On the Significance of Neuronal Giantism in Gastropods
... question that looms is: why do the pulmonates and opisthobranchs display such pronounced neuron giantism whereas other gastropod taxa do not? The best answer will probably rest on future comparative observations on species chosen for particular nervous system characters, but the context for such com ...
... question that looms is: why do the pulmonates and opisthobranchs display such pronounced neuron giantism whereas other gastropod taxa do not? The best answer will probably rest on future comparative observations on species chosen for particular nervous system characters, but the context for such com ...
Dynamics of Propofol-Induced Loss of Consciousness Across
... from wakefulness to unconsciousness is not a continuous process, but rather a series of discrete neural changes. Key words: general anesthesia; local field potential; loss of consciousness; primate; sensory premotor network; single-neuron activity ...
... from wakefulness to unconsciousness is not a continuous process, but rather a series of discrete neural changes. Key words: general anesthesia; local field potential; loss of consciousness; primate; sensory premotor network; single-neuron activity ...
Program booklet - Munich Center for NeuroSciences
... with changes in the number and stability of spines. However, to date, the contribution of excitatory synaptogenesis to the strengthening of synaptic connections remains elusive. Do new spines form functional synapses with the inputs stimulated during LTP induction and thereby follow Hebbian co-activ ...
... with changes in the number and stability of spines. However, to date, the contribution of excitatory synaptogenesis to the strengthening of synaptic connections remains elusive. Do new spines form functional synapses with the inputs stimulated during LTP induction and thereby follow Hebbian co-activ ...
Comprehensive imaging of cortical networks
... Even the simplest perceptual behaviors engage thousands of neurons across multiple regions of cortex [1,2]. In contrast, typical electrophysiological studies sample only a handful of neurons in a single brain area [3]. Moreover, the type of neuron recorded and its position within the neural circuit ...
... Even the simplest perceptual behaviors engage thousands of neurons across multiple regions of cortex [1,2]. In contrast, typical electrophysiological studies sample only a handful of neurons in a single brain area [3]. Moreover, the type of neuron recorded and its position within the neural circuit ...
Mechanism of Irregular Firing of Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Neurons
... firing pattern of spontaneous action potentials could be divided into regular and irregular, based on the interspike interval (ISI) histogram and the membrane potential trajectory between action potentials. Similar to previous studies, regular neurons had a firing rate about ⬎3.5 Hz and irregular ne ...
... firing pattern of spontaneous action potentials could be divided into regular and irregular, based on the interspike interval (ISI) histogram and the membrane potential trajectory between action potentials. Similar to previous studies, regular neurons had a firing rate about ⬎3.5 Hz and irregular ne ...
IMPROVING OF ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS
... Sridhar [1] says that the main advantage of GPU over CPU is high computational parallelism and efficiency with a relatively low cost.However, it is difficult to design an algorithm. Also, the author says that although exist Integrated Circuits (IC) for high parallelism, it is very difficult to trans ...
... Sridhar [1] says that the main advantage of GPU over CPU is high computational parallelism and efficiency with a relatively low cost.However, it is difficult to design an algorithm. Also, the author says that although exist Integrated Circuits (IC) for high parallelism, it is very difficult to trans ...
Luczak, 2015 - University of Lethbridge
... a | The toneevoked responses in the auditory cortex of unanaesthetized rats are heterogeneous across different neurons. The responses of three representative neurons to 60‑dB tones at a range of frequencies are shown. Blue lines represent individual spikes and the grey region represents the tone dur ...
... a | The toneevoked responses in the auditory cortex of unanaesthetized rats are heterogeneous across different neurons. The responses of three representative neurons to 60‑dB tones at a range of frequencies are shown. Blue lines represent individual spikes and the grey region represents the tone dur ...
Slide 1
... show burst firing during sleep and the resultant synchronized low-frequency, high amplitude occipital EEG. The bottom 4 traces show recordings from these same sites during waking along with the resultant desynchronized, high-frequency EEG. Asterisks indicate bursting periods and the third trace show ...
