Symbolic Music Representations
... The naming of intervals (and absolute pitches) is not unique meaning that the same exact note can have two different names as in C # and Db. Similarly the same interval can be a minor third or an augmented second. The spelling comes from the role an interval plays as part of a scale as well as the h ...
... The naming of intervals (and absolute pitches) is not unique meaning that the same exact note can have two different names as in C # and Db. Similarly the same interval can be a minor third or an augmented second. The spelling comes from the role an interval plays as part of a scale as well as the h ...
Composing In the Flesh: Perceptually
... dissonance. The degree of roughness of an interval or chord depends on the extent to which it has spectral components within the same critical band. The critical band is related to the smallest frequency difference that will allow two pure tones to be perceptually identified as two autonomous tones ...
... dissonance. The degree of roughness of an interval or chord depends on the extent to which it has spectral components within the same critical band. The critical band is related to the smallest frequency difference that will allow two pure tones to be perceptually identified as two autonomous tones ...
Slide 1 - moorsscience
... between what is music and noise. Music is sound that originates from a vibrating source with one or more frequencies (usually harmonious and pleasant). Noise on the other hand is sound that originates from a source with constantly changing frequencies and is usually not ‘pleasant’ to the ear. On an ...
... between what is music and noise. Music is sound that originates from a vibrating source with one or more frequencies (usually harmonious and pleasant). Noise on the other hand is sound that originates from a source with constantly changing frequencies and is usually not ‘pleasant’ to the ear. On an ...
Text S2.
... compared the spectra of negative/subdued and positive/excited speech to the tonality of the Western melodies composed in the major and minor modes. Similarities were found with respect to (1) the fundamental frequencies of speech and the implied fundamentals of major and minor intervals, and (2) the ...
... compared the spectra of negative/subdued and positive/excited speech to the tonality of the Western melodies composed in the major and minor modes. Similarities were found with respect to (1) the fundamental frequencies of speech and the implied fundamentals of major and minor intervals, and (2) the ...
Handout on Set Theory: Intervals and Atonality
... century analysis course such as 21M.310 is probably just the trick. We’re going to be moving a bit too fast in this class to get into things in detail). Interval number sets also allow us to see if two sets of pitches are related to each other by transposition. That is to say, is there an interval u ...
... century analysis course such as 21M.310 is probably just the trick. We’re going to be moving a bit too fast in this class to get into things in detail). Interval number sets also allow us to see if two sets of pitches are related to each other by transposition. That is to say, is there an interval u ...
On Ben Johnston`s Notation and the Performance
... to learn about musical intervals, the sound of two tones in relation to each other. Without any technical intervention other than a pitch-pipe, I learned to tune my open strings to the notes G - D - A - E by playing two notes at once, listening carefully to eliminate beating between overtone-unisons ...
... to learn about musical intervals, the sound of two tones in relation to each other. Without any technical intervention other than a pitch-pipe, I learned to tune my open strings to the notes G - D - A - E by playing two notes at once, listening carefully to eliminate beating between overtone-unisons ...
Revision Pack for: MUSIC AS
... Romantic a term denoting an era of Western classical music that began in the late 18th or early 19th century. Inversion rearrangement of the top-to-bottom elements in an interval, a chord, a melody, or a group of contrapuntal lines of music. Rondo form a piece of music where the musical material sta ...
... Romantic a term denoting an era of Western classical music that began in the late 18th or early 19th century. Inversion rearrangement of the top-to-bottom elements in an interval, a chord, a melody, or a group of contrapuntal lines of music. Rondo form a piece of music where the musical material sta ...
Lecture Set 07
... The octave and the fifth represent an interval, or a “difference” between two reasonable consonant tones. ...
... The octave and the fifth represent an interval, or a “difference” between two reasonable consonant tones. ...
What is music? most basically, music is “organized” sound. Any
... Style can be associated with cultures, with time periods, or with the work of a specific composer. Style comprises the distinctive use of musical elements. Some of these elements are explained below and you need to know them. • Melody / ies (this is the horizontal element in the fabric of music) are ...
... Style can be associated with cultures, with time periods, or with the work of a specific composer. Style comprises the distinctive use of musical elements. Some of these elements are explained below and you need to know them. • Melody / ies (this is the horizontal element in the fabric of music) are ...
