17. CV II - EKG-mechanical
... isovolumetric contraction (IVC) - both sets of valves closed ventricular ejection - ventricular P exceeds arterial P and opens SL valves b. Diastole: relaxation of ventricles - ventricular P drops: SL valves close isovolumetric relaxation (IVR) - both sets of valves closed ventricular filling - vent ...
... isovolumetric contraction (IVC) - both sets of valves closed ventricular ejection - ventricular P exceeds arterial P and opens SL valves b. Diastole: relaxation of ventricles - ventricular P drops: SL valves close isovolumetric relaxation (IVR) - both sets of valves closed ventricular filling - vent ...
Slide ()
... Disturbance of Cardiac Rate and Rhythm III.As in previous diagrams, only the audible heart sounds are the physical signs of these disorders.A.Normal rhythm is interspersed with two random premature beats: If such beats are very frequent, the ear may not be able to distinguish them from atrial fibril ...
... Disturbance of Cardiac Rate and Rhythm III.As in previous diagrams, only the audible heart sounds are the physical signs of these disorders.A.Normal rhythm is interspersed with two random premature beats: If such beats are very frequent, the ear may not be able to distinguish them from atrial fibril ...
17. CV II - EKG-mechanical.doc
... QRS Wave or Complex: caused by depolarization of ventricles (atrial repolarization masked by this) T Wave: caused by repolarization of ventricles PR Interval: time elapsed between start of P wave and R wave (period of delay at AV node) (called PQ interval in text) • ECG Leads (12 combinations of ele ...
... QRS Wave or Complex: caused by depolarization of ventricles (atrial repolarization masked by this) T Wave: caused by repolarization of ventricles PR Interval: time elapsed between start of P wave and R wave (period of delay at AV node) (called PQ interval in text) • ECG Leads (12 combinations of ele ...
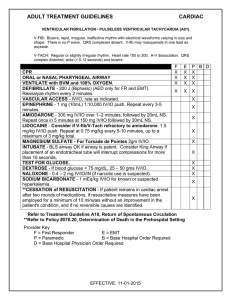
Ventricular Fibrillation / Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia
... If AED is applied prior to ALS arrival, perform CPR and reassess the rhythm as indicated. After each intervention resume CPR immediately and reassess the rhythm after each 2 minute or 5 cycle interval. For Biphasic devices shock with energy levels following manufacturers’ recommendations (120 – 200 ...
... If AED is applied prior to ALS arrival, perform CPR and reassess the rhythm as indicated. After each intervention resume CPR immediately and reassess the rhythm after each 2 minute or 5 cycle interval. For Biphasic devices shock with energy levels following manufacturers’ recommendations (120 – 200 ...
2-9 VFib PulselessVT - Detroit East Medical Control Authority
... If AED is applied prior to ALS arrival, perform CPR and reassess the rhythm as indicated. After each intervention resume CPR immediately and reassess the rhythm after each 2 minute or 5 cycle interval. For Biphasic devices shock with energy levels following manufacturers’ recommendations (120 – 200 ...
... If AED is applied prior to ALS arrival, perform CPR and reassess the rhythm as indicated. After each intervention resume CPR immediately and reassess the rhythm after each 2 minute or 5 cycle interval. For Biphasic devices shock with energy levels following manufacturers’ recommendations (120 – 200 ...
isovolumic ventricular contraction
... • In Rapid Ventricular Ejection phase, aortic valve finally opens and blood exits the ventricle. • In this phase, atrium relaxes and the blood starts to fill the atrium. • In Reduced Ventricular Ejection phase, ejection velocity decreases (reduced ejection). • At the end of this phase, aortic valve ...
... • In Rapid Ventricular Ejection phase, aortic valve finally opens and blood exits the ventricle. • In this phase, atrium relaxes and the blood starts to fill the atrium. • In Reduced Ventricular Ejection phase, ejection velocity decreases (reduced ejection). • At the end of this phase, aortic valve ...
Chapter 6 - Boone County Schools
... • Pacemaker cells emit electrical impulses; heart muscle contracts ...
... • Pacemaker cells emit electrical impulses; heart muscle contracts ...
ABCD- Airway, Breathing, Circulation, and Defibrillation
... Defibrillation- shocking the heart to stop fibrillation Emergency Medical Services (EMS)- A rapid response system that responds to emergencies by providing emergency care and transport Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)- An entry-level EMS worker trained to provide basic emergency care and transport ...
... Defibrillation- shocking the heart to stop fibrillation Emergency Medical Services (EMS)- A rapid response system that responds to emergencies by providing emergency care and transport Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)- An entry-level EMS worker trained to provide basic emergency care and transport ...
