Slide 1
... Nervous System • There are two divisions of the peripheral nervous system: – the somatic, or voluntary portion – the autonomic, or involuntary portion Somatic Nervous System: The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles ...
... Nervous System • There are two divisions of the peripheral nervous system: – the somatic, or voluntary portion – the autonomic, or involuntary portion Somatic Nervous System: The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles ...
optical imaging and control of genetically designated neurons in
... synaptic potentials or currents, for example, or the active conductances and passive cable properties that modulate them. Used as an actuator, the electrode can control membrane potential near the site of impalement but not necessarily in more remote locations, particularly if the cellular geometry ...
... synaptic potentials or currents, for example, or the active conductances and passive cable properties that modulate them. Used as an actuator, the electrode can control membrane potential near the site of impalement but not necessarily in more remote locations, particularly if the cellular geometry ...
Electrical Synapses between Dopaminergic Neurons of the
... not significantly different from those measured in P7–P10 rats. Attempts were made to pharmacologically block gap junctional communication between DA neurons. Transjunctional currents were totally abolished in the presence of 2 mM octanol (n ⫽ 4; data not shown). However, unsaturated alcohols (hepta ...
... not significantly different from those measured in P7–P10 rats. Attempts were made to pharmacologically block gap junctional communication between DA neurons. Transjunctional currents were totally abolished in the presence of 2 mM octanol (n ⫽ 4; data not shown). However, unsaturated alcohols (hepta ...
Local functions for FMRP in axon growth cone motility and activity
... with phalloidin, synapsin and FMRP (Fig. 1). In the second scheme, neurons were triple stained with phalloidin, MAP2 and synapsin (Fig. 2). Fluorescence images were acquired through a Z-series, deconvolved and 3D-reconstructed. Visual analysis of 3D reconstructions frequently depicted an excess of l ...
... with phalloidin, synapsin and FMRP (Fig. 1). In the second scheme, neurons were triple stained with phalloidin, MAP2 and synapsin (Fig. 2). Fluorescence images were acquired through a Z-series, deconvolved and 3D-reconstructed. Visual analysis of 3D reconstructions frequently depicted an excess of l ...
Simulation of signal flow in 3D reconstructions of an anatomically
... neuronal cell types. The single neuron represents the elemental functional unit of these networks. Depending on their dendrite morphology, as well as their synaptic innervations and conductance distributions, neurons perform (non-) linear computations that generate a variety of electrical responses ...
... neuronal cell types. The single neuron represents the elemental functional unit of these networks. Depending on their dendrite morphology, as well as their synaptic innervations and conductance distributions, neurons perform (non-) linear computations that generate a variety of electrical responses ...
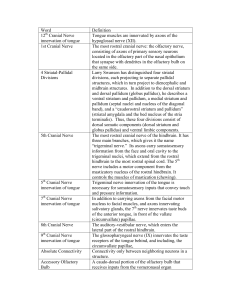
Word Definition 12 Cranial Nerve innervation of
... The very large layer 5 pyramidal cells of the motor cortex (Brodmann’s area 4). The Betz cell axons project to the spinal cord. (Vladimir Betz described them in a paper published in 1874.) Transection, by a surgical knife cut, of the pyramidal tract on both sides of the hindbrain. Neurons that can b ...
... The very large layer 5 pyramidal cells of the motor cortex (Brodmann’s area 4). The Betz cell axons project to the spinal cord. (Vladimir Betz described them in a paper published in 1874.) Transection, by a surgical knife cut, of the pyramidal tract on both sides of the hindbrain. Neurons that can b ...
Course of spinocerebellar axons in the ventral and lateral funiculi of
... tracts following injections into areas of termination. In a previous study in the cat we localized spinocerebellar fibers with projections to the anterior lobe of the cerebellum, the main area of termination of the spinocerebellar tracts (Xu and Grant 1994). This was also done later in the North Ame ...
... tracts following injections into areas of termination. In a previous study in the cat we localized spinocerebellar fibers with projections to the anterior lobe of the cerebellum, the main area of termination of the spinocerebellar tracts (Xu and Grant 1994). This was also done later in the North Ame ...
FlyEM`s formal project plan
... and adult stages. Simply having this “wiring-diagram” is necessary but not sufficient to understand how the fly’s nervous system functions. We are, however, confident that the wiring diagram will be a foundational tool, necessary to develop that greater understanding, in much the same way that genom ...