... show burst firing during sleep and the resultant synchronized low-frequency, high amplitude occipital EEG. The bottom 4 traces show recordings from these same sites during waking along with the resultant desynchronized, high-frequency EEG. Asterisks indicate bursting periods and the third trace show ...
Coherence a measure of the brain networks: past and present
... Effective and Functional Connectivity measurements can be analyzed in the Frequency Domain with methods such as Coherence and Phase synchrony or in the Time Domain with methods such as Correlation and Granger Causality. Coherence and Phase synchrony are common mathematical methods for quantifying fr ...
... Effective and Functional Connectivity measurements can be analyzed in the Frequency Domain with methods such as Coherence and Phase synchrony or in the Time Domain with methods such as Correlation and Granger Causality. Coherence and Phase synchrony are common mathematical methods for quantifying fr ...
BCM Theory
... Figure S2A. The signal triggers spikes in some IO cells that are in an upswing phase of their potential. An example of this upswing is shown in Figure S2B, where an external input (arrow in the figure) triggers a spike. Typically, when an IO neuron is in a downswing phase of its potential, the exter ...
... Figure S2A. The signal triggers spikes in some IO cells that are in an upswing phase of their potential. An example of this upswing is shown in Figure S2B, where an external input (arrow in the figure) triggers a spike. Typically, when an IO neuron is in a downswing phase of its potential, the exter ...
Optimal Neural Spike Classification
... the response properties of sets of adjacent and therefore likely related neurons. However, to do this, it is necessary to correctly classify the signals generated by these different neurons. This paper considers this problem of classifying the signals in such an extracellular recording, based upon t ...
... the response properties of sets of adjacent and therefore likely related neurons. However, to do this, it is necessary to correctly classify the signals generated by these different neurons. This paper considers this problem of classifying the signals in such an extracellular recording, based upon t ...
Modeling goal-directed spatial navigation in the rat based on physiological
... We investigated the importance of hippocampal theta oscillations and the significance of phase differences of theta modulation in the cortical regions that are involved in goal-directed spatial navigation. Our models used representations of entorhinal cortex layer III (ECIII), hippocampus and prefro ...
... We investigated the importance of hippocampal theta oscillations and the significance of phase differences of theta modulation in the cortical regions that are involved in goal-directed spatial navigation. Our models used representations of entorhinal cortex layer III (ECIII), hippocampus and prefro ...
Does the Conventional Leaky Integrate-and
... Considerable evidence indicates that neurons in different cortical areas are capable of producing synchronous action potentials on the time scale of millisecond (Bair 1994, Bair 1996, Marsalek 1997) and the synchronization may play functional roles in neural processing (Abeles 1993, Prut 1998, Riehl ...
... Considerable evidence indicates that neurons in different cortical areas are capable of producing synchronous action potentials on the time scale of millisecond (Bair 1994, Bair 1996, Marsalek 1997) and the synchronization may play functional roles in neural processing (Abeles 1993, Prut 1998, Riehl ...
Untitled
... how can neurons synchronize in noisy networks? By exploiting a high-speed multineuron imaging technique and a large-scale synapse mapping method, we directly compared spontaneous activity patterns and anatomical connectivity in hippocampal CA3 networks ex vivo. As compared to non-synaptic pairs, syn ...
... how can neurons synchronize in noisy networks? By exploiting a high-speed multineuron imaging technique and a large-scale synapse mapping method, we directly compared spontaneous activity patterns and anatomical connectivity in hippocampal CA3 networks ex vivo. As compared to non-synaptic pairs, syn ...
Neurotransmitter and Neuromodulator Activity in
... sharp electrodes to record from the rNST neurons, but even with the very stable recording conditions provided by a brain slice it proved difficult to obtain and hold neurons (Bradley and Sweazey, 1990). These problems were overcome by using the whole cell configuration of the patch clamp technique t ...
... sharp electrodes to record from the rNST neurons, but even with the very stable recording conditions provided by a brain slice it proved difficult to obtain and hold neurons (Bradley and Sweazey, 1990). These problems were overcome by using the whole cell configuration of the patch clamp technique t ...
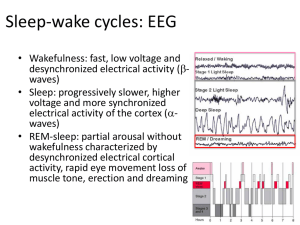
Sleep-wake cycles: EEG
... voltage and more synchronized electrical activity of the cortex (awaves) • REM-sleep: partial arousal without wakefulness characterized by desynchronized electrical cortical activity, rapid eye movement loss of muscle tone, erection and dreaming ...
... voltage and more synchronized electrical activity of the cortex (awaves) • REM-sleep: partial arousal without wakefulness characterized by desynchronized electrical cortical activity, rapid eye movement loss of muscle tone, erection and dreaming ...
Artificial Neural Networks
... The neurons are connected by weighted links passing signals from one neuron to another. The human brain incorporates nearly 10 billion neurons and 60 trillion connections, synapses, between them. By using multiple neurons simultaneously, the brain can perform its functions much faster than the faste ...
... The neurons are connected by weighted links passing signals from one neuron to another. The human brain incorporates nearly 10 billion neurons and 60 trillion connections, synapses, between them. By using multiple neurons simultaneously, the brain can perform its functions much faster than the faste ...
Neural Syntax: Cell Assemblies, Synapsembles, and
... Another reader mechanism may respond to another set of combination of firing patterns. A simple and ubiquitous example of a reader mechanism in the brain is the integration of presynaptic spikes by neurons, constrained by their membrane time constant t.4 A group of upstream neurons, whose spike disc ...
... Another reader mechanism may respond to another set of combination of firing patterns. A simple and ubiquitous example of a reader mechanism in the brain is the integration of presynaptic spikes by neurons, constrained by their membrane time constant t.4 A group of upstream neurons, whose spike disc ...
PDF file
... and its effectors without using the handcrafted (or genespecified) content or the handcrafted boundaries for concepts about the extra-body environments. Feed-forward [36], [34] and recurrent [12], [49] networks, use images (numeric patterns) as representations. Recurrent networks can run continuousl ...
... and its effectors without using the handcrafted (or genespecified) content or the handcrafted boundaries for concepts about the extra-body environments. Feed-forward [36], [34] and recurrent [12], [49] networks, use images (numeric patterns) as representations. Recurrent networks can run continuousl ...
The Third Generation of Neural Networks
... are often called dense layers, because every neuron is connected to the next layer. Prior to the third generation of neural networks, every layer was dense. Dropout layers are not dense, as will be demonstrated later. You will also notice that the layers of the neural network decrease in their numbe ...
... are often called dense layers, because every neuron is connected to the next layer. Prior to the third generation of neural networks, every layer was dense. Dropout layers are not dense, as will be demonstrated later. You will also notice that the layers of the neural network decrease in their numbe ...
Epilepsy in Small
... Structure of the network and connectivity. We generated simple network models of excitatory neurons in hippocampus. To keep the number of free parameters manageable, to more easily constrain activity to spread in a controlled manner, and to eliminate the effects of boundary conditions, we restricted ...
... Structure of the network and connectivity. We generated simple network models of excitatory neurons in hippocampus. To keep the number of free parameters manageable, to more easily constrain activity to spread in a controlled manner, and to eliminate the effects of boundary conditions, we restricted ...
the manuscript as pdf
... In addition, recent efforts to extend DBS to ‘closed-loop’ systems in which particular events or signals trigger a ‘contingent’ or ‘demand’ pacemaking have begun in small clinical studies of refractory epilepsy (Osorio et al., 2001). Such closed-loop methods will extend the flexibility and range of ...
... In addition, recent efforts to extend DBS to ‘closed-loop’ systems in which particular events or signals trigger a ‘contingent’ or ‘demand’ pacemaking have begun in small clinical studies of refractory epilepsy (Osorio et al., 2001). Such closed-loop methods will extend the flexibility and range of ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.