Causes of stopped circulation
... Electro-mechanical disociation (EMD) Pulseless ventricular activity (PVA) ...
... Electro-mechanical disociation (EMD) Pulseless ventricular activity (PVA) ...
ventricular fibrillation - pulseless ventricular tachycardia (a01)
... VENTILATE with BVM and 100% OXYGEN. DEFIBRILLATE - 200 J (Biphasic) (AED only for FR and EMT) Reanalyze rhythm every 2 minutes. VASCULAR ACCESS - IV/IO, rate as indicated. EPINEPHRINE - 1 mg (10mL) 1:10,000 IV/IO push. Repeat every 3-5 minutes. AMIODARONE - 300 mg IV/IO over 1–2 minutes, followed by ...
... VENTILATE with BVM and 100% OXYGEN. DEFIBRILLATE - 200 J (Biphasic) (AED only for FR and EMT) Reanalyze rhythm every 2 minutes. VASCULAR ACCESS - IV/IO, rate as indicated. EPINEPHRINE - 1 mg (10mL) 1:10,000 IV/IO push. Repeat every 3-5 minutes. AMIODARONE - 300 mg IV/IO over 1–2 minutes, followed by ...
Management of cardiac arrhythmias and conduction disorders
... Atrial fibrillation with normal ejection fraction Patients with atrial fibrillation and thyroid disease Patients with history of seizure disorder and atrial fibrillation ...
... Atrial fibrillation with normal ejection fraction Patients with atrial fibrillation and thyroid disease Patients with history of seizure disorder and atrial fibrillation ...
Cardiac physiology
... 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period) 2- Ventricular filling (diastole) 3- Ventricular contraction/ejection (systole) Cardiac cycle last about 0.8 seconds 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period): In the beginning of this phase all four chamber are at rest. As the pressure inside the vent ...
... 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period) 2- Ventricular filling (diastole) 3- Ventricular contraction/ejection (systole) Cardiac cycle last about 0.8 seconds 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period): In the beginning of this phase all four chamber are at rest. As the pressure inside the vent ...
Cardiac Auscultation
... according to the sequence of occurrence and are produced at specific points in the cardiac cycle. The initial heart sound is called the first heart sound or S1. It occurs at the beginning of ventricular systole when the ventricular volume is maximal. The S1 corresponds to a point very early in the r ...
... according to the sequence of occurrence and are produced at specific points in the cardiac cycle. The initial heart sound is called the first heart sound or S1. It occurs at the beginning of ventricular systole when the ventricular volume is maximal. The S1 corresponds to a point very early in the r ...
Cardiac Arrhythmias
... No organized ventricular contractions, no pulse, loss of consciousness Most common cause: AMI, drug toxicity, electrolyte disturbances, electric shock, end stage of many disease processes Management: non-synchronized DC defibrillation, cardiopulmonary resuscitation ...
... No organized ventricular contractions, no pulse, loss of consciousness Most common cause: AMI, drug toxicity, electrolyte disturbances, electric shock, end stage of many disease processes Management: non-synchronized DC defibrillation, cardiopulmonary resuscitation ...
Biochemistry - U
... 3) To understand the concept of cardiomyopathy and to distinguish between primary and secondary cardiomyopathies. Cardiomyopathy refers to diseases of the heart muscle (myocardium) that are noninflammatory and not associated with hypertension, congenital heart disease, valvular disease, or coronary ...
... 3) To understand the concept of cardiomyopathy and to distinguish between primary and secondary cardiomyopathies. Cardiomyopathy refers to diseases of the heart muscle (myocardium) that are noninflammatory and not associated with hypertension, congenital heart disease, valvular disease, or coronary ...
Two Cardiology Zebras - Iowa Heart Foundation
... • The majority of patients survive this problem • The only autopsy report is that of a patient who died of multiple organs system failure who also developed Takotsubo’s Syndrome. – The patient had no macroscopic signs of recent myocardial infarction or scars. – Microscopic examination revealed n ...
... • The majority of patients survive this problem • The only autopsy report is that of a patient who died of multiple organs system failure who also developed Takotsubo’s Syndrome. – The patient had no macroscopic signs of recent myocardial infarction or scars. – Microscopic examination revealed n ...
I. Atrial tachy
... B. Ventricular fibrillation: The effects of ventricular fibrillation: The fibrillating ventricles, like the fibrillating atria, look like a quivering "bag of worms". The fibrillating ventricles cannot pump blood effectively and circulation of the blood stops. Therefore, in the absence of emergency ...
