Elements of Music: Sound, Melody, Rhythm, and
... music. Although these varied types of music sound quite different, they all involve the same components: sound, rhythm, melody, and harmony. In order to understand how these elements contribute to the music, it is necessary to become familiar with these elements and how they combine. It is also help ...
... music. Although these varied types of music sound quite different, they all involve the same components: sound, rhythm, melody, and harmony. In order to understand how these elements contribute to the music, it is necessary to become familiar with these elements and how they combine. It is also help ...
document - Far Western District
... 3. Use of “tension and release”: This characteristic is what people often associate with barbershop music without realizing the theory behind it, and that’s just fine. Since barbershop has its roots as “ear music,” harmony singers would often use tense chords (minor, diminished, augmented, suspended ...
... 3. Use of “tension and release”: This characteristic is what people often associate with barbershop music without realizing the theory behind it, and that’s just fine. Since barbershop has its roots as “ear music,” harmony singers would often use tense chords (minor, diminished, augmented, suspended ...
Grade 4 Music I Can... Rhythm I can show that beats may be
... I can tell that an interval is the space between two sounds. • I know that an interval may be changed by an accidental. • I can tell that intervals can give shape or contour to a melody I can tell the melody is based on the C major scale. Harmony I can tell the IV and V chords are used to accompany ...
... I can tell that an interval is the space between two sounds. • I know that an interval may be changed by an accidental. • I can tell that intervals can give shape or contour to a melody I can tell the melody is based on the C major scale. Harmony I can tell the IV and V chords are used to accompany ...
An Exhibition as a Tool to Approach Didactical and
... of a musical note and Fourier Series of the function which represents such a note. Making use of an oscilloscope, this room presents analogically the experiment of Galileo (Cohen, 1984), which associates the musical sound to a periodical function and extends it promoting a multi-representation of th ...
... of a musical note and Fourier Series of the function which represents such a note. Making use of an oscilloscope, this room presents analogically the experiment of Galileo (Cohen, 1984), which associates the musical sound to a periodical function and extends it promoting a multi-representation of th ...
MUL 2010 “Enjoyment of Music
... What can you organize? The 4 Parameters of Sound • Pitch = the frequency of vibration (heard as “high” vs. “low”) • Duration = the length of time a sound lasts (heard as aspects of rhythm) • Timbre = tone color (the source of the sound, i.e., instrument, voice, other) • Dynamics = Loudness/Softness ...
... What can you organize? The 4 Parameters of Sound • Pitch = the frequency of vibration (heard as “high” vs. “low”) • Duration = the length of time a sound lasts (heard as aspects of rhythm) • Timbre = tone color (the source of the sound, i.e., instrument, voice, other) • Dynamics = Loudness/Softness ...
Bringing some science to music
... Properties of the octave Two tones, one octave apart, sound well when played together. ...
... Properties of the octave Two tones, one octave apart, sound well when played together. ...
Other diatonic 7th chords
... The IV7 can be a major seventh chord (in major) and minor seventh chord (in minor) and rarely a majorminor seventh chord in the melodic minor mode. Like its triad version, the IV7 usually goes to V or viio6, and may first pass through ii(7) or I/i6/4 VI7 The VI7 can be a minor seventh chord (in majo ...
... The IV7 can be a major seventh chord (in major) and minor seventh chord (in minor) and rarely a majorminor seventh chord in the melodic minor mode. Like its triad version, the IV7 usually goes to V or viio6, and may first pass through ii(7) or I/i6/4 VI7 The VI7 can be a minor seventh chord (in majo ...
Traditional composition techniques
... interval contraction smaller intervals, same contour; e.g., Liszt's Les Preludes interval expansion larger intervals, same contour; e.g., Liszt's Les Preludes inversion mirrored contour; e.g., subject and inversion in Bartok's Music for Strings, Percussion and Celeste, first movement isomelos same n ...
... interval contraction smaller intervals, same contour; e.g., Liszt's Les Preludes interval expansion larger intervals, same contour; e.g., Liszt's Les Preludes inversion mirrored contour; e.g., subject and inversion in Bartok's Music for Strings, Percussion and Celeste, first movement isomelos same n ...
Document
... which indicate how many beats there are in a bar. Dorian Mode – a scale running from D to D on the keyboard using only white notes Jig – an Irish Dance ...
... which indicate how many beats there are in a bar. Dorian Mode – a scale running from D to D on the keyboard using only white notes Jig – an Irish Dance ...
Music History Lecture Notes
... • Sound happens all around us – what separates music from noise? • Noise just happens, music is organized • The difference between music and a random set of sounds has to do with how the fundamental aspects combine and relate. – Just like dance isn’t a raging sea of unrelated body movements ...
