Chapter 7: The Nervous System
... • Do not divide: fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception • High metabolic rate: require abundant amounts of oxygen and glucose ...
... • Do not divide: fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception • High metabolic rate: require abundant amounts of oxygen and glucose ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... In terms of sensory receptors, _____respond to variations in light, but ______respond to changes in temperature. ...
... In terms of sensory receptors, _____respond to variations in light, but ______respond to changes in temperature. ...
Sensory neurons
... Sensory Neurons are a part of the bodies nervous system that are responsible for detecting external signals. These neurons are rather important and special as they do not receive signals from the body, but from external sources like sound, light and temperature. In complex organisms like Humans, mos ...
... Sensory Neurons are a part of the bodies nervous system that are responsible for detecting external signals. These neurons are rather important and special as they do not receive signals from the body, but from external sources like sound, light and temperature. In complex organisms like Humans, mos ...
Key - Cornell
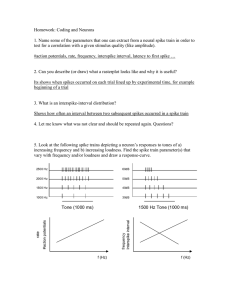
... test for a correlation with a given stimulus quality (like amplitude). #action potentials, rate, frequency, interspike interval, latency to first spike … ...
... test for a correlation with a given stimulus quality (like amplitude). #action potentials, rate, frequency, interspike interval, latency to first spike … ...
MS WORD file
... are interoceptors and sense stimuli within the body instead of from the outside world. In the vertebrate system, it appears that many of the joint and tension receptors are not necessary to detect gross proprioceptive information. The annulospiral and flowerspray (sensory nerve endings) receptors on ...
... are interoceptors and sense stimuli within the body instead of from the outside world. In the vertebrate system, it appears that many of the joint and tension receptors are not necessary to detect gross proprioceptive information. The annulospiral and flowerspray (sensory nerve endings) receptors on ...
Muscle Receptor Organs in the Crayfish Abdomen: A Student
... are interoceptors and sense stimuli within the body instead of from the outside world. In the vertebrate system, it appears that many of the joint and tension receptors are not necessary to detect gross proprioceptive information. The annulospiral and flowerspray (sensory nerve endings) receptors on ...
... are interoceptors and sense stimuli within the body instead of from the outside world. In the vertebrate system, it appears that many of the joint and tension receptors are not necessary to detect gross proprioceptive information. The annulospiral and flowerspray (sensory nerve endings) receptors on ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
Crayfish Dissection
... Examine the external anatomy of your crayfish. Typically, arthropod bodes are divided into three sections: head thorax and abdomen. In the crayfish, the head and the thorax are fused into a single cephalothorax. Find the cephalothorax and abdomen of your crayfish. Notice that the crayfish has a ha ...
... Examine the external anatomy of your crayfish. Typically, arthropod bodes are divided into three sections: head thorax and abdomen. In the crayfish, the head and the thorax are fused into a single cephalothorax. Find the cephalothorax and abdomen of your crayfish. Notice that the crayfish has a ha ...
neurons
... the neuron to carry out its functions. The cell body also contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dendrites. Dendrites receive messages from other neurons or specia ...
... the neuron to carry out its functions. The cell body also contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dendrites. Dendrites receive messages from other neurons or specia ...
Slide 1 - AccessPhysiotherapy
... potentials, as explained later in this chapter. A projection neuron sends its output to other neurons. A sensory neuron (B) has a different structure. There is Source: Neuronal Structure and Function, Neurologic Rehabilitation: Neuroscience and Neuroplasticity in Physical Therapy Practice a distal p ...
... potentials, as explained later in this chapter. A projection neuron sends its output to other neurons. A sensory neuron (B) has a different structure. There is Source: Neuronal Structure and Function, Neurologic Rehabilitation: Neuroscience and Neuroplasticity in Physical Therapy Practice a distal p ...
Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VI. Growth Factors
... This growth is not due to new neurons, as the vast majority of nerve cells are present at birth. Surprisingly, two thirds of all neurons born during fetal development will die during the first decade of life in a process termed apoptosis, or programmed cell death. The remarkable growth of the brain ...
