Introduction to electrophysiological recordings
... EEG recording corresponds to the electrical potential difference between two electrodes: either between one active electrode on the scalp and one reference electrode located far from the recording site, or between two active electrodes. ...
... EEG recording corresponds to the electrical potential difference between two electrodes: either between one active electrode on the scalp and one reference electrode located far from the recording site, or between two active electrodes. ...
Neurotransmission
... The nervous system is a network of specialized cells, which coordinate the actions of an individual by sending signals from one part of the body to the other. ...
... The nervous system is a network of specialized cells, which coordinate the actions of an individual by sending signals from one part of the body to the other. ...
CISC 3250: Systems Neuroscience Homework 5 due April 27 or
... 2. Computing neural dynamics by hand takes a while – though our neurons are performing these computations tens to hundreds of times per second. We can, instead, use a program I have written for Scilab to compute behaviors of many inter-connected neurons across tens of time steps. You will not be ask ...
... 2. Computing neural dynamics by hand takes a while – though our neurons are performing these computations tens to hundreds of times per second. We can, instead, use a program I have written for Scilab to compute behaviors of many inter-connected neurons across tens of time steps. You will not be ask ...
Optogenetics: Molecular and Optical Tools for Controlling Life with
... Over the last several years we and our colleagues have developed a toolbox of fully genetically encoded molecules that, when expressed in neurons, enable the electrical potentials of the neurons to be controlled in a temporally precise fashion by brief pulses of light. Some of the molecules enable t ...
... Over the last several years we and our colleagues have developed a toolbox of fully genetically encoded molecules that, when expressed in neurons, enable the electrical potentials of the neurons to be controlled in a temporally precise fashion by brief pulses of light. Some of the molecules enable t ...
Slide ()
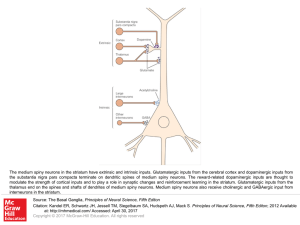
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
Chapter 3
... Pituitary Gland (pea) located in the brain master gland thermostat closely connected to nervous system Thyroid Gland located next to trachea & larynx controls metabolism effects energy level and mood Adrenal Gland located above the kidneys ...
... Pituitary Gland (pea) located in the brain master gland thermostat closely connected to nervous system Thyroid Gland located next to trachea & larynx controls metabolism effects energy level and mood Adrenal Gland located above the kidneys ...
Chapter 2
... Pituitary Gland (pea) located in the brain master gland thermostat closely connected to nervous system Thyroid Gland located next to trachea & larynx controls metabolism effects energy level and mood Adrenal Gland located above the kidneys ...
... Pituitary Gland (pea) located in the brain master gland thermostat closely connected to nervous system Thyroid Gland located next to trachea & larynx controls metabolism effects energy level and mood Adrenal Gland located above the kidneys ...
Nervous System
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
Parts and Functions of a Nervous System
... Nerve cells or ______________ are highly specialized body cells that convey impulses from one part of the body to the CNS or vice versa. Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consi ...
... Nerve cells or ______________ are highly specialized body cells that convey impulses from one part of the body to the CNS or vice versa. Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consi ...
Cognitive Activity in Artificial Neural Networks
... that even an elementary understanding of the microstructure of the brain funds a fertile and quite different conception of what cognitive activity really consists in. ...
... that even an elementary understanding of the microstructure of the brain funds a fertile and quite different conception of what cognitive activity really consists in. ...
Laminar and Columnar organization of the cerebral cortex
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
bio12_sm_11_1
... messages to effector tissues; interneurons transmit and integrate neural messages from the afferent neurons to the efferent neurons; effectors are the tissues where the appropriate response/stimulus takes place (for example, muscles, glands, and organs). (b) Afferent neurons, interneurons, efferent ...
... messages to effector tissues; interneurons transmit and integrate neural messages from the afferent neurons to the efferent neurons; effectors are the tissues where the appropriate response/stimulus takes place (for example, muscles, glands, and organs). (b) Afferent neurons, interneurons, efferent ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... Nothing is happening. The gates are closed and the positive ions are on the outside with the negative ions on the inside of the cell. “Negative Ions inside the Neuron is Natural” ...
... Nothing is happening. The gates are closed and the positive ions are on the outside with the negative ions on the inside of the cell. “Negative Ions inside the Neuron is Natural” ...
Slide ()
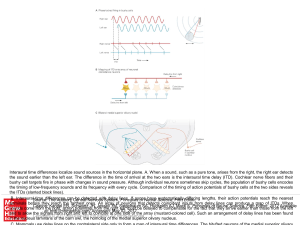
... bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy cells encodes the timing of low-frequency sounds and its frequency with every cycle. Comparison of the timing of action potentials of bushy cells at the two sid ...
... bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy cells encodes the timing of low-frequency sounds and its frequency with every cycle. Comparison of the timing of action potentials of bushy cells at the two sid ...
Chapter 8: Sensation and Perception
... Located within the brain/spinal cord Communicate internally between sensory inputs and motor outputs E.g. Reflexes ...
... Located within the brain/spinal cord Communicate internally between sensory inputs and motor outputs E.g. Reflexes ...
Slide ()
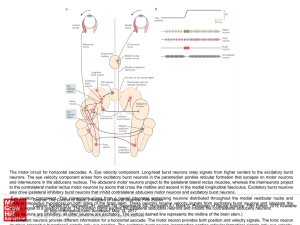
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
Object Recognition and Learning using the BioRC Biomimetic Real
... BioRC Solutions to Complexities Moderately-Large Neurons – a hypothetical argument If we decide instead to model the same exact computation with simpler neurons that only have 300 inputs, there are “N choose M” or “10,000 choose 300” combinations of inputs that make the neural circuit fire at the f ...
... BioRC Solutions to Complexities Moderately-Large Neurons – a hypothetical argument If we decide instead to model the same exact computation with simpler neurons that only have 300 inputs, there are “N choose M” or “10,000 choose 300” combinations of inputs that make the neural circuit fire at the f ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
... • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
Handout - Science in the News
... Ion channel: Openings in the membrane that surround all cells to allow and control the flow of ions. The membrane is otherwise impermeable to ions. Membrane voltage: Electrical force due to the imbalance of ions inside and outside of a neuron. This voltage is affected by neurotransmitters and change ...
... Ion channel: Openings in the membrane that surround all cells to allow and control the flow of ions. The membrane is otherwise impermeable to ions. Membrane voltage: Electrical force due to the imbalance of ions inside and outside of a neuron. This voltage is affected by neurotransmitters and change ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.