Astro 27 Solar System Formation and ExoPlanets Slide Show
... 1. Mg 26 is uniformly distributed throughout the solar system and throughout studied meteorites. 2. CAI’s (calcium rich inclusions) within meteorites have a very narrow (~1600K) temperature range within which they solidify, and this corresponds to a very narrow time range when they could incorporate ...
... 1. Mg 26 is uniformly distributed throughout the solar system and throughout studied meteorites. 2. CAI’s (calcium rich inclusions) within meteorites have a very narrow (~1600K) temperature range within which they solidify, and this corresponds to a very narrow time range when they could incorporate ...
6 Minute English
... It’s just a big ball of gas. And we measure it… it’s made mostly of hydrogen. So it’s roughly 90% hydrogen, it’s maybe 8% helium, and the rest of it’s made up of things like iron, carbon, oxygen, nickel. Neil So the main gas is hydrogen, which accounts for 90% of the sun’s matter. Now, 'matter' mean ...
... It’s just a big ball of gas. And we measure it… it’s made mostly of hydrogen. So it’s roughly 90% hydrogen, it’s maybe 8% helium, and the rest of it’s made up of things like iron, carbon, oxygen, nickel. Neil So the main gas is hydrogen, which accounts for 90% of the sun’s matter. Now, 'matter' mean ...
DR The Sun File
... ______________________________________________________________ 57. How does the mass of the sun compare with the mass of Earth? ______________________________________________________________ 58. What effect does the sun’s large mass have on the density of the sun’s core? ____________________________ ...
... ______________________________________________________________ 57. How does the mass of the sun compare with the mass of Earth? ______________________________________________________________ 58. What effect does the sun’s large mass have on the density of the sun’s core? ____________________________ ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... 34. Type II supernovae are important because (a) the resulting burst of neutrinos keeps the galaxy from collapsing. (b) the elements heavier than iron are synthesized and the elements heavier than helium are dispersed through space. (c) all of star’s hydrogen is returned to the interstellar medium. ...
... 34. Type II supernovae are important because (a) the resulting burst of neutrinos keeps the galaxy from collapsing. (b) the elements heavier than iron are synthesized and the elements heavier than helium are dispersed through space. (c) all of star’s hydrogen is returned to the interstellar medium. ...
Planets
... The surface geology of Venus includes volcanic features that include large elevated plateaus, large and small volcanic cones and shields, and pancake-shaped formations of lava ...
... The surface geology of Venus includes volcanic features that include large elevated plateaus, large and small volcanic cones and shields, and pancake-shaped formations of lava ...
The Science of Sunshine
... would look bleak” In a very simplified nutshell, the Sun, like every other main sequence star generates energy deep in its core by converting hydrogen into helium. Exactly the same process occurs in a detonating thermonuclear bomb, so the core of the Sun can be thought of as one enormous nuclear exp ...
... would look bleak” In a very simplified nutshell, the Sun, like every other main sequence star generates energy deep in its core by converting hydrogen into helium. Exactly the same process occurs in a detonating thermonuclear bomb, so the core of the Sun can be thought of as one enormous nuclear exp ...
The Earth in Context: Universe and Solar System
... suggests past climate capable of supporting water cycle ...
... suggests past climate capable of supporting water cycle ...
ppt
... (planetesimal→ planetesimals collide with each other protoplanet) building larger, a few 1000 km size objects (Moon-size), the protoplanets. Last stage The few dozens protoplanets on a ~108 (protoplanet→ million year timescale undergo giant planet) impacts resulting in a few terrestrial planets on w ...
... (planetesimal→ planetesimals collide with each other protoplanet) building larger, a few 1000 km size objects (Moon-size), the protoplanets. Last stage The few dozens protoplanets on a ~108 (protoplanet→ million year timescale undergo giant planet) impacts resulting in a few terrestrial planets on w ...
The science behind our Sun and its interaction with Earth The
... becoming capable of sustaining nuclear fusion and the Sun was born. At this point the pressure of hot gas pushing outward precisely balanced the inward pull of gravity as the energy generation came into balance with the energy lost from the surface in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The sourc ...
... becoming capable of sustaining nuclear fusion and the Sun was born. At this point the pressure of hot gas pushing outward precisely balanced the inward pull of gravity as the energy generation came into balance with the energy lost from the surface in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The sourc ...
