Document
... Figure 3A.8 The dual functions of the autonomic nervous system The autonomic nervous system controls the more autonomous (or self-regulating) internal functions. Its sympathetic division arouses and expends energy. Its parasympathetic division calms and conserves energy, allowing routine ...
... Figure 3A.8 The dual functions of the autonomic nervous system The autonomic nervous system controls the more autonomous (or self-regulating) internal functions. Its sympathetic division arouses and expends energy. Its parasympathetic division calms and conserves energy, allowing routine ...
Neural representation of action sequences: how far can
... motion processing respectively). For the processing of articulated actions, prior work has shown that even a small population of STS neurons contains sufficient information for the decoding of actor invariant to action, action invariant to actor, as well as the specific conjunction of actor and acti ...
... motion processing respectively). For the processing of articulated actions, prior work has shown that even a small population of STS neurons contains sufficient information for the decoding of actor invariant to action, action invariant to actor, as well as the specific conjunction of actor and acti ...
READING And YOUR BRAIN YOUR BRAIN YOUR BRAIN
... networks. And as you can see, learning actually changes the physical structure of the brain as new neural networks are formed. The term for this is neural plasticity. It refers to the brain’s ability to organize and reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout one’s life. Right now ...
... networks. And as you can see, learning actually changes the physical structure of the brain as new neural networks are formed. The term for this is neural plasticity. It refers to the brain’s ability to organize and reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout one’s life. Right now ...
Primary motor cortex (M1)
... Sometimes the pain associated with the missing limb may be related to the fact that the patient’s motor system send commands to the missing limb to move it, but it does not receive feedback indicating that it has moved. To test this, one can place a mirror so that the patient views their normal lim ...
... Sometimes the pain associated with the missing limb may be related to the fact that the patient’s motor system send commands to the missing limb to move it, but it does not receive feedback indicating that it has moved. To test this, one can place a mirror so that the patient views their normal lim ...
The neuroscience of depression: why does it matter?
... • Reabsorbed through active transport; recycled and reused ...
... • Reabsorbed through active transport; recycled and reused ...
3A & 3B PowerPoint
... The neuron is a mini decision maker. It received info from thousands of other neurons-some excitatory (like pushing the gas pedal). Others are inhibitory (like pushing the breaks). If the excitatory signals, minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity, called the absolute threshold, then ...
... The neuron is a mini decision maker. It received info from thousands of other neurons-some excitatory (like pushing the gas pedal). Others are inhibitory (like pushing the breaks). If the excitatory signals, minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity, called the absolute threshold, then ...
No Slide Title - Computer Science Home
... • The brain is a highly complex, nonlinear, and parallel processor. • Brain is superior in performing pattern recognition, perception, and motor control), e.g., it takes a brain 100-200 msec to recognize a familiar face embedded in an unfamiliar scene (will take days for the computer to do the simil ...
... • The brain is a highly complex, nonlinear, and parallel processor. • Brain is superior in performing pattern recognition, perception, and motor control), e.g., it takes a brain 100-200 msec to recognize a familiar face embedded in an unfamiliar scene (will take days for the computer to do the simil ...
P312Ch11_Auditory III (Coding Frequency And Intensity
... Each hair cell is a frequency-specific receptor If a sound is composed of several frequencies, it will activate several receptors – one for each of the frequencies comprising the sound. Analogy: 100s of different cone types in the eye - a different type of cone for each wavelength of light. Since ea ...
... Each hair cell is a frequency-specific receptor If a sound is composed of several frequencies, it will activate several receptors – one for each of the frequencies comprising the sound. Analogy: 100s of different cone types in the eye - a different type of cone for each wavelength of light. Since ea ...
Text S1.
... by the population transduction function. This provides the average population rates after a period of dynamical transients as a function of the average input current. Such stationary rates can be found as the stable solutions of a self-consistency condition and correspond to the stable attractors of ...
... by the population transduction function. This provides the average population rates after a period of dynamical transients as a function of the average input current. Such stationary rates can be found as the stable solutions of a self-consistency condition and correspond to the stable attractors of ...
