Nerve Tissue Notes
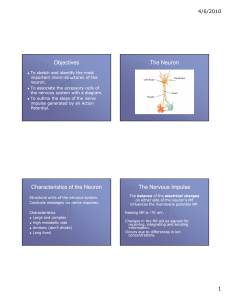
... Nerve Cell – The Neuron • Axon sends impulses – Myelin sheath, made of Schwann cells, wraps around axons and speeds up signals ...
... Nerve Cell – The Neuron • Axon sends impulses – Myelin sheath, made of Schwann cells, wraps around axons and speeds up signals ...
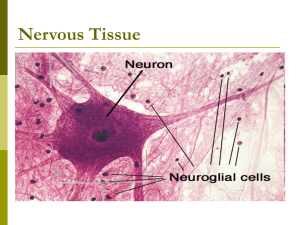
Nervous Tissue
... sensory (afferent) neurons carry info to CNS Interneurons in CNS interpret info and stimulate motor neurons motor (efferent) neurons carry info to effectors ...
... sensory (afferent) neurons carry info to CNS Interneurons in CNS interpret info and stimulate motor neurons motor (efferent) neurons carry info to effectors ...
The Brain and Behavior
... • Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have ...
... • Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have ...
Lecture 2 (Neurons)
... ER, mitochondria, golgi complex, etc). Is where most the synthesis of new cellular products occurs. ...
... ER, mitochondria, golgi complex, etc). Is where most the synthesis of new cellular products occurs. ...
Neuron and Neuroglial Review Worksheet
... provided in Column A. Place the correct term or letter response in the answer blanks. Column A 1. Releases neurotransmitters ____B_____ 2. Conducts electrical currents ___C_____ towards the cell body 3. Increases the speed of impulse ____D_____ transmission 4. Location of the nucleus _____E_______ 5 ...
... provided in Column A. Place the correct term or letter response in the answer blanks. Column A 1. Releases neurotransmitters ____B_____ 2. Conducts electrical currents ___C_____ towards the cell body 3. Increases the speed of impulse ____D_____ transmission 4. Location of the nucleus _____E_______ 5 ...
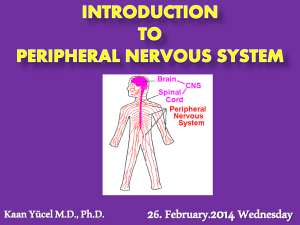
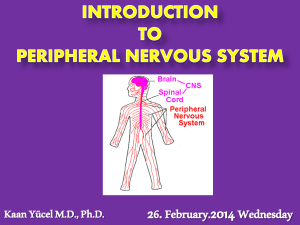
The Neural Control of Behavior
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
My Reaction Test Score = Neural Transmission
... The interior of an axon has a resting potential (electrical charge) that is negative. The exterior of the axon is positively charged. Ions flow both in and out of the axon when the surface membrane of the axon is disturbed by a Ions flow and change the charges to positive inside stimulus. This raise ...
... The interior of an axon has a resting potential (electrical charge) that is negative. The exterior of the axon is positively charged. Ions flow both in and out of the axon when the surface membrane of the axon is disturbed by a Ions flow and change the charges to positive inside stimulus. This raise ...
Frontiers in , Ph.D. Pharmacology Proudly Presents
... The electrical properties of neurons depend not only on the types of ion channels and receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localiz ...
... The electrical properties of neurons depend not only on the types of ion channels and receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localiz ...
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
... Oligodendrocytes – makes the myelin sheath that provides insulation to the axon ...
... Oligodendrocytes – makes the myelin sheath that provides insulation to the axon ...
Types of neurons - Brigham Young University
... -70 mV across 3nm is equivalent to 200,000V across 1cm ...
... -70 mV across 3nm is equivalent to 200,000V across 1cm ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... ▪ In Dendrites: passive propagation ● Lose power ▪ In Axons: Active Propagation ● Myelin sheath isolate the axon and preserve voltage ● Regenerate the voltage at the nodes of Ranvier Rate Law o Greater the stimulant the greater the number of action potentials o Spontaneous (weak) vs. Elicite ...
... ▪ In Dendrites: passive propagation ● Lose power ▪ In Axons: Active Propagation ● Myelin sheath isolate the axon and preserve voltage ● Regenerate the voltage at the nodes of Ranvier Rate Law o Greater the stimulant the greater the number of action potentials o Spontaneous (weak) vs. Elicite ...
Slide 1 - AccessPhysiotherapy
... dendrites and also on its cell body, the soma. The soma of this type of cell integrates the electrical information and also provides metabolic support for the cell as a whole. The place where the axon comes out of the soma is called the axon hillock, and this is where the information is encoded into ...
... dendrites and also on its cell body, the soma. The soma of this type of cell integrates the electrical information and also provides metabolic support for the cell as a whole. The place where the axon comes out of the soma is called the axon hillock, and this is where the information is encoded into ...
The Synaptic Cleft or Synapse
... A neuron’s axon ends in many small swellings called axon terminals. At the axon terminal the neuron may meet dendrites of another axon or an effector, like a muscle or gland. The space where neurons meet other neurons or effectors is called the synapse. There are presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic ...
... A neuron’s axon ends in many small swellings called axon terminals. At the axon terminal the neuron may meet dendrites of another axon or an effector, like a muscle or gland. The space where neurons meet other neurons or effectors is called the synapse. There are presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic ...
Neurons: What They`re Made Of and How They
... called the "node of Ranvier." An impulse is able to jump from node to node, making the signal travel down the myelinated axon much faster. The junction of one neuron's axon with another neuron's dendrite is called the "synapse," and is where the cells are able to communicate with each other. What ha ...
... called the "node of Ranvier." An impulse is able to jump from node to node, making the signal travel down the myelinated axon much faster. The junction of one neuron's axon with another neuron's dendrite is called the "synapse," and is where the cells are able to communicate with each other. What ha ...
File
... – 1. Sensory: carry impulses from sense organs to the brain – 2. Motor: carry impulses from the brain to ...
... – 1. Sensory: carry impulses from sense organs to the brain – 2. Motor: carry impulses from the brain to ...
Nervous System Cells
... • Myelin sheathing allows these neurons to conduct nerve impulses faster than in non-myelinated neurons. ...
... • Myelin sheathing allows these neurons to conduct nerve impulses faster than in non-myelinated neurons. ...
the nervous system
... • Long axons are covered in a myelin sheath • Nodes of Ranvier are intermittent gaps in the sheath ...
... • Long axons are covered in a myelin sheath • Nodes of Ranvier are intermittent gaps in the sheath ...
Lecture 2 - Nerve Impulse
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
Psychobiology Neurons= transmit information, human brain has 86
... Neurons= transmit information, human brain has 86 billion ...
... Neurons= transmit information, human brain has 86 billion ...
The Neuron MMHS Advanced Biomed Chitraroff
... • A type of fatty connective tissue that surround the axons of large neurons. • Also covers parts of the spinal cord, white matter of brain and most peripheral nerves. • Nodes of Ranvier= gaps in myelin sheath. • Acts as an insulator that speeds up nerve impulses. White Matter = Myelinated Grey Matt ...
... • A type of fatty connective tissue that surround the axons of large neurons. • Also covers parts of the spinal cord, white matter of brain and most peripheral nerves. • Nodes of Ranvier= gaps in myelin sheath. • Acts as an insulator that speeds up nerve impulses. White Matter = Myelinated Grey Matt ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.