... and adult stages. Simply having this “wiring-diagram” is necessary but not sufficient to understand how the fly’s nervous system functions. We are, however, confident that the wiring diagram will be a foundational tool, necessary to develop that greater understanding, in much the same way that genom ...
PRESENTATION NAME
... – Chemicals that carry messages across the synapse to a dendrite of a receiving neuron • Excitatory messages – Increase likelihood that neuron will fire • Inhibitory messages – Decrease likelihood that neuron will fire ...
... – Chemicals that carry messages across the synapse to a dendrite of a receiving neuron • Excitatory messages – Increase likelihood that neuron will fire • Inhibitory messages – Decrease likelihood that neuron will fire ...
Paying attention to correlated neural activity
... are made up of odorant mixtures that evoke complex patterns of neural activity, and it is rare for an odor to have the exact same components in the exact same proportions. Encoding these odorant mixtures therefore requires both the identification of individual odorants (pattern separation) and perce ...
... are made up of odorant mixtures that evoke complex patterns of neural activity, and it is rare for an odor to have the exact same components in the exact same proportions. Encoding these odorant mixtures therefore requires both the identification of individual odorants (pattern separation) and perce ...
Endocrine and nervous systems
... The tips of fingers are sensitive enough to discriminate raised points on a surface, as well as the locations of these points. Knowing this, in the 19th century Louis Braille invented the Braille system of reading for the blind. Each letter of a language alphabet is represented by up to six raised d ...
... The tips of fingers are sensitive enough to discriminate raised points on a surface, as well as the locations of these points. Knowing this, in the 19th century Louis Braille invented the Braille system of reading for the blind. Each letter of a language alphabet is represented by up to six raised d ...
Seminar High Performance Computers
... ion-streams are permitted to pass, where this mechanism is realised through specific ion-channels on the cell-membrane. At the end of the axons which lead to another neuron, the signal is conducted via chemical gradients which are achieved via vesicle based neurotransmitter release. Neurons fire in ...
... ion-streams are permitted to pass, where this mechanism is realised through specific ion-channels on the cell-membrane. At the end of the axons which lead to another neuron, the signal is conducted via chemical gradients which are achieved via vesicle based neurotransmitter release. Neurons fire in ...
neural mechanisms of animal behavior
... the evasive response in relation to the circadial changes in activity for which cockroaches are well known. This lability of the evasive response makes the situation behaviorally interesting, and one would like to know its neural basis. Individual segments of the neural pathway can be checked electr ...
... the evasive response in relation to the circadial changes in activity for which cockroaches are well known. This lability of the evasive response makes the situation behaviorally interesting, and one would like to know its neural basis. Individual segments of the neural pathway can be checked electr ...
Mammalian Models of CNS Regeneration - Wiley-VCH
... Anterograde tracing of axons provides the ‘‘gold standard’’ for assessing the extent of regeneration following injury because it allows the course of regenerating axons to be followed around or through a lesion site. Retrograde tracing has the disadvantage that cell bodies may become labeled by spre ...
... Anterograde tracing of axons provides the ‘‘gold standard’’ for assessing the extent of regeneration following injury because it allows the course of regenerating axons to be followed around or through a lesion site. Retrograde tracing has the disadvantage that cell bodies may become labeled by spre ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... nature of the action potential, it is time to describe the ways in which neurons can communicate with each other. These communications make it possible for circuits of neurons to gather sensory information, make plans, and initiate behaviors via ...
... nature of the action potential, it is time to describe the ways in which neurons can communicate with each other. These communications make it possible for circuits of neurons to gather sensory information, make plans, and initiate behaviors via ...
Supplementary Figure Legends - Word file
... Supplementary Figure 1: Example responses to pure tones and harmonic complex tones from a pitchselective neuron (a, d) (Unit M36n-514) and a non-pitch-selective neuron (b, e) (Unit M2p-140). a. Pure tone frequency response from a pitch-selective neuron. b. Pure tone frequency response from a non-pit ...