Lesson Overviews and Content Standards
... Key concepts include: • Stars are different ages. • Stars are born in giant clouds of gas and dust. • Many more low mass (cool) stars are born than high mass (hot) stars. Lifetimes of Stars: In this activity, students return to the concept of a scale model to make a scale model of time rather than d ...
... Key concepts include: • Stars are different ages. • Stars are born in giant clouds of gas and dust. • Many more low mass (cool) stars are born than high mass (hot) stars. Lifetimes of Stars: In this activity, students return to the concept of a scale model to make a scale model of time rather than d ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... Accretion disks are often found in close, interacting pairs of stars, such as the cataclysmic variables (CVs). One star, originally more massive, evolves to a compact companion: a white dwarf or perhaps a neutron star (pulsar) or a black hole. The other, originally less massive, star bloats toward ...
... Accretion disks are often found in close, interacting pairs of stars, such as the cataclysmic variables (CVs). One star, originally more massive, evolves to a compact companion: a white dwarf or perhaps a neutron star (pulsar) or a black hole. The other, originally less massive, star bloats toward ...
Goal: To understand how the sun works
... • Average density is water. • This is a stable region, kind of like the Stratosphere on the earth. • Starts 200k km below the photosphere, and ends 200k km above the center of the sun. That is 50% of the radius of the sun! • Energy is transferred by radiation. • Temperature ranges from 2 to 7 millio ...
... • Average density is water. • This is a stable region, kind of like the Stratosphere on the earth. • Starts 200k km below the photosphere, and ends 200k km above the center of the sun. That is 50% of the radius of the sun! • Energy is transferred by radiation. • Temperature ranges from 2 to 7 millio ...
02_LectureOutline
... Astronomical unit: mean distance from Earth to Sun First measured during transits of Mercury and Venus, using triangulation ...
... Astronomical unit: mean distance from Earth to Sun First measured during transits of Mercury and Venus, using triangulation ...
Chapter 2 The Copernican Revolution
... Astronomical unit: mean distance from Earth to Sun First measured during transits of Mercury and Venus, using triangulation ...
... Astronomical unit: mean distance from Earth to Sun First measured during transits of Mercury and Venus, using triangulation ...
chapter 04
... • Solar system consists of Sun and everything orbiting it. • Asteroids are rocky, and most orbit between orbits of Mars and Jupiter. • Comets are icy, and are believed to have formed early in the solar system’s life. • Major planets orbit Sun in same sense, and all but Venus rotate in that sense as ...
... • Solar system consists of Sun and everything orbiting it. • Asteroids are rocky, and most orbit between orbits of Mars and Jupiter. • Comets are icy, and are believed to have formed early in the solar system’s life. • Major planets orbit Sun in same sense, and all but Venus rotate in that sense as ...
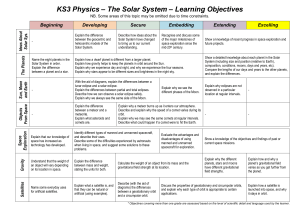
KS3 Physics – The Solar System
... Describe and explain why the speed of a comet varies during its orbit. Explain why we may see the same comets at regular intervals. Describe what could happen if a comet were to hit the Earth. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using manned and unmanned spacecraft for exploration. ...
... Describe and explain why the speed of a comet varies during its orbit. Explain why we may see the same comets at regular intervals. Describe what could happen if a comet were to hit the Earth. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using manned and unmanned spacecraft for exploration. ...
So What All Is Out There, Anyway?
... You continue to grow and you start to notice other galaxies nearby. Many of these galaxies have hundreds of billions of stars just like our Milky Way, and others have even more. It is likely that many of these stars have orbiting planets and moons. One or 2 galaxies seem close enough to touch, but m ...
... You continue to grow and you start to notice other galaxies nearby. Many of these galaxies have hundreds of billions of stars just like our Milky Way, and others have even more. It is likely that many of these stars have orbiting planets and moons. One or 2 galaxies seem close enough to touch, but m ...
STAR UNIT FLASH BACKS
... process on our planet earth; the climate would still change even if we did not pollute. 2. MOST scientists agree that the climate change that is occurring NOW is: A.) caused by the Sun’s activity ...
... process on our planet earth; the climate would still change even if we did not pollute. 2. MOST scientists agree that the climate change that is occurring NOW is: A.) caused by the Sun’s activity ...
AE Module 5 Presentation
... showed Uranus’ orbit was being influenced by another planet. Neptune and Uranus are both very similar to each other. Neptune however, orbits 3 billion miles from the Sun – a little over twice as far as Uranus. ...