... • Sound happens all around us – what separates music from noise? • Noise just happens, music is organized • The difference between music and a random set of sounds has to do with how the fundamental aspects combine and relate. – Just like dance isn’t a raging sea of unrelated body movements ...
Musician’s Toolbox Christina Lipson ‘14 Advisor: Professor John Ridgway
... (Train, Create, Analyze, Reference) act as categories and each contain different musical functions. The application was built using Ruby on Rails and other assisting web development languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript). I utilized open source code for the sound and visual components of my application i ...
... (Train, Create, Analyze, Reference) act as categories and each contain different musical functions. The application was built using Ruby on Rails and other assisting web development languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript). I utilized open source code for the sound and visual components of my application i ...
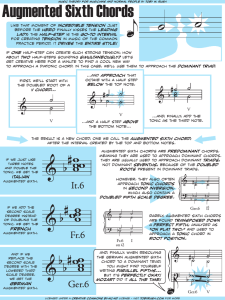
Augmented Sixth Chords
... Augmented Sixth Chords like that moment of incredible tension just before the hero finally kisses the leading lady, the half-step is the go-to interval for creating tension in music of the common practice period. it drives the entire style! ...
... Augmented Sixth Chords like that moment of incredible tension just before the hero finally kisses the leading lady, the half-step is the go-to interval for creating tension in music of the common practice period. it drives the entire style! ...
Elements of Music
... Intervals - The distance between the pitches of the melody may be steps from one note to an adjacent note, or skips where pitches leap from one to another skipping a tone or tones. Conjunct – notes in melody change by small intervals. Notes move in stepwise motion or are very close to each other o ...
... Intervals - The distance between the pitches of the melody may be steps from one note to an adjacent note, or skips where pitches leap from one to another skipping a tone or tones. Conjunct – notes in melody change by small intervals. Notes move in stepwise motion or are very close to each other o ...
MUSC 1000 Intro to Music
... Sometimes longer pieces of music change from one tonal center to another during the flow of the music – when this happens, we call it MODULATION We think of the horizontal alignment of the notes as the MELODY and the vertical alignment of the notes as the HARMONY – the way that these two elements a ...
... Sometimes longer pieces of music change from one tonal center to another during the flow of the music – when this happens, we call it MODULATION We think of the horizontal alignment of the notes as the MELODY and the vertical alignment of the notes as the HARMONY – the way that these two elements a ...
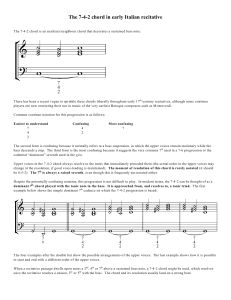
The 7-4-2 chord in early Italian recitative
... The second form is confusing because it normally refers to a bass suspension, in which the upper voices remain stationary while the bass descends a step. The third form is the most confusing because it suggests the very common 7 th used in a 7-6 progression or the cadential “dominant” seventh used i ...
... The second form is confusing because it normally refers to a bass suspension, in which the upper voices remain stationary while the bass descends a step. The third form is the most confusing because it suggests the very common 7 th used in a 7-6 progression or the cadential “dominant” seventh used i ...
Inner Octaves and Eastern Music
... material vibrating at a definite frequency inducing waves of acoustical energy in a medium of transmission. The essence of sound, as in all other natural phenomena, is vibration. A vibration is a continuously and smoothly alternating pulse of energy. Vibrations are scaled by their frequencies (rates ...
... material vibrating at a definite frequency inducing waves of acoustical energy in a medium of transmission. The essence of sound, as in all other natural phenomena, is vibration. A vibration is a continuously and smoothly alternating pulse of energy. Vibrations are scaled by their frequencies (rates ...
The Musical - Year 9 – Stage 5 Good Samaritan
... Finding out the distance between notes can be challenging. To help, count the number of half steps between the notes of the interval you are trying to find. From C to D is 1 half-step – that’s a minor second interval. From C to D there are 2 steps C#/Db and D – That’s an interval of a major second. ...
... Finding out the distance between notes can be challenging. To help, count the number of half steps between the notes of the interval you are trying to find. From C to D is 1 half-step – that’s a minor second interval. From C to D there are 2 steps C#/Db and D – That’s an interval of a major second. ...
Time Signatures and Intervals
... on the left - does it affect the notes in the interval. Look left. ...
... on the left - does it affect the notes in the interval. Look left. ...
View printable PDF of 6.7 Contemporary Chords and Harmonic
... Tone cluster with 2 notes raised an octave ...
... Tone cluster with 2 notes raised an octave ...
Higher Concepts - Garnock Academy
... 17th-century opera. In a Concerto grosso, the ritornello is the main theme played by the Ripieno group (the orchestra) and sometimes by Concertino (the soloists). The ritornello may return frequently throughout the movement, similar to a Rondo. Sometimes known as first movement form. This term is us ...
... 17th-century opera. In a Concerto grosso, the ritornello is the main theme played by the Ripieno group (the orchestra) and sometimes by Concertino (the soloists). The ritornello may return frequently throughout the movement, similar to a Rondo. Sometimes known as first movement form. This term is us ...
Higher Concepts - Dunblane High School Music Website
... opera. In a Concerto grosso, the ritornello is the main theme played by the Ripieno group (the orchestra) and sometimes by Concertino (the soloists). The ritornello may return frequently throughout the movement, similar to a Rondo. Sometimes known as first movement form. This term is used to describ ...
... opera. In a Concerto grosso, the ritornello is the main theme played by the Ripieno group (the orchestra) and sometimes by Concertino (the soloists). The ritornello may return frequently throughout the movement, similar to a Rondo. Sometimes known as first movement form. This term is used to describ ...
Higher Concepts Higher Music Listening 2014 Onwards Music
... 17th-century opera. In a Concerto grosso, the ritornello is the main theme played by the Ripieno group (the orchestra) and sometimes by Concertino (the soloists). The ritornello may return frequently throughout the movement, similar to a Rondo. Sometimes known as first movement form. This term is us ...
... 17th-century opera. In a Concerto grosso, the ritornello is the main theme played by the Ripieno group (the orchestra) and sometimes by Concertino (the soloists). The ritornello may return frequently throughout the movement, similar to a Rondo. Sometimes known as first movement form. This term is us ...
1 Elements of Music Olli F16
... The two most fundamental dimensions of music are rhythm (time) and pitch. In fact, every staff of written music is essentially an X-Y coordinate system where the horizontal axis is rhythm and the vertical axis is pitch. Notes occurring at the same time – chords - are stacked vertically on top of eac ...
... The two most fundamental dimensions of music are rhythm (time) and pitch. In fact, every staff of written music is essentially an X-Y coordinate system where the horizontal axis is rhythm and the vertical axis is pitch. Notes occurring at the same time – chords - are stacked vertically on top of eac ...
Consonance and dissonance

In music, consonance and dissonance form a structural dichotomy in which the terms define each other by mutual exclusion: a consonance is what is not dissonant, and reciprocally. However, a finer consideration shows that the distinction forms a gradation, from the most consonant to the most dissonant. Consonance and dissonance define a level of sweetness / harshness, pleasantness / unpleasantness, acceptability / unacceptability, of the sounds or intervals under consideration. As Hindemith stressed, ""The two concepts have never been completely explained, and for a thousand years the definitions have varied"" (Hindemith 1942, p. 85).The opposition can be made in different contexts:In acoustics or psychophysiology, the distinction may be objective. In modern times, it usually is based on the perception of harmonic partials of the sounds considered, to such an extent that the distinction really holds only in the case of harmonic sounds (i.e. sounds with harmonic partials).In music, even if the opposition often is founded of the preceding, objective distinction, it more often is subjective, conventional, cultural, and style-dependent. Dissonance can then be defined as a combination of sounds that does not belong to the style under consideration; in recent music, what is considered stylistically dissonant may even correspond to what is said consonant in the context of acoustics (e.g. a major triad in atonal music).In both cases, the distinction mainly concerns simultaneous sounds; if successive sounds are considered, their consonance or dissonance depends on the memorial retention of the first sound while the second is heard. For this reason, consonance and dissonance have been considered particularly in the case of polyphonic Occidental music, and the present article is concerned mainly with this case.Most historical definitions of consonance and dissonance since about the 16th century have stressed their pleasant/unpleasant, or agreeable/disagreeable character. This may be justifiable in a psychophysiological context, but much less in a musical context properly speaking: dissonances often play a decisive role in making music pleasant, even in a generally consonant context – which is one of the reasons why the musical definition of consonance/dissonance cannot match the psychophysiologic definition. In addition, the oppositions pleasant/unpleasant or agreeable/disagreeable evidence a confusion between the concepts of 'dissonance' and of 'noise'. (See also Noise in music, Noise music and Noise (acoustic).)While consonance and dissonance exist only between sounds and therefore necessarily describe intervals (or chords), Occidental music theory often considers that, in a dissonant chord, one of the tones alone is in itself the dissonance: it is this tone in particular that needs ""resolution"" through a specific voice leading.