Introduction to Neural Networks
... means of directed communication links, each with associated weight. ...
... means of directed communication links, each with associated weight. ...
The Autonomic Nervous System - Ashland Independent Schools
... • Axons of motor nerves (from T1-L2) exit through ventral root of spinal nerves, branch and enter sympathetic ganglia (trunks) located in chains along vertebral column – Sympathetic preganglionic neurons exit the spinal cord only between levels T1-L2 • Short pre-ganglionic fiber releases acetylcholi ...
... • Axons of motor nerves (from T1-L2) exit through ventral root of spinal nerves, branch and enter sympathetic ganglia (trunks) located in chains along vertebral column – Sympathetic preganglionic neurons exit the spinal cord only between levels T1-L2 • Short pre-ganglionic fiber releases acetylcholi ...
ch 16 sensory motor systems
... a. During sleep, a state of altered consciousness or partial unconsciousness from which an individual can be aroused by different stimuli, activity in the RAS is very low. b. Normal sleep consists of two types: non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM) and rapid eye movement sleep (REM). 1) Non-rapid eye ...
... a. During sleep, a state of altered consciousness or partial unconsciousness from which an individual can be aroused by different stimuli, activity in the RAS is very low. b. Normal sleep consists of two types: non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM) and rapid eye movement sleep (REM). 1) Non-rapid eye ...
NOB Ch 6 Answers - MCC Year 12 Biology
... Why is it important for all individuals to have regular eye checks, particularly as they age? Many eye defects can occur as one ages. In some cases where treatment is available, early detection means that treatment can begin sooner, and this may halt or slow the progress of the disease. ...
... Why is it important for all individuals to have regular eye checks, particularly as they age? Many eye defects can occur as one ages. In some cases where treatment is available, early detection means that treatment can begin sooner, and this may halt or slow the progress of the disease. ...
chapter 8 lecture ppt
... • Local Current: movement of Na+ which causes inside of cell to be more positive (depolarize) ...
... • Local Current: movement of Na+ which causes inside of cell to be more positive (depolarize) ...
relating nerve cells to behavior
... visual system response due to ~ stimulus other neural systems ~ attention (& ~ activity ...
... visual system response due to ~ stimulus other neural systems ~ attention (& ~ activity ...
Abstract - BMB Reports
... Abstract The central nervous system (CNS) controls food intake and energy expenditure via tight co-ordinations between multiple neuronal populations. Specifically, two distinct neuronal populations exist in the arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus (ARH): the anorexigenic (appetite-suppressing) proopiomel ...
... Abstract The central nervous system (CNS) controls food intake and energy expenditure via tight co-ordinations between multiple neuronal populations. Specifically, two distinct neuronal populations exist in the arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus (ARH): the anorexigenic (appetite-suppressing) proopiomel ...
Introduction to Machine Intelligence
... know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across neuronal membranes. Recording devices must intercept voltag ...
... know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across neuronal membranes. Recording devices must intercept voltag ...
Language within our grasp:
... • Mirror neurons were discovered in single-cell recording in area F5: ventral [= lower] premotor cortex • They discharge during active movements of the hand and/or mouth • They are sensitive to different purposes – Some discharge during grasping; some during (specific kinds of) holding; some during ...
... • Mirror neurons were discovered in single-cell recording in area F5: ventral [= lower] premotor cortex • They discharge during active movements of the hand and/or mouth • They are sensitive to different purposes – Some discharge during grasping; some during (specific kinds of) holding; some during ...
Introduction to Machine Intelligence
... know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across neuronal membranes. Recording devices must intercept voltag ...
... know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across neuronal membranes. Recording devices must intercept voltag ...
The Nervous System - leavingcertbiology.net
... Interneurons • Interneurons (central nervous system) – Interneurons are the most numerous type of neuron found in the human body – Interneurons receive messages from sensory neurons and other interneurons in the brain – Interneurons integrate messages received and relay them onto motor neurons ...
... Interneurons • Interneurons (central nervous system) – Interneurons are the most numerous type of neuron found in the human body – Interneurons receive messages from sensory neurons and other interneurons in the brain – Interneurons integrate messages received and relay them onto motor neurons ...
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... 1. 31 pairs of mixed nerves arise from spinal cord; Supplies all of body except the head 2. Named according to their point of issue a. 8 cervical (C1-C8) b. 12 thoracic (T1-T12) c. 5 Lumbar (L1-L5) d. 5 Sacral (S1-S5) e. 1 Coccygeal (C0) 3. Roots ...
... 1. 31 pairs of mixed nerves arise from spinal cord; Supplies all of body except the head 2. Named according to their point of issue a. 8 cervical (C1-C8) b. 12 thoracic (T1-T12) c. 5 Lumbar (L1-L5) d. 5 Sacral (S1-S5) e. 1 Coccygeal (C0) 3. Roots ...
