Right Ventricular Compression as a Sign of Cardiac
... Transducer location was usually in the fourth intercostal space near the left sternal border. The transducer was pointed superiorly and medially and swept inferiorly and laterally to provide images of all intracardiac chambers and valves. End-diastolic and end-systolic dimensions of the ventricles w ...
... Transducer location was usually in the fourth intercostal space near the left sternal border. The transducer was pointed superiorly and medially and swept inferiorly and laterally to provide images of all intracardiac chambers and valves. End-diastolic and end-systolic dimensions of the ventricles w ...
Wall Thickness and Diastolic Properties of the Left Ventricle
... independent of the presence or absence of increased left ventricular mass. Certain limitations of this study must be emphasized. First, wall thickness was not determined directly (e.g., at surgery or autopsy) in our patients, but rather by an indirect ultrasonic technique. We have relied upon the wo ...
... independent of the presence or absence of increased left ventricular mass. Certain limitations of this study must be emphasized. First, wall thickness was not determined directly (e.g., at surgery or autopsy) in our patients, but rather by an indirect ultrasonic technique. We have relied upon the wo ...
chapter 13 defibrillators and cardioverters (draft)
... devices, mechanical signals related to ventricular tachycardia and myocardial fibrillation were used to determine the need for a fibrillation pulse. Energy storage adequate to provide pulses of from 5 to 30 J is necessary in the implantable defibrillator. This is considerably less than the amount of ...
... devices, mechanical signals related to ventricular tachycardia and myocardial fibrillation were used to determine the need for a fibrillation pulse. Energy storage adequate to provide pulses of from 5 to 30 J is necessary in the implantable defibrillator. This is considerably less than the amount of ...
Conversion of Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation: Which Drug is
... atrial fibrillation (AF) to sinus rhythm compared to placebo, amiodarone, propafenone and flecainide in clinical studies with few patients. At present no study has been conducted comparing these three drugs with a more substantial number of patients. The aim of our study is to compare the time to co ...
... atrial fibrillation (AF) to sinus rhythm compared to placebo, amiodarone, propafenone and flecainide in clinical studies with few patients. At present no study has been conducted comparing these three drugs with a more substantial number of patients. The aim of our study is to compare the time to co ...
Modeling Pathologies of Diastolic and Systolic Heart Failure
... efforts during the past 20 years, heart failure remains one of the most common, costly, disabling, and deadly medical conditions affecting more than 25 million people worldwide.40 Heart failure usually worsens over time; it is the major cause of hospitalization in the elderly with a 5-year mortality ...
... efforts during the past 20 years, heart failure remains one of the most common, costly, disabling, and deadly medical conditions affecting more than 25 million people worldwide.40 Heart failure usually worsens over time; it is the major cause of hospitalization in the elderly with a 5-year mortality ...
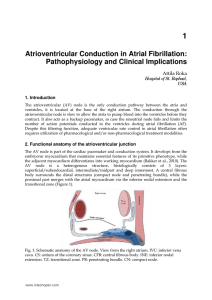
Atrioventricular Conduction in Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiology
... patients where high ventricular rate plays the major role in the development of heart failure, thus may benefit from aggressive rate and/or rhythm control, prospective identification of these cases is difficult, so far heart failure associated with relatively small left ventricular size seems to be ...
... patients where high ventricular rate plays the major role in the development of heart failure, thus may benefit from aggressive rate and/or rhythm control, prospective identification of these cases is difficult, so far heart failure associated with relatively small left ventricular size seems to be ...
Dobutamine-induced augmentation of left ventricular ejection
... as end-diastolic counts minus end-systolic counts, divided by end-diastolic counts. Using this software the lower limit of normal left ventricular ejection fraction is 0·50 and right ventricular ejection fraction 0·40. Left ventricular end-diastolic volume was determined using the Massardo count rat ...
... as end-diastolic counts minus end-systolic counts, divided by end-diastolic counts. Using this software the lower limit of normal left ventricular ejection fraction is 0·50 and right ventricular ejection fraction 0·40. Left ventricular end-diastolic volume was determined using the Massardo count rat ...
Outline for OHP CPR Macerato
... to save someone’s life. B. 10 or more facts about sub topic #2; include citations 1. The American Medical Association (AMA) called mouth to mouth resuscitation “An easily learned life saving procedure.” (The Advent of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation”). 2. American physicians named James Elam and Peter ...
... to save someone’s life. B. 10 or more facts about sub topic #2; include citations 1. The American Medical Association (AMA) called mouth to mouth resuscitation “An easily learned life saving procedure.” (The Advent of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation”). 2. American physicians named James Elam and Peter ...
Spatio-Temporal Shape Parameterization of the Human Ventricles
... There exist several methods to determine the shape and structure of the ventricles. The anatomy of the whole heart and the overall placement of the cardiac muscle fibers is described by Streeter and Hanna [14], while the orientation changes from epicardium to endocardium is presented by Arts et al [ ...
... There exist several methods to determine the shape and structure of the ventricles. The anatomy of the whole heart and the overall placement of the cardiac muscle fibers is described by Streeter and Hanna [14], while the orientation changes from epicardium to endocardium is presented by Arts et al [ ...