... B. Ventricular fibrillation: The effects of ventricular fibrillation: The fibrillating ventricles, like the fibrillating atria, look like a quivering "bag of worms". The fibrillating ventricles cannot pump blood effectively and circulation of the blood stops. Therefore, in the absence of emergency ...
Dysrhythmia (BASIC) Exam Content Outline
... Ventricular Fibrillation (VFib) Ventricular Tachycardia (VTach) ...
... Ventricular Fibrillation (VFib) Ventricular Tachycardia (VTach) ...
Autocorrelation of Electrocardiographs Activity during Ventricular
... analysis which detects and extracts any periodic components present in a record which, on inspection, may show an apparently irregular type of activity. The theory and some of the applications of the method have been reviewed by Wiener.2 Basically, it is a method of harmonic analysis with major emph ...
... analysis which detects and extracts any periodic components present in a record which, on inspection, may show an apparently irregular type of activity. The theory and some of the applications of the method have been reviewed by Wiener.2 Basically, it is a method of harmonic analysis with major emph ...
Intra Aortic Balloon Pump
... Countrepulsation is the active process of mechanically displacing intra aortic blood by inflating and deflating opposite to the heart’s activity. This is were it gets the name . The IAB System is comprised basically of two entities: 1. Balloon. 2. Console. The intra aortic balloon comes in various ...
... Countrepulsation is the active process of mechanically displacing intra aortic blood by inflating and deflating opposite to the heart’s activity. This is were it gets the name . The IAB System is comprised basically of two entities: 1. Balloon. 2. Console. The intra aortic balloon comes in various ...
Cardio I
... 1. List four factors that determine the rate of diffusion of a solute across a membrane. a. Concentration gradient b. Permeability/surface area of the capillary wall c. Molecular Weight (bigger molecules diffuse more slowly) d. Distance (greater the distance the longer it takes to diffuse) 2. Identi ...
... 1. List four factors that determine the rate of diffusion of a solute across a membrane. a. Concentration gradient b. Permeability/surface area of the capillary wall c. Molecular Weight (bigger molecules diffuse more slowly) d. Distance (greater the distance the longer it takes to diffuse) 2. Identi ...
Heart and Circulatory System?Arrhythmia (Irregular Heartbeat)
... satisfied that proper anticoagulation is being achieved with aspirin only. If other risk factors are present, anticoagulation must include warfarin (Coumadin). In the age group of 6575 with no risk factors, either aspirin or warfarin will be acceptable. If over age 75, warfarin is required. When o ...
... satisfied that proper anticoagulation is being achieved with aspirin only. If other risk factors are present, anticoagulation must include warfarin (Coumadin). In the age group of 6575 with no risk factors, either aspirin or warfarin will be acceptable. If over age 75, warfarin is required. When o ...
Glossary of Cardiology Terms
... ventricular arrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac arrest. Advanced devices can terminate potentially lethal arrhythmias painlessly in some cases. Ischemia: a decrease in the supply of oxygenated blood to vital organs or body tissue due to obstruction of blood vessels. Cardiac ischemia is marke ...
... ventricular arrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac arrest. Advanced devices can terminate potentially lethal arrhythmias painlessly in some cases. Ischemia: a decrease in the supply of oxygenated blood to vital organs or body tissue due to obstruction of blood vessels. Cardiac ischemia is marke ...
V. Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG
... Heart Contraction Overview V. Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)- record impulses by detecting electrical currents in heart; measures voltage (mV), not contractions. Impulses lead to contractions. 1. Unique characteristics of cardiac muscle: 1.Stimulation- autorhythmicicity; depolarize spontaneously 2.O ...
... Heart Contraction Overview V. Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)- record impulses by detecting electrical currents in heart; measures voltage (mV), not contractions. Impulses lead to contractions. 1. Unique characteristics of cardiac muscle: 1.Stimulation- autorhythmicicity; depolarize spontaneously 2.O ...
Ventricular fibrillation

Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients. While there is some activity, the lay person is usually unable to detect it by palpating (feeling) the major pulse points of the carotid and femoral arteries. Such an arrhythmia is only confirmed by electrocardiography. Ventricular fibrillation is a medical emergency that requires prompt Advanced Life Support interventions. If this arrhythmia continues for more than a few seconds, it will likely degenerate further into asystole (""flatline""). This condition results in cardiogenic shock and cessation of effective blood circulation. As a consequence, sudden cardiac death (SCD) will result in a matter of minutes. If the patient is not revived after a sufficient period (within roughly 5 minutes at room temperature), the patient could sustain irreversible brain damage and possibly become brain-dead, due to the effects of cerebral hypoxia. On the other hand, death often occurs if sinus rhythm is not restored within 90 seconds of the onset of VF, especially if it has degenerated further into asystole.