Presentation Package - faculty.coe.unt.edu
... Muscles controlling fine movements, such as those controlling the eyes, have a small number of muscle fibers per motor neuron (about 1 neuron for every 15 muscle fibers). Muscles with more general function, such as those controlling the calf muscle in the leg, have many fibers per motor neuron (abou ...
... Muscles controlling fine movements, such as those controlling the eyes, have a small number of muscle fibers per motor neuron (about 1 neuron for every 15 muscle fibers). Muscles with more general function, such as those controlling the calf muscle in the leg, have many fibers per motor neuron (abou ...
Document
... • A motor unit consists of a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates • Three types of motor units (muscles): • Fast fatigable (FF) Powerful, but fatigue with repetitive stimulation muscle fiber: thick, large, white (anaerobic, use glycolytic pathway to generate ATP) Motor neuron large, ...
... • A motor unit consists of a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates • Three types of motor units (muscles): • Fast fatigable (FF) Powerful, but fatigue with repetitive stimulation muscle fiber: thick, large, white (anaerobic, use glycolytic pathway to generate ATP) Motor neuron large, ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another target cell; a neuron, muscle cell or cell of a gland. Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter an ...
... Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another target cell; a neuron, muscle cell or cell of a gland. Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter an ...
The Nervous System
... • Dendrites are thin, branched processes whose main function is to receive incoming signals. • They effectively increase the surface area of a neuron to increase its ability to communicate with other neurons. • Small, mushroom-shaped dendritic spines further increase the SA ...
... • Dendrites are thin, branched processes whose main function is to receive incoming signals. • They effectively increase the surface area of a neuron to increase its ability to communicate with other neurons. • Small, mushroom-shaped dendritic spines further increase the SA ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
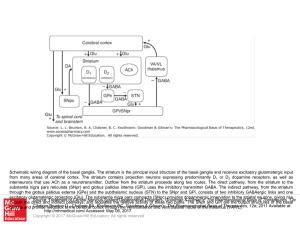
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Readings to Accompany “Nerves” Worksheet (adapted from France
... When dendrites of a neuron receive sufficient stimulation, the axon hillock of the neuron will transmit that impulse toward the axon. This is the first step in transmitting a stimulus called the action potential. Sodium (Na+) ions will rush into the axon through Na+ channels resulting in a change in ...
... When dendrites of a neuron receive sufficient stimulation, the axon hillock of the neuron will transmit that impulse toward the axon. This is the first step in transmitting a stimulus called the action potential. Sodium (Na+) ions will rush into the axon through Na+ channels resulting in a change in ...
Neural Anatomy and Function
... Sensitive to muscle tension and active ORGAN contraction Protect muscle from excess contraction force Stimulation of GTO an afferent impulse is sent to the central nervous system In turn, efferent impulses are sent to the… …Agonist muscle causing it to relax ...
... Sensitive to muscle tension and active ORGAN contraction Protect muscle from excess contraction force Stimulation of GTO an afferent impulse is sent to the central nervous system In turn, efferent impulses are sent to the… …Agonist muscle causing it to relax ...
Certain Histological and Anatomical Features of the Central Nervous
... devoid of synaptic endings (Bullock and Horridge, 1965). The neuropile, which can be distinguished by its finer and more tangled texture, thus becomes the most important region, because this is the only known place of neuronal contacts. Hence it has acquired functional significance as the primary pl ...
... devoid of synaptic endings (Bullock and Horridge, 1965). The neuropile, which can be distinguished by its finer and more tangled texture, thus becomes the most important region, because this is the only known place of neuronal contacts. Hence it has acquired functional significance as the primary pl ...
Invariant selectivity of auditory neurons due to predictive coding
... We propose a dynamic Bayesian inference model and train it on a large database of natural speech to predict this invariant selectivity, i.e. predictive fields (PFs). The model can account for nonlinear contextual effects such as two-tone and forward suppression. The model neurons adapt rapidly to ne ...
... We propose a dynamic Bayesian inference model and train it on a large database of natural speech to predict this invariant selectivity, i.e. predictive fields (PFs). The model can account for nonlinear contextual effects such as two-tone and forward suppression. The model neurons adapt rapidly to ne ...
November 12
... Cerebellum supplies input to the motor cortex via the pons (pontine nuclei) and area VLc of the thalamus. Feedback from the sensory cortex guides activity of the cerebellum to create and store learned programs of movement. ...
... Cerebellum supplies input to the motor cortex via the pons (pontine nuclei) and area VLc of the thalamus. Feedback from the sensory cortex guides activity of the cerebellum to create and store learned programs of movement. ...
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding glial
... b) The neuron is negatively charged while the extra-cellular medium is positively charged c) The neuron predominantly contains negatively charged ions while the extra-cellular medium contains positively charged ...
... b) The neuron is negatively charged while the extra-cellular medium is positively charged c) The neuron predominantly contains negatively charged ions while the extra-cellular medium contains positively charged ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.