Chapter 39
... A. A synapse may occur between neurons or a neuron and a muscle cell 1. The neuron that ends at the synapse is the presynaptic neuron; the neuron that begins at a synapse is the postsynaptic neuron 2. Signals across synapses can be electrical or chemical a) Electrical synapses involve very close con ...
... A. A synapse may occur between neurons or a neuron and a muscle cell 1. The neuron that ends at the synapse is the presynaptic neuron; the neuron that begins at a synapse is the postsynaptic neuron 2. Signals across synapses can be electrical or chemical a) Electrical synapses involve very close con ...
Neural Correlates of Anticipation in Cerebellum, Basal Ganglia, and
... transit that region rather than originating or being processed there. Also the lack of disruption when a lesion occurs does not indicate the region is not involved in the behavior under some circumstances — parallel pathways could be compensating for the damaged region. 3. Imaging studies: Using mag ...
... transit that region rather than originating or being processed there. Also the lack of disruption when a lesion occurs does not indicate the region is not involved in the behavior under some circumstances — parallel pathways could be compensating for the damaged region. 3. Imaging studies: Using mag ...
Monday, June 20, 2005
... Neurons in the cerebral cortex are organized into anatomical columns, with ensembles of cells arranged from the surface to the white matter. Within a column, neurons often share functional properties, such as selectivity for stimulus orientation; columns with distinct properties, such as different p ...
... Neurons in the cerebral cortex are organized into anatomical columns, with ensembles of cells arranged from the surface to the white matter. Within a column, neurons often share functional properties, such as selectivity for stimulus orientation; columns with distinct properties, such as different p ...
Lecture 4: Development of nervous system. Neural plate. Brain
... − exencephaly, anencephaly – the cranial neuropore fails to close → the skull vault is missing → the brain is not covered and protected − hydrocephalus with abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid; mostly caused by an obstruction of the aquaeduct of Sylvius) → skull bones are expanding Myelinat ...
... − exencephaly, anencephaly – the cranial neuropore fails to close → the skull vault is missing → the brain is not covered and protected − hydrocephalus with abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid; mostly caused by an obstruction of the aquaeduct of Sylvius) → skull bones are expanding Myelinat ...
Psychology 210
... Information processing and communicating nerve cells Glia Addressed later What do you know about neurons coming into this class? How does a neuron communicate with another neuron? What type of signal is processed in a neuron? What are the parts of a neuron? Parts of a Neuron 3 main parts ___________ ...
... Information processing and communicating nerve cells Glia Addressed later What do you know about neurons coming into this class? How does a neuron communicate with another neuron? What type of signal is processed in a neuron? What are the parts of a neuron? Parts of a Neuron 3 main parts ___________ ...
The Nervous System
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
Diseases of the Basal Ganglia
... thalamic MD nucleus is thought to be involved in the ability to switch behavioral set. The limbic circuit involves the anterior cingulate area (ACA)-medial orbitofrontal cortex (MOFC)-ventral striatum-ventralpallidum-MD projections. This circuit is closed by thalamocortical projections from MD thala ...
... thalamic MD nucleus is thought to be involved in the ability to switch behavioral set. The limbic circuit involves the anterior cingulate area (ACA)-medial orbitofrontal cortex (MOFC)-ventral striatum-ventralpallidum-MD projections. This circuit is closed by thalamocortical projections from MD thala ...
Evolution and analysis of minimal neural circuits for klinotaxis in
... C. elegans chemotaxis specific predictions 1. Neck motor neurons need not be bistable. 2. Interneurons could be acting as passive conduits of activity. 3. Model suggests an antagonistic pathway between sensory and neck motor neurons. 4. ON/OFF cell activation during forward locomotion should reduce ...
... C. elegans chemotaxis specific predictions 1. Neck motor neurons need not be bistable. 2. Interneurons could be acting as passive conduits of activity. 3. Model suggests an antagonistic pathway between sensory and neck motor neurons. 4. ON/OFF cell activation during forward locomotion should reduce ...
Slide ()
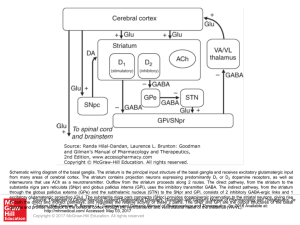
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
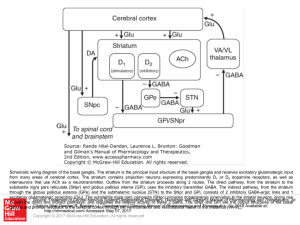
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Overview of Neuromorphic Computing Chris Carothers, CCI Director
... multipolar according to the number of processes that originate from the cell body. A. Unipolar cells have a single process, with different segments serving as receptive surfaces or releasing terminals. Unipolar cells are characteristic of the invertebrate nervous system. B. Bipolar cells have two pr ...
... multipolar according to the number of processes that originate from the cell body. A. Unipolar cells have a single process, with different segments serving as receptive surfaces or releasing terminals. Unipolar cells are characteristic of the invertebrate nervous system. B. Bipolar cells have two pr ...
The Nervous System - Valhalla High School
... the cell body and sent along the axon. The myelin sheath helps increase the speed the impulse travels. The message reaches the axon terminals which causes a release of chemical neurotransmitters. chemicals are received by the dendrites of the adjacent neuron and converted back into an electrical imp ...