... This growth is not due to new neurons, as the vast majority of nerve cells are present at birth. Surprisingly, two thirds of all neurons born during fetal development will die during the first decade of life in a process termed apoptosis, or programmed cell death. The remarkable growth of the brain ...
Nervous System
... autonomic nervous system Somatic nervous system: controls skeletal muscles and external sensory organs such as the skin. System is voluntary, except for reflex reactions of skeletal muscles. ...
... autonomic nervous system Somatic nervous system: controls skeletal muscles and external sensory organs such as the skin. System is voluntary, except for reflex reactions of skeletal muscles. ...
The synapse.
... • Adherents of the electrical synapse have no circuit of neurons, in real anatomy, that can account for the irreducible delay. ...
... • Adherents of the electrical synapse have no circuit of neurons, in real anatomy, that can account for the irreducible delay. ...
Name
... An example of a TAGMA is the CEPHALOTHORAX in a crayfish. The head and middle body sections (thorax) are joined together to make one piece. You can see the fused dividing line between them. The portion of the exoskeleton that covers the cephalothorax is called the CARAPACE. The visor-like ROSTRUM co ...
... An example of a TAGMA is the CEPHALOTHORAX in a crayfish. The head and middle body sections (thorax) are joined together to make one piece. You can see the fused dividing line between them. The portion of the exoskeleton that covers the cephalothorax is called the CARAPACE. The visor-like ROSTRUM co ...
Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by
... Interneurons – receive information in the CNS and send it to a motor neuron These essentially connect the sensory and motor neurons o Motor – take impulses from the CNS to an effector (i.e. gland or muscle fiber) Nerve impulses move from the dendrite through the cell body and then down the axon ...
... Interneurons – receive information in the CNS and send it to a motor neuron These essentially connect the sensory and motor neurons o Motor – take impulses from the CNS to an effector (i.e. gland or muscle fiber) Nerve impulses move from the dendrite through the cell body and then down the axon ...
Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... nerves leading to and from the CNS, often through junctions known as ganglia. 2. Using what you know about the processes of the central nervous system, describe the path an impulse would take that would make you move in response to a tap on the shoulder. The tap on the shoulder would be picked up by ...
... nerves leading to and from the CNS, often through junctions known as ganglia. 2. Using what you know about the processes of the central nervous system, describe the path an impulse would take that would make you move in response to a tap on the shoulder. The tap on the shoulder would be picked up by ...
Nervous System - Phoenix Union High School District
... d) oligodendrocytes- branched; connect thick nerve fibers; produce a myelin sheath around neurons. ...
... d) oligodendrocytes- branched; connect thick nerve fibers; produce a myelin sheath around neurons. ...
Slide 1
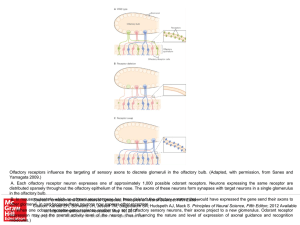
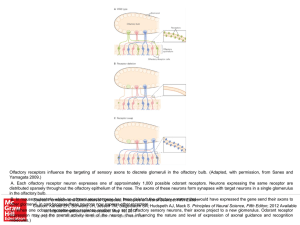
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Slide ()
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Neuron Anatomy Activity - Ask a Biologist
... 1. Synapses: Send electrical impulses to neighboring neurons. 2. Myelin sheaths: Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly. 3. Axon: Transfers electrical impulse signals from the cell body to the synapse. 4. Soma: ...
... 1. Synapses: Send electrical impulses to neighboring neurons. 2. Myelin sheaths: Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly. 3. Axon: Transfers electrical impulse signals from the cell body to the synapse. 4. Soma: ...
The Nervous System- Nervous Tissue
... • transmit motor information from the CNS to effectors (muscles/glands/adipose tissue) in the periphery of the body • Association (interneurons) – • transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, coordinate outputs • most common type of neuron (20 billion) ...
... • transmit motor information from the CNS to effectors (muscles/glands/adipose tissue) in the periphery of the body • Association (interneurons) – • transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, coordinate outputs • most common type of neuron (20 billion) ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.