... showed Uranus’ orbit was being influenced by another planet. Neptune and Uranus are both very similar to each other. Neptune however, orbits 3 billion miles from the Sun – a little over twice as far as Uranus. ...
Scale in the Solar System
... Four different sized poster board circles with diameters of 22in, 36in, 55in, and 70in 1. Begin the discussion with why the sun is important to us on earth: light, energy for green plants, part of the food chain, helps drive the water cycle, and heat. 2. Begin with a large sheet of newspaper for eac ...
... Four different sized poster board circles with diameters of 22in, 36in, 55in, and 70in 1. Begin the discussion with why the sun is important to us on earth: light, energy for green plants, part of the food chain, helps drive the water cycle, and heat. 2. Begin with a large sheet of newspaper for eac ...
i. relative age of rock strata or events
... CHAPTER 3 - DYNAMIC ( “CHANGING”) CRUST I. EARTHQUAKES -FAULT: . TERMINOLOGY 1) FOCUS2) EPICENTER -MEASURING THE STRENGTH OF EQ’S -INTENSITY- *MERCALLI SCALES (RATED I-XII) -MAGNITUDE: -SEISMOGRAPH -RICHTER SCALE: 1-9 TYPES OF WAVES - PRIMARY, OR P-WAVES -SECONDARY, OR S-WAVES -SURFACE WAVES - LOCAT ...
... CHAPTER 3 - DYNAMIC ( “CHANGING”) CRUST I. EARTHQUAKES -FAULT: . TERMINOLOGY 1) FOCUS2) EPICENTER -MEASURING THE STRENGTH OF EQ’S -INTENSITY- *MERCALLI SCALES (RATED I-XII) -MAGNITUDE: -SEISMOGRAPH -RICHTER SCALE: 1-9 TYPES OF WAVES - PRIMARY, OR P-WAVES -SECONDARY, OR S-WAVES -SURFACE WAVES - LOCAT ...
Lecture 2 Abundances
... believed to have formed very early in the presolar nebula accreted together and remained largely unchanged since then Carbonaceous Chondrites have lots of organic compounds that indicate very little heating (some were never heated above 50 degrees) ...
... believed to have formed very early in the presolar nebula accreted together and remained largely unchanged since then Carbonaceous Chondrites have lots of organic compounds that indicate very little heating (some were never heated above 50 degrees) ...
Solar System

The Solar System comprises the Sun and the planetary system that orbits it, either directly or indirectly. Of those objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest eight are the planets, with the remainder being significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies such as comets and asteroids. Of those that orbit the Sun indirectly, two are larger than the smallest planet.The Solar System formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in Jupiter. The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, are terrestrial planets, being primarily composed of rock and metal. The four outer planets are giant planets, being substantially more massive than the terrestrials. The two largest, Jupiter and Saturn, are gas giants, being composed mainly of hydrogen and helium; the two outermost planets, Uranus and Neptune, are ice giants, being composed largely of substances with relatively high melting points compared with hydrogen and helium, called ices, such as water, ammonia and methane. All planets have almost circular orbits that lie within a nearly flat disc called the ecliptic.The Solar System also contains smaller objects. The asteroid belt, which lies between Mars and Jupiter, mostly contains objects composed, like the terrestrial planets, of rock and metal. Beyond Neptune's orbit lie the Kuiper belt and scattered disc, populations of trans-Neptunian objects composed mostly of ices, and beyond them a newly discovered population of sednoids. Within these populations are several dozen to possibly tens of thousands of objects large enough to have been rounded by their own gravity. Such objects are categorized as dwarf planets. Identified dwarf planets include the asteroid Ceres and the trans-Neptunian objects Pluto and Eris. In addition to these two regions, various other small-body populations, including comets, centaurs and interplanetary dust, freely travel between regions. Six of the planets, at least three of the dwarf planets, and many of the smaller bodies are orbited by natural satellites, usually termed ""moons"" after the Moon. Each of the outer planets is encircled by planetary rings of dust and other small objects.The solar wind, a stream of charged particles flowing outwards from the Sun, creates a bubble-like region in the interstellar medium known as the heliosphere. The heliopause is the point at which pressure from the solar wind is equal to the opposing pressure of interstellar wind; it extends out to the edge of the scattered disc. The Oort cloud, which is believed to be the source for long-period comets, may also exist at a distance roughly a thousand times further than the heliosphere. The Solar System is located in the Orion Arm, 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way.