Voice leading from IV-V
... is repeated in the V chord. These progressions are known as parallel fifths and parallel octaves, and should be avoided when writing homophonic and homorhythmic music. One correct way of voice leading from IV to V is to use the non-common tone technique, as shown in bar 2. Raise the bass (we're stil ...
... is repeated in the V chord. These progressions are known as parallel fifths and parallel octaves, and should be avoided when writing homophonic and homorhythmic music. One correct way of voice leading from IV to V is to use the non-common tone technique, as shown in bar 2. Raise the bass (we're stil ...
species counterpoint
... In 1725, Johann Fux published his epoch-making Gradus ad Parnassum, a counterpoint manual that quickly became the primary influence in polyphonic training for generations of composers to follow, including most of the major figures of the Classical period. Although his knowledge of the music appeared ...
... In 1725, Johann Fux published his epoch-making Gradus ad Parnassum, a counterpoint manual that quickly became the primary influence in polyphonic training for generations of composers to follow, including most of the major figures of the Classical period. Although his knowledge of the music appeared ...
Le contenance anglois
... o Top voice goes from b natural, down to the a and then up a 3 rd to the final c. Middle voice o Cadence notated as f natural leading to final g o However, as a performer, you would know to add the sharp leading tone to the final g and example of musica ficta Listening: Music for this piece o ...
... o Top voice goes from b natural, down to the a and then up a 3 rd to the final c. Middle voice o Cadence notated as f natural leading to final g o However, as a performer, you would know to add the sharp leading tone to the final g and example of musica ficta Listening: Music for this piece o ...
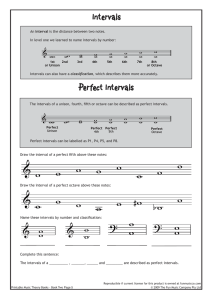
Intervals Perfect Intervals
... Intervals An Interval is the distance between two notes. In level one we learned to name intervals by number: ...
... Intervals An Interval is the distance between two notes. In level one we learned to name intervals by number: ...
Twentieth Century New scales New chords (almost any combination
... Musical style was an outgrowth of Romanticism but more subtle and understated ...
... Musical style was an outgrowth of Romanticism but more subtle and understated ...
lesson 2: musical alphabet, scale degrees and solfeggio
... Since there are seven letters in the Musical Alphabet, there are also 7 scale degrees in a major scale. ...
... Since there are seven letters in the Musical Alphabet, there are also 7 scale degrees in a major scale. ...
MUSC 101 – Introduction to Music Study Guide
... Minor Scale - A seven tone pattern first distinguished from the Major scale by its third tone which is a half-step lower in pitch than in the major scale. Songs in a Minor keys often sound serious or melancholy, such as: Greensleeves, Eleanor Rigby, Scarborough Fair, and many traditional blues and ' ...
... Minor Scale - A seven tone pattern first distinguished from the Major scale by its third tone which is a half-step lower in pitch than in the major scale. Songs in a Minor keys often sound serious or melancholy, such as: Greensleeves, Eleanor Rigby, Scarborough Fair, and many traditional blues and ' ...
Elements of Music: Sound, Melody, Rhythm, and Harmony
... 4. What is an arpeggio? How does it relate to a chord? 5. Can you draw a picture of a melody? What are some interesting melodies that you know? Suggest: Draw a picture of a melody you know. What makes it interesting to you? What materials would you use in order to recreate that melody? Are the pitch ...
... 4. What is an arpeggio? How does it relate to a chord? 5. Can you draw a picture of a melody? What are some interesting melodies that you know? Suggest: Draw a picture of a melody you know. What makes it interesting to you? What materials would you use in order to recreate that melody? Are the pitch ...
Music Theory 171 Questions on Chapters 3A, 3B and 3C 3A
... 2. What does this say about the relationship between the fifth, the fourth and the octave? 3. What is created between the fifth and the fourth, and what is its ratio? 4. The notes of the major, minor, Phrygian and Middle Eastern tetrachords and listed on this page. Transpose them to the key of D and ...
... 2. What does this say about the relationship between the fifth, the fourth and the octave? 3. What is created between the fifth and the fourth, and what is its ratio? 4. The notes of the major, minor, Phrygian and Middle Eastern tetrachords and listed on this page. Transpose them to the key of D and ...
Document
... To fill out the Pythagorean scale, we need F. If we take 2C to be the 5th above F, then 2C= 3/2F, or F = 4/3 C ...