QUIZ # 1 - Cognella Titles Store
... notice on the EKG strip shown above occurs after the P wave. It is a rather large and noticeable deviation, and it is known as the QRS complex. It is really three waves in one—the Q, the R, and the S. It is supposed to look something like the one illustrated in Figure 1-3. Sometimes it may look diff ...
... notice on the EKG strip shown above occurs after the P wave. It is a rather large and noticeable deviation, and it is known as the QRS complex. It is really three waves in one—the Q, the R, and the S. It is supposed to look something like the one illustrated in Figure 1-3. Sometimes it may look diff ...
Left Ventricular Structural and Functional Changes in the Metabolic
... compared with controls showed a significant relationship between subclinical left ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction and the degree of metabolic burden; these changes were associated with reduced cardiorespiratory fitness.10 The effects of MS on cardiac structure and function have been i ...
... compared with controls showed a significant relationship between subclinical left ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction and the degree of metabolic burden; these changes were associated with reduced cardiorespiratory fitness.10 The effects of MS on cardiac structure and function have been i ...
Left Ventricular Mass in Healthy Subjects of the City of Buenos Aires
... weight and height was not significant, whereas with age there was a weak though statistically significant correlation. Consistent with this finding, it has been described that age is associated with increased wall thickness and reduced LVIDd. (26) There are different ways to express the reference va ...
... weight and height was not significant, whereas with age there was a weak though statistically significant correlation. Consistent with this finding, it has been described that age is associated with increased wall thickness and reduced LVIDd. (26) There are different ways to express the reference va ...
Right Heart Dysfunction After Left Ventricular Assist Device
... to the ascending aorta without bypass whenever possible. After the institution of cardiopulmonary bypass, an apical ventriculotomy was made and the inflow cannula was placed in the left ventricular apex. The pump was then activated; after deairing, patients were weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass. O ...
... to the ascending aorta without bypass whenever possible. After the institution of cardiopulmonary bypass, an apical ventriculotomy was made and the inflow cannula was placed in the left ventricular apex. The pump was then activated; after deairing, patients were weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass. O ...
BALLOON VALVULPLASTY OF PULMONIC STENOSIS
... hypoplasia. However as a guideline in our experience >85% of cases will show a significant clinical improvement with a 40 - 60% drop in the pressure gradient through the stenosis. The procedure is not without risk and a small number of patients (approx. 5 - 7%) do not survive anaesthesia and surgery ...
... hypoplasia. However as a guideline in our experience >85% of cases will show a significant clinical improvement with a 40 - 60% drop in the pressure gradient through the stenosis. The procedure is not without risk and a small number of patients (approx. 5 - 7%) do not survive anaesthesia and surgery ...
Mutant ryanodine receptors in catecholaminergic polymorphic
... study the underlying mechanisms, we expressed two types of mutant RyR2 (P2328S and V4653F) causing CPVT as well as wild-type RyR2 in HEK 293 cells. Confocal microscopy of Fluo-3 loaded cells transfected with any of the three RyR2s showed no spontaneous subcellular Ca2þ release events at baseline. Me ...
... study the underlying mechanisms, we expressed two types of mutant RyR2 (P2328S and V4653F) causing CPVT as well as wild-type RyR2 in HEK 293 cells. Confocal microscopy of Fluo-3 loaded cells transfected with any of the three RyR2s showed no spontaneous subcellular Ca2þ release events at baseline. Me ...
7-Days Holter
... permanent AF; (2) serious left main coronary artery disease identified by coronary angiography; (3) heart failure (New York Heart Association (NYHA) III or IV); (4) acute myocardial infarction in 3 months; (5) with surgical/interventional indications of valvular heart disease; (6) uncontrolled thyro ...
... permanent AF; (2) serious left main coronary artery disease identified by coronary angiography; (3) heart failure (New York Heart Association (NYHA) III or IV); (4) acute myocardial infarction in 3 months; (5) with surgical/interventional indications of valvular heart disease; (6) uncontrolled thyro ...
Ghsy4y\y45y45y5
... rhythms (Yehia et al., 1997), depending on the stimulus amplitude (analogous results are seen in spontaneously beating re-aggregates of embryonic chick ventricular cells (Guevara et al., 1990)). In a similar vein, not all period-4 rhythms necessarily arise from a period-doubling of a period-doubled ...
... rhythms (Yehia et al., 1997), depending on the stimulus amplitude (analogous results are seen in spontaneously beating re-aggregates of embryonic chick ventricular cells (Guevara et al., 1990)). In a similar vein, not all period-4 rhythms necessarily arise from a period-doubling of a period-doubled ...
Relation between Depolarization and Repolarization Phases in
... ischemic cells’ action potential shape and duration. Geselowitz in his work has shown that the spatial variations of the ventricular gradient are related to the local spatial variation of action potential area and hence to changes in action potential associated with cardiac pathologies such as ische ...