OCULAR HEMORRHAGE IN CHILDREN
... this compactness gives the lateral ventricles their shape. In callosal agenesis, posterior portions of ventricles expand, resulting in dilatation of the trigones and occipital horns of lateral ventricles (colpocephaly). Colpocephaly refers to massive dilatation of occipital horns with normal size of ...
... this compactness gives the lateral ventricles their shape. In callosal agenesis, posterior portions of ventricles expand, resulting in dilatation of the trigones and occipital horns of lateral ventricles (colpocephaly). Colpocephaly refers to massive dilatation of occipital horns with normal size of ...
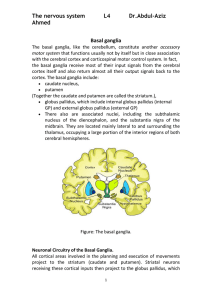
1.In the direct pathway
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
Kuliah4-anatomi2
... The preganglionic neuron may do one of three things in the sympathetic ganglion: 1. synapse with postganglionic neurons (shown in white) which then re-enter the spinal nerve and ultimately pass out to the sweat glands and the walls of blood vessels near the surface of the body. 2. pass up or down t ...
... The preganglionic neuron may do one of three things in the sympathetic ganglion: 1. synapse with postganglionic neurons (shown in white) which then re-enter the spinal nerve and ultimately pass out to the sweat glands and the walls of blood vessels near the surface of the body. 2. pass up or down t ...
Neural Modeling and Computational Neuroscience
... computational brain, modeling neuron-astrocyte interaction, neuronastrocyte networks, The role of computational neuroscience in neuro-biology and statistics for In- ...
... computational brain, modeling neuron-astrocyte interaction, neuronastrocyte networks, The role of computational neuroscience in neuro-biology and statistics for In- ...
PDF
... The required parameters and modes of the light beam need to be changed according to the purpose of the experiments. In one of the first technical reports (Boyden et al., 2005) was demonstrated reliable, millisecondtimescale control of neuronal firing, as well as control of excitatory and inhibitory ...
... The required parameters and modes of the light beam need to be changed according to the purpose of the experiments. In one of the first technical reports (Boyden et al., 2005) was demonstrated reliable, millisecondtimescale control of neuronal firing, as well as control of excitatory and inhibitory ...
The Deferred Event Model for Hardware-Oriented Spiking
... this feasible for spiking neural networks having real axonal and synaptic delays, by abstracting a spike to an event. During the time between events, it is in effect “outside time”, and can perform necessary background processing without affecting the model update. Having previously demonstrated a ...
... this feasible for spiking neural networks having real axonal and synaptic delays, by abstracting a spike to an event. During the time between events, it is in effect “outside time”, and can perform necessary background processing without affecting the model update. Having previously demonstrated a ...
Lecture 6 - School of Computing | University of Leeds
... that a nerve cell will fire an impulse only if its threshold value is exceeded. MP neurons are hard-wired devices, reading pre-defined input-output associations to determine their final output. Despite their simplicity, M&P proved that a single MP neuron can perform universal logic operations. A net ...
... that a nerve cell will fire an impulse only if its threshold value is exceeded. MP neurons are hard-wired devices, reading pre-defined input-output associations to determine their final output. Despite their simplicity, M&P proved that a single MP neuron can perform universal logic operations. A net ...
sion to superior salivatory neurons in rats
... The GABAergic excitatory action induced Ca2+ entry into neurons via NMDA receptors and voltagedependent Ca2+ channels. This Ca2+ influx is thought to be important in the regulation of various transcription factors which are involved in synapse development. The GABA-induced excitation may have a func ...
... The GABAergic excitatory action induced Ca2+ entry into neurons via NMDA receptors and voltagedependent Ca2+ channels. This Ca2+ influx is thought to be important in the regulation of various transcription factors which are involved in synapse development. The GABA-induced excitation may have a func ...
2806nn1
... A signal-flow graph is a network of directed links that are interconnected at certain points called nodes. A typical node j has an associated node signal xj. A typical directed link originates at node j and terminates on node k. It has an associated transfer function (transmittance) that specifies t ...
... A signal-flow graph is a network of directed links that are interconnected at certain points called nodes. A typical node j has an associated node