EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... How neurons communicate • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... How neurons communicate • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Synaptic Cleft: Information Transfer Nerve impulses (AP) reach the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
... Synaptic Cleft: Information Transfer Nerve impulses (AP) reach the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... leading to demyelination.[1] Disease onset usually occurs in young adults, and it is more common in women.[2] It has a prevalence that ranges between 2 and 150 per 100,000.[3] ...
... leading to demyelination.[1] Disease onset usually occurs in young adults, and it is more common in women.[2] It has a prevalence that ranges between 2 and 150 per 100,000.[3] ...
Neurotransmitter - Pamoja Education Blogs
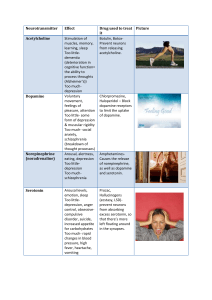
... Too little- some form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
... Too little- some form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]
... Neuron Structure • Dendrites – branched projections of a neuron that act to conduct the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body or soma • Soma – the cell body, contains the nucleus • Axon – long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses ...
... Neuron Structure • Dendrites – branched projections of a neuron that act to conduct the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body or soma • Soma – the cell body, contains the nucleus • Axon – long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses ...
The Nervous System
... Neurons are often arranged in a pattern called a reflex arc. Basically, a reflex arc is a signal conduction route to and from the CNS. The most common form of reflex arc is the three-neuron arc. It consists of an afferent neuron, and an efferent neuron. Afferent or sensory, neuron conducts signals t ...
... Neurons are often arranged in a pattern called a reflex arc. Basically, a reflex arc is a signal conduction route to and from the CNS. The most common form of reflex arc is the three-neuron arc. It consists of an afferent neuron, and an efferent neuron. Afferent or sensory, neuron conducts signals t ...
File
... 1) The axon membrane is at a resting potential of 70mV, and then rises to the threshold potential of 50mV, either due to a stimulus, or the binding of a neurotransmitter at a synapse. 2) Them membrane depolarizes due to voltage-gated Na+ channels opening and Na+ rapidly moving in. 3) The membrane re ...
... 1) The axon membrane is at a resting potential of 70mV, and then rises to the threshold potential of 50mV, either due to a stimulus, or the binding of a neurotransmitter at a synapse. 2) Them membrane depolarizes due to voltage-gated Na+ channels opening and Na+ rapidly moving in. 3) The membrane re ...
Inhibition
... more easily and faster oriented in a direction of a location in which it already has been rather than shifting to another location ...
... more easily and faster oriented in a direction of a location in which it already has been rather than shifting to another location ...
LectureTest22011, the new questions
... D. 35. In this course, we learned the names of only five specific types of neurons. Which one of them is most important for the cerebellum, in calculating how to make our movements smooth, precise, and coordinated? A. pseudo-unipolar neuron B. pyramidal neuron C. ganglion neuron D. Purkinje neuron ...
... D. 35. In this course, we learned the names of only five specific types of neurons. Which one of them is most important for the cerebellum, in calculating how to make our movements smooth, precise, and coordinated? A. pseudo-unipolar neuron B. pyramidal neuron C. ganglion neuron D. Purkinje neuron ...
1. Cell body - greinerudsd
... into the synaptic cleft (via exocytosis) – Neurotransmitters diffuse across gap & bind to receptors on the adjacent neuron – Cause the impulse to continue (if threshold is reached) • Neurotransmitters are either broken down or recycled • This is where drugs interfere ...
... into the synaptic cleft (via exocytosis) – Neurotransmitters diffuse across gap & bind to receptors on the adjacent neuron – Cause the impulse to continue (if threshold is reached) • Neurotransmitters are either broken down or recycled • This is where drugs interfere ...
Nervous System Notes
... respond appropriately to the information is receives. – If you are hungry, your nervous system tells you to eat! = homeostasis! – Homeostasis = the things your body does to keep you alive in that “just right” kind of way. ...
... respond appropriately to the information is receives. – If you are hungry, your nervous system tells you to eat! = homeostasis! – Homeostasis = the things your body does to keep you alive in that “just right” kind of way. ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... • A single synaptic event is not sufficient to initiate an action potential in the postganglionic neurons, but the summation of multiple events is required to initiate it • Divergence: relatively few preganglionic neurons synapse with many postganglionic neurons located within one or several nearb ...
... • A single synaptic event is not sufficient to initiate an action potential in the postganglionic neurons, but the summation of multiple events is required to initiate it • Divergence: relatively few preganglionic neurons synapse with many postganglionic neurons located within one or several nearb ...
