Chapter 4
... electrical impulse from one end of cell to other (neurotransmission) -Electrical signals within neurons are converted at synapse into chemical signals through release of molecules called neurotransmitters, which elicit electrical signals on other side of synapse, which enable information processing ...
... electrical impulse from one end of cell to other (neurotransmission) -Electrical signals within neurons are converted at synapse into chemical signals through release of molecules called neurotransmitters, which elicit electrical signals on other side of synapse, which enable information processing ...
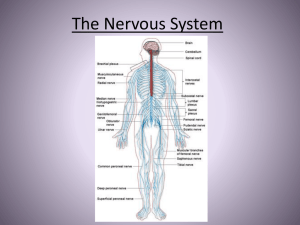
The Nervous System
... body’s activities = regulation. • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
... body’s activities = regulation. • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
Chapter 4 - coachburke
... there are various brain areas and several neurotransmitters that control the sleep-wake cycle ...
... there are various brain areas and several neurotransmitters that control the sleep-wake cycle ...
Abstract
... be regulated by neurons in the hypothalamus. Orexin, also called hypocretin is a neuropeptide recently identified as a natural ligand for orphan G protein coupled receptor1. Orexin-producing neurons (orexin neurons) are located specifically in the hypothalamus but project their efferents throughout ...
... be regulated by neurons in the hypothalamus. Orexin, also called hypocretin is a neuropeptide recently identified as a natural ligand for orphan G protein coupled receptor1. Orexin-producing neurons (orexin neurons) are located specifically in the hypothalamus but project their efferents throughout ...
Psychopharmacology and Other Biologic Treatments
... • Present in the presynaptic terminal • Released into the synaptic cleft, causing a particular effect on the postsynaptic receptors • An exogenous form of the chemical is administered as a drug causes identical action. • Chemical is removed from the synaptic cleft by a specific mechanism. ...
... • Present in the presynaptic terminal • Released into the synaptic cleft, causing a particular effect on the postsynaptic receptors • An exogenous form of the chemical is administered as a drug causes identical action. • Chemical is removed from the synaptic cleft by a specific mechanism. ...
Intro-The neuron
... • Scans show damage to left frontal lobe - which abilities should be assessed? • P can't recognize faces- what can his/her family expect? ...
... • Scans show damage to left frontal lobe - which abilities should be assessed? • P can't recognize faces- what can his/her family expect? ...
Module 9: Synaptic Transmission
... neurons in the substantia nigra • Symptoms include – difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements – tremors at rest – stooped posture – rigidity – poor balance ...
... neurons in the substantia nigra • Symptoms include – difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements – tremors at rest – stooped posture – rigidity – poor balance ...
The Nervous System
... Dopamine - cont’d • Dopamine also sends signals that help coordinate your skeletal muscle movements • Parkinson’s Disease – deficient dopamine production – tremors ...
... Dopamine - cont’d • Dopamine also sends signals that help coordinate your skeletal muscle movements • Parkinson’s Disease – deficient dopamine production – tremors ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
Cellular Neuroscience - How Your Brain Works
... • MPPP is a synthetic heroin substitute • MPTP is a contaminant that can arise from MPPP synthesis. It kills dopaminergic neurons and makes people (or animals) instantly Parkinsonian. • Some successes have been reported in treating MPTP poisoned addicts with embryonic tissue grafts. ...
... • MPPP is a synthetic heroin substitute • MPTP is a contaminant that can arise from MPPP synthesis. It kills dopaminergic neurons and makes people (or animals) instantly Parkinsonian. • Some successes have been reported in treating MPTP poisoned addicts with embryonic tissue grafts. ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
Diseases and Disorders of the Nervous System
... • Treatments: focus on drugs that block dopamine receptors, although evidence indicates that the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine & glutamate are also involved • Drugs that reduce symptoms often have negative side effects ...
... • Treatments: focus on drugs that block dopamine receptors, although evidence indicates that the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine & glutamate are also involved • Drugs that reduce symptoms often have negative side effects ...
Etiopathogenesis of Alzem - Nursing Powerpoint Presentations
... are converted to long-term memories • Thalamus: receives sensory and limbic information and sends to cerebral cortex • Hypothalamus: monitors certain activities and controls body’s internal clock • Limbic system: controls emotions and instinctive behavior (includes the hippocampus and parts of the c ...
... are converted to long-term memories • Thalamus: receives sensory and limbic information and sends to cerebral cortex • Hypothalamus: monitors certain activities and controls body’s internal clock • Limbic system: controls emotions and instinctive behavior (includes the hippocampus and parts of the c ...
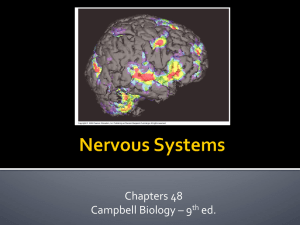
Nervous Systems
... depolarization of postsynaptic membrane Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane ...
... depolarization of postsynaptic membrane Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane ...
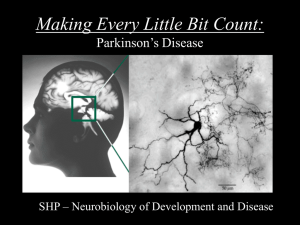
Lewy Body Diseases
... don't correlate with severity, but good marker for parts of brain affected by disease soluble aggregate-precursers are probably the actual causes of dysfunction Idiopathic Parkinson's Disease commonest form of parkinsonism (hereditary defect in alpha-synuclein quite rare) resting tremor, bra ...
... don't correlate with severity, but good marker for parts of brain affected by disease soluble aggregate-precursers are probably the actual causes of dysfunction Idiopathic Parkinson's Disease commonest form of parkinsonism (hereditary defect in alpha-synuclein quite rare) resting tremor, bra ...
MPTP - Columbia University
... • After 2-4yrs of treatment, patients develop a “wearing off” where the drug seems to stop working in between doses. Now the effect of the drug is dependent on serum concentration (known as the short duration effect. • Longterm use is associated with levodopa-induced dyskinesias. • Taking too much o ...
... • After 2-4yrs of treatment, patients develop a “wearing off” where the drug seems to stop working in between doses. Now the effect of the drug is dependent on serum concentration (known as the short duration effect. • Longterm use is associated with levodopa-induced dyskinesias. • Taking too much o ...
Synaptic Transmission
... • Neurotransmitter (NT) released into synapse • NT locks onto receptor molecule in postsynaptic ...
... • Neurotransmitter (NT) released into synapse • NT locks onto receptor molecule in postsynaptic ...
Neurobiology of Addiction
... If drug is not available to the neuron, unpleasant emotional and physical effects occur, because the normal activating and inhibitory neurotransmitter levels have been altered See example, next slide ...
... If drug is not available to the neuron, unpleasant emotional and physical effects occur, because the normal activating and inhibitory neurotransmitter levels have been altered See example, next slide ...
Synaptic Transmission - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... • Neurotransmitter (NT) released into synapse • NT locks onto receptor molecule in postsynaptic ...
... • Neurotransmitter (NT) released into synapse • NT locks onto receptor molecule in postsynaptic ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.