... To fill out the Pythagorean scale, we need F. If we take 2C to be the 5th above F, then 2C= 3/2F, or F = 4/3 C ...
Study Sheet for Keyboards Resource on the wiki
... Treble and Bass Clefs - Know how to read notes in both clefs. Know where to locate any specific note on the keyboard Rhythm-understand how time signatures function-how many beats there are in a measure (can be any #) and what types of notes get one beat (can only be half notes (2), quarter notes (4) ...
... Treble and Bass Clefs - Know how to read notes in both clefs. Know where to locate any specific note on the keyboard Rhythm-understand how time signatures function-how many beats there are in a measure (can be any #) and what types of notes get one beat (can only be half notes (2), quarter notes (4) ...
Music Vocabulary Terms
... Key: The sequence or scale that the musician performs during the piece. Key Signature: Located at the beginning of the piece or after a double bar line, the key signature will tell the musician what notes are sharp or flat and which key they are playing in Equal Temperament Tuning: Each note is tune ...
... Key: The sequence or scale that the musician performs during the piece. Key Signature: Located at the beginning of the piece or after a double bar line, the key signature will tell the musician what notes are sharp or flat and which key they are playing in Equal Temperament Tuning: Each note is tune ...
notes from guest lecturer from the
... can be read by musicians in any country. the notation stays the same. conductors conduct from a score. the history of music reflects its time, environment, feeling, even racial/ cultural make up. uses for music: all occasions, weddings, funerals,etc. live music - has moments that can never be recapt ...
... can be read by musicians in any country. the notation stays the same. conductors conduct from a score. the history of music reflects its time, environment, feeling, even racial/ cultural make up. uses for music: all occasions, weddings, funerals,etc. live music - has moments that can never be recapt ...
Harmony, Key, and Texture from 11/13/14 and
... • Polyphonic - two or more melodies at the same time.May be with or without accompaniment. This is "the crowning achievement of Western Music". ...
... • Polyphonic - two or more melodies at the same time.May be with or without accompaniment. This is "the crowning achievement of Western Music". ...
Consonance and dissonance

In music, consonance and dissonance form a structural dichotomy in which the terms define each other by mutual exclusion: a consonance is what is not dissonant, and reciprocally. However, a finer consideration shows that the distinction forms a gradation, from the most consonant to the most dissonant. Consonance and dissonance define a level of sweetness / harshness, pleasantness / unpleasantness, acceptability / unacceptability, of the sounds or intervals under consideration. As Hindemith stressed, ""The two concepts have never been completely explained, and for a thousand years the definitions have varied"" (Hindemith 1942, p. 85).The opposition can be made in different contexts:In acoustics or psychophysiology, the distinction may be objective. In modern times, it usually is based on the perception of harmonic partials of the sounds considered, to such an extent that the distinction really holds only in the case of harmonic sounds (i.e. sounds with harmonic partials).In music, even if the opposition often is founded of the preceding, objective distinction, it more often is subjective, conventional, cultural, and style-dependent. Dissonance can then be defined as a combination of sounds that does not belong to the style under consideration; in recent music, what is considered stylistically dissonant may even correspond to what is said consonant in the context of acoustics (e.g. a major triad in atonal music).In both cases, the distinction mainly concerns simultaneous sounds; if successive sounds are considered, their consonance or dissonance depends on the memorial retention of the first sound while the second is heard. For this reason, consonance and dissonance have been considered particularly in the case of polyphonic Occidental music, and the present article is concerned mainly with this case.Most historical definitions of consonance and dissonance since about the 16th century have stressed their pleasant/unpleasant, or agreeable/disagreeable character. This may be justifiable in a psychophysiological context, but much less in a musical context properly speaking: dissonances often play a decisive role in making music pleasant, even in a generally consonant context – which is one of the reasons why the musical definition of consonance/dissonance cannot match the psychophysiologic definition. In addition, the oppositions pleasant/unpleasant or agreeable/disagreeable evidence a confusion between the concepts of 'dissonance' and of 'noise'. (See also Noise in music, Noise music and Noise (acoustic).)While consonance and dissonance exist only between sounds and therefore necessarily describe intervals (or chords), Occidental music theory often considers that, in a dissonant chord, one of the tones alone is in itself the dissonance: it is this tone in particular that needs ""resolution"" through a specific voice leading.