 30 different neurotransmitters have been classified as amino acids, amines, and neuropeptides. • Amino acid neurotransmitters: - Glutamate, GABA, and glycine. Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter ...
Metabotropic Neurot
... – Target of anti-psychotic drugs and anti-depressants (striatum) – Antagonists increase Ach transmission, improve learning and memory ...
... – Target of anti-psychotic drugs and anti-depressants (striatum) – Antagonists increase Ach transmission, improve learning and memory ...
The Nervous System
... neuron to neuron across gaps called synapses. A sending neuron synthesizes neurotransmitter molecules and bundles them into packages; when the neuron becomes electrically excited, it releases the neurotransmitter molecules into the synapse. Once in the synapse, each molecule may: Dock on a receptor ...
... neuron to neuron across gaps called synapses. A sending neuron synthesizes neurotransmitter molecules and bundles them into packages; when the neuron becomes electrically excited, it releases the neurotransmitter molecules into the synapse. Once in the synapse, each molecule may: Dock on a receptor ...
CNS NEUROTRANSMITTERS
... There are two primary dopamine receptor-types, both of which act through G-proteins : - D1 (stimulatory) - D2 (inhibitory), D2 receptors often occur on the dopaminergic neurons.They are called autoreceptors and upon stimulation can inhibit both dopamine synthesis and release. ...
... There are two primary dopamine receptor-types, both of which act through G-proteins : - D1 (stimulatory) - D2 (inhibitory), D2 receptors often occur on the dopaminergic neurons.They are called autoreceptors and upon stimulation can inhibit both dopamine synthesis and release. ...
E.4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses
... it is reabsorbed by the neuron that released it. This reabsorption happens with the help of a protein called the dopamine transporter. Crack interrupts this cycle. It attaches to the dopamine transporter, preventing the normal reabsorption process. As dopamine builds up in the synapse, it continues ...
... it is reabsorbed by the neuron that released it. This reabsorption happens with the help of a protein called the dopamine transporter. Crack interrupts this cycle. It attaches to the dopamine transporter, preventing the normal reabsorption process. As dopamine builds up in the synapse, it continues ...
UCLA Molecular Biology Institute
... Sleep regulation is a very mysterious phenomenon. Despite the fact that sleep is an essential component of the human experience occupying ~ 1/3 of our lives, little is known about what sleep is and what purposes it serves. It is clear that chronic disruption of sleep leads to increased risks of not ...
... Sleep regulation is a very mysterious phenomenon. Despite the fact that sleep is an essential component of the human experience occupying ~ 1/3 of our lives, little is known about what sleep is and what purposes it serves. It is clear that chronic disruption of sleep leads to increased risks of not ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Sensory Neurons – take info from the world Inter neurons make the connection between motor and sensory neurons – they do the thinking makes the connection between sensation and action Motor neurons - dictate to the muscles ...
... Sensory Neurons – take info from the world Inter neurons make the connection between motor and sensory neurons – they do the thinking makes the connection between sensation and action Motor neurons - dictate to the muscles ...
fleming_Oct
... Excitatory paths are shown in green; inhibitory are in red. The substantia nigra’s axons inhibit the putamen. Axon loss increases excitatory communication to the globus pallidus. The result is increased inhibition from the globus pallidus to the thalamus and decreased excitation from the thalamus to ...
... Excitatory paths are shown in green; inhibitory are in red. The substantia nigra’s axons inhibit the putamen. Axon loss increases excitatory communication to the globus pallidus. The result is increased inhibition from the globus pallidus to the thalamus and decreased excitation from the thalamus to ...
is here
... 5-HT action helps -ve symptoms NMDA (glutamate) receptors blocked by phencyclidine, relieves many symptoms ...
... 5-HT action helps -ve symptoms NMDA (glutamate) receptors blocked by phencyclidine, relieves many symptoms ...
Clinical Day
... • Progressive neurodegenerative disease that attacks nerve cells in brain and spinal cord • As neurons die, body functions lost ...
... • Progressive neurodegenerative disease that attacks nerve cells in brain and spinal cord • As neurons die, body functions lost ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
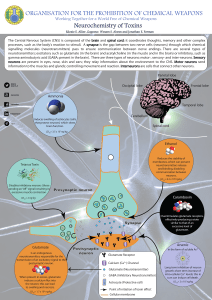
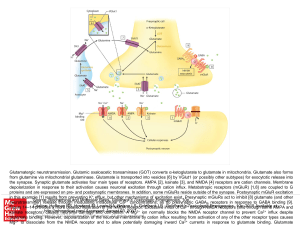
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
Dr. Carlos Paladini
... The dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta, located within the ventral mesencephalon, encode perhaps one of the most important signals for reinforcement learning in the brain: reward prediction error. This signal is encoded by the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons, which con ...
... The dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta, located within the ventral mesencephalon, encode perhaps one of the most important signals for reinforcement learning in the brain: reward prediction error. This signal is encoded by the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons, which con ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.