... Supplementary Figure 1: Example responses to pure tones and harmonic complex tones from a pitchselective neuron (a, d) (Unit M36n-514) and a non-pitch-selective neuron (b, e) (Unit M2p-140). a. Pure tone frequency response from a pitch-selective neuron. b. Pure tone frequency response from a non-pit ...
neonatal 6-hydroxydopamine treatment eliminates cholinergic
... to 15 axons are observed coursing through the secretory portion. In any single section, profiles of both axonal varicosities, which contain numerous clear synaptic vesicles and occasional large dense-core vesicles, and intervaricose regions, which are characterized by the presence of microtubules, c ...
... to 15 axons are observed coursing through the secretory portion. In any single section, profiles of both axonal varicosities, which contain numerous clear synaptic vesicles and occasional large dense-core vesicles, and intervaricose regions, which are characterized by the presence of microtubules, c ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... needed in stressful or frightening situations. During these fight-orflight events, the sympathetic division exhibits a mass activation response, whereby all components receiving sympathetic innervation get stimulated. (In contrast, the parasympathetic division is discrete and localized, meaning only ...
... needed in stressful or frightening situations. During these fight-orflight events, the sympathetic division exhibits a mass activation response, whereby all components receiving sympathetic innervation get stimulated. (In contrast, the parasympathetic division is discrete and localized, meaning only ...
neuro 13 descending tracts student
... Typical descending pathway consists of a series of two motor neurons: Upper motor neurons (UMNs) Lower motor neurons (LMNs) Does not take into consideration the association neurons between UMNs and ...
... Typical descending pathway consists of a series of two motor neurons: Upper motor neurons (UMNs) Lower motor neurons (LMNs) Does not take into consideration the association neurons between UMNs and ...
Neural Axis Representing Target Range in the Auditory
... the frequency-modulated-signal processing area of the auditory cortex of the mustache bat (Pteronotus parnellii rubiginosus), neurons respond poorly or not at all to synthesized orientation sounds or echoes alone but respond vigorously to echoes following the emitted sound with a specific delay from ...
... the frequency-modulated-signal processing area of the auditory cortex of the mustache bat (Pteronotus parnellii rubiginosus), neurons respond poorly or not at all to synthesized orientation sounds or echoes alone but respond vigorously to echoes following the emitted sound with a specific delay from ...
A comparative study of the mammalian amygdala
... recognised according to the differences in the dendritic arbour morphology. They can be found in various configurations in all portions of BLC and in any species. Many Type I cells have a single thick, long “apical” dendrite that arises from one pole of the cell body and several shorter, thinner “ba ...
... recognised according to the differences in the dendritic arbour morphology. They can be found in various configurations in all portions of BLC and in any species. Many Type I cells have a single thick, long “apical” dendrite that arises from one pole of the cell body and several shorter, thinner “ba ...
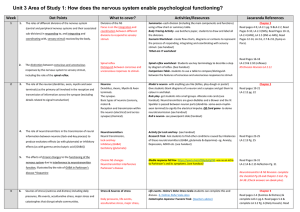
Unit 3 Area of Study 1: How does the nervous system
... Media response MJ Fox- https://youtu.be/vZQhp3yEgYM -use as an intro to Parkinson’s and its symptoms. (see handout) ...
... Media response MJ Fox- https://youtu.be/vZQhp3yEgYM -use as an intro to Parkinson’s and its symptoms. (see handout) ...
The NEURON Simulation Environment
... the implementation of the built−in integrate and fire models, but these topics are beyond the scope of this paper. NEURON’s strategy for dealing with synaptic connections emerged from techniques initially developed by Destexhe et al. (1994) and Lytton (1996). This strategy is based on a very simple ...
... the implementation of the built−in integrate and fire models, but these topics are beyond the scope of this paper. NEURON’s strategy for dealing with synaptic connections emerged from techniques initially developed by Destexhe et al. (1994) and Lytton (1996). This strategy is based on a very simple ...
Slide 1
... and proximal apical/basal dendrites (green) receive separate synaptic inputs in a variety of types of pyramidal cells. (B) Summation of inputs onto a single dendritic branch (but not between branches) leads to a dendritic spike that remains below threshold for an action potential at the soma. It has ...
... and proximal apical/basal dendrites (green) receive separate synaptic inputs in a variety of types of pyramidal cells. (B) Summation of inputs onto a single dendritic branch (but not between branches) leads to a dendritic spike that remains below threshold for an action potential at the soma. It has ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.