APPLICATION FOR MRC STUDENTSHIPS TO COMMENCE 2009
... group of dopamine neurons using mice and embryonic stem (ES) cell models. We will direct the differentiation of ES cells towards dopamine neurons to model neurodevelopmental disorders in vitro. Background: Dopamine neurons are a highly diverse neuronal population controlling important brain function ...
... group of dopamine neurons using mice and embryonic stem (ES) cell models. We will direct the differentiation of ES cells towards dopamine neurons to model neurodevelopmental disorders in vitro. Background: Dopamine neurons are a highly diverse neuronal population controlling important brain function ...
neurons - haltliappsych
... • If no, the sending neuron will reuptake (vacuum up) the neurotransmitters that it sent into the synapse! ...
... • If no, the sending neuron will reuptake (vacuum up) the neurotransmitters that it sent into the synapse! ...
Note 11.1 - The Nervous System
... junction called an axon hillock. The axon will branch at its end, with each branch ending in a small button like swelling called an axon terminal. The axon terminals are the points where the signal is enabled to be transmitted from one neuron to another other or to an effector. ...
... junction called an axon hillock. The axon will branch at its end, with each branch ending in a small button like swelling called an axon terminal. The axon terminals are the points where the signal is enabled to be transmitted from one neuron to another other or to an effector. ...
Principles of Sensory Coding
... optic nerve is always interpreted by the brain as visual input etc. This extends to much finer discriminations: the connections of “pain” and “touch” fibers in the somatosensory system are entirely different and electrical stimulation of either leads to the appropriate sensation. Intensity: the esti ...
... optic nerve is always interpreted by the brain as visual input etc. This extends to much finer discriminations: the connections of “pain” and “touch” fibers in the somatosensory system are entirely different and electrical stimulation of either leads to the appropriate sensation. Intensity: the esti ...
Slide ()
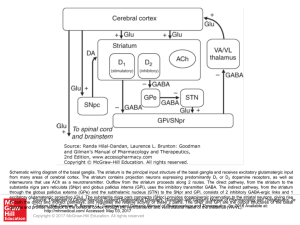
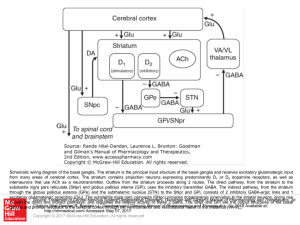
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Control Coordination
... • sensory nerves take impulse from stimulus (sensory receptors) to the the CNS • motor nerves take impulse from the CNS to the muscles and glands that take action. ...
... • sensory nerves take impulse from stimulus (sensory receptors) to the the CNS • motor nerves take impulse from the CNS to the muscles and glands that take action. ...
Slide ()
... The muscle spindle detects changes in muscle length. A. The main components of the muscle spindle are intrafusal muscle fibers, afferent sensory endings, and efferent motor endings. The intrafusal fibers are specialized muscle fibers with central regions that are not contractile. Gamma motor neurons ...
... The muscle spindle detects changes in muscle length. A. The main components of the muscle spindle are intrafusal muscle fibers, afferent sensory endings, and efferent motor endings. The intrafusal fibers are specialized muscle fibers with central regions that are not contractile. Gamma motor neurons ...
control systems of the body - chapter 11
... nervous system is by far the more rapid acting & complex. Nervous cells communicate by means of electrochemical signals, which are rapid & specific, usually causing almost immediate responses. It involves ions like Na+ (sodium) and K+ (potassium) crossing the membrane of neurons. An action potential ...
... nervous system is by far the more rapid acting & complex. Nervous cells communicate by means of electrochemical signals, which are rapid & specific, usually causing almost immediate responses. It involves ions like Na+ (sodium) and K+ (potassium) crossing the membrane of neurons. An action potential ...
nervous system development and histology
... most sensory neurons are unipolar, a few are bipolar• Motor (efferent) neurons – • transmit motor information from the CNS to effectors (muscles/glands/adipose • tissue) in the periphery of the body all are multipolar• Association (interneurons) –• transmit information between neurons within the CNS ...
... most sensory neurons are unipolar, a few are bipolar• Motor (efferent) neurons – • transmit motor information from the CNS to effectors (muscles/glands/adipose • tissue) in the periphery of the body all are multipolar• Association (interneurons) –• transmit information between neurons within the CNS ...
Lecture 14 - School of Computing
... Experimental Results (cont.) Question: Which neurons are important, if any? Answer: An examination of the weights that contribute most to the output in the Kohonen net revealed that a small subset of neurons (<50) that are not category-specific yet respond with different intensities to different ca ...
... Experimental Results (cont.) Question: Which neurons are important, if any? Answer: An examination of the weights that contribute most to the output in the Kohonen net revealed that a small subset of neurons (<50) that are not category-specific yet respond with different intensities to different ca ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.




![Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008568661_1-062fb6959798aae5bb439e7880889016-300x300.png)