... ischemic cells’ action potential shape and duration. Geselowitz in his work has shown that the spatial variations of the ventricular gradient are related to the local spatial variation of action potential area and hence to changes in action potential associated with cardiac pathologies such as ische ...
HeartStart MRx and XL AED Algorithm
... First, the average waveform amplitude is used to identify very small rhythms, such as asystole and agonal rhythms, as nonshockable. Then, isoelectric baseline content is used to identify narrow QRS-complex or slow rhythms as non-shockable. Finally, QRS morphology features are used to identify rhythm ...
... First, the average waveform amplitude is used to identify very small rhythms, such as asystole and agonal rhythms, as nonshockable. Then, isoelectric baseline content is used to identify narrow QRS-complex or slow rhythms as non-shockable. Finally, QRS morphology features are used to identify rhythm ...
Signaling and expression for mitochondrial membrane proteins
... coronary artery (LCX) was dissected free and completely occluded with a ligature. After coronary ligation the animals were observed in the open chest state for 60 min. When ventricular fibrillation occurred, electrical defibrillation was performed immediately. This procedure was usually successful. ...
... coronary artery (LCX) was dissected free and completely occluded with a ligature. After coronary ligation the animals were observed in the open chest state for 60 min. When ventricular fibrillation occurred, electrical defibrillation was performed immediately. This procedure was usually successful. ...
Paced ECG Morphology–Reveals More than What It Conceals
... increased r in lead V1 is very specific for anterior wall myocardial infarction in the setting of LBBB. In right ventricular pacing, these Q waves however could simply reflect differences in the lead tip position rather than myocardial infarction.1,2 Thus Q in leads V5 and V6 could be normal finding ...
... increased r in lead V1 is very specific for anterior wall myocardial infarction in the setting of LBBB. In right ventricular pacing, these Q waves however could simply reflect differences in the lead tip position rather than myocardial infarction.1,2 Thus Q in leads V5 and V6 could be normal finding ...
GENERAL ANESTHESIA FOR A PATIENT WITH BRUGADA SYNDROME K -K
... (SIDS) and the sudden unexpected nocturnal death syndrome (SUNDS), a typical presentation in young males from Southeast Asia. Many factors during general anesthesia, such as medications, temperature changes, and heart rate variations, could precipitate lethal arrhythmias in this patient population. ...
... (SIDS) and the sudden unexpected nocturnal death syndrome (SUNDS), a typical presentation in young males from Southeast Asia. Many factors during general anesthesia, such as medications, temperature changes, and heart rate variations, could precipitate lethal arrhythmias in this patient population. ...
Ventricular Fibrillation Detection Algorithm Implemented in a Cell
... One of the most common causes of sudden death in patients with cardiac diseases is Ventricular Fibrillation (VF). It is a malignant arrythmia characterized by a rapid heart rate and an uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart [1]. VF is usually diagnosed on the ...
... One of the most common causes of sudden death in patients with cardiac diseases is Ventricular Fibrillation (VF). It is a malignant arrythmia characterized by a rapid heart rate and an uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart [1]. VF is usually diagnosed on the ...
Noninvasive Assessment of Myocardial Composition
... conditions is an important compensatory mechanism that tends to minimize abnormalities in myocardial stress related to the inciting load.4 However, recent See p 925 studies have indicated that hypertrophied muscle differs from normal muscle in many respects, including its structure, mechanical prope ...
... conditions is an important compensatory mechanism that tends to minimize abnormalities in myocardial stress related to the inciting load.4 However, recent See p 925 studies have indicated that hypertrophied muscle differs from normal muscle in many respects, including its structure, mechanical prope ...
Dimensional Changes of the Human Left Ventricle Prior
... a basal chord occurred, while the apical chord decreased, suggesting nonhomogeneous myocardial involvement. In eight patients with mitral regurgitation, the reduction in equatorial diameter averaged 2.8 mm and volume decreased by 16.7 ml or 8.0% of EDV. In normal patients the occurrence of circumfer ...
... a basal chord occurred, while the apical chord decreased, suggesting nonhomogeneous myocardial involvement. In eight patients with mitral regurgitation, the reduction in equatorial diameter averaged 2.8 mm and volume decreased by 16.7 ml or 8.0% of EDV. In normal patients the occurrence of circumfer ...
Ventricular fibrillation

Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients. While there is some activity, the lay person is usually unable to detect it by palpating (feeling) the major pulse points of the carotid and femoral arteries. Such an arrhythmia is only confirmed by electrocardiography. Ventricular fibrillation is a medical emergency that requires prompt Advanced Life Support interventions. If this arrhythmia continues for more than a few seconds, it will likely degenerate further into asystole (""flatline""). This condition results in cardiogenic shock and cessation of effective blood circulation. As a consequence, sudden cardiac death (SCD) will result in a matter of minutes. If the patient is not revived after a sufficient period (within roughly 5 minutes at room temperature), the patient could sustain irreversible brain damage and possibly become brain-dead, due to the effects of cerebral hypoxia. On the other hand, death often occurs if sinus rhythm is not restored within 90 seconds of the onset of VF, especially if it has degenerated further into asystole.