... the cell body and sent along the axon. The myelin sheath helps increase the speed the impulse travels. The message reaches the axon terminals which causes a release of chemical neurotransmitters. chemicals are received by the dendrites of the adjacent neuron and converted back into an electrical imp ...
Networks of Neurons (2001)
... The soma and dendrites act as the input surface; the axon carries the outputs. The tips of the branches of the axon form synapses upon other neurons or upon effectors (though synapses may occur along the branches of an axon as well as the ends). The arrows indicate the direction of "typical" informa ...
... The soma and dendrites act as the input surface; the axon carries the outputs. The tips of the branches of the axon form synapses upon other neurons or upon effectors (though synapses may occur along the branches of an axon as well as the ends). The arrows indicate the direction of "typical" informa ...
Student Cortical Organization
... Thes current flows between soma & dendrites , when summated from many cells , contribute to production of EEG waves Saturday, April 2010 ,10 ...
... Thes current flows between soma & dendrites , when summated from many cells , contribute to production of EEG waves Saturday, April 2010 ,10 ...
PDF
... and proposal for switching in neural circuits by Anderson and Van Essen (1987) and expanded upon by Olshausen, Anderson, and Van Essen (1993). An observed correlate of this form of switching may be the up- and down-state behavior seen in intracellular in vivo recordings (see Stern, Jaeger, and Wilso ...
... and proposal for switching in neural circuits by Anderson and Van Essen (1987) and expanded upon by Olshausen, Anderson, and Van Essen (1993). An observed correlate of this form of switching may be the up- and down-state behavior seen in intracellular in vivo recordings (see Stern, Jaeger, and Wilso ...
The Nervous System
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
The mind`s mirror
... But that story is just at its beginning. Researchers haven't yet been able to prove that humans have individual mirror neurons like monkeys, although they have shown that humans have a more general mirror system. And researchers are just beginning to branch out from the motor cortex to try to figure ...
... But that story is just at its beginning. Researchers haven't yet been able to prove that humans have individual mirror neurons like monkeys, although they have shown that humans have a more general mirror system. And researchers are just beginning to branch out from the motor cortex to try to figure ...
The Nervous System * Crash Course Biology
... When an action potential begins _Na+ (sodium)__ channels open and _Na+__ rushes in making it less negative inside. With enough stimulus it reaches a threshold and more _Na+_ channels respond and open and let ____ ions in. This happens in one tiny area of the neuron but the change in voltage creeps o ...
... When an action potential begins _Na+ (sodium)__ channels open and _Na+__ rushes in making it less negative inside. With enough stimulus it reaches a threshold and more _Na+_ channels respond and open and let ____ ions in. This happens in one tiny area of the neuron but the change in voltage creeps o ...
Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Neurons Burst with Theta during
... were filled with 0.5 M NaCl and ⬃5% Nb (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) and an intracellular amplifier (Neurodata IR-283A; Cygnus Technology, Delaware Water Gap, PA). The unit signal was amplified (2000⫻) and filtered (0.3–3 kHz) using CyberAmp 380 (Axon Instruments, Union City, CA) and then ac ...
... were filled with 0.5 M NaCl and ⬃5% Nb (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) and an intracellular amplifier (Neurodata IR-283A; Cygnus Technology, Delaware Water Gap, PA). The unit signal was amplified (2000⫻) and filtered (0.3–3 kHz) using CyberAmp 380 (Axon Instruments, Union City, CA) and then ac ...
Neural Mechanisms of Bias and Sensitivity in Hiroshi Nishida Muneyoshi Takahashi
... Hiroshi Nishida1 , Muneyoshi Takahashi2 , Gary D. Bird3 , and Jan Lauwereyns4 , Non-members ABSTRACT Animals perceive stimuli in their environment and are required to make motor responses according to this perception. The perception-to-action mechanisms rely on the accumulation of neural activity in ...
... Hiroshi Nishida1 , Muneyoshi Takahashi2 , Gary D. Bird3 , and Jan Lauwereyns4 , Non-members ABSTRACT Animals perceive stimuli in their environment and are required to make motor responses according to this perception. The perception-to-action mechanisms rely on the accumulation of neural activity in ...
Honors Thesis
... Favorov and Dr. Murrow were experimenting with the model, they increased this parameter as research suggested, and we immediately saw output that very closely resembled real life readings recorded in the operating room. Other parameters include the sparsity of connections between the STN and the GPE ...
... Favorov and Dr. Murrow were experimenting with the model, they increased this parameter as research suggested, and we immediately saw output that very closely resembled real life readings recorded in the operating room. Other parameters include the sparsity of connections between the STN and the GPE ...
CNS DEVELOPMENT - University of Kansas Medical Center
... Tube differentiates into two concentric rings by day 26: Mantle layer and marginal layer. ...
... Tube differentiates into two concentric rings by day 26: Mantle layer and marginal layer. ...
Neural Mechanism of Language
... model supported by existing evidences. Firstly, we briefly introduce this model in this paper, and then we explain the neural mechanism of language and reasoning with it. Moreover, we find that the position of an area determines its importance. Specifically, language relevant areas are in the capita ...
... model supported by existing evidences. Firstly, we briefly introduce this model in this paper, and then we explain the neural mechanism of language and reasoning with it. Moreover, we find that the position of an area determines its importance. Specifically, language relevant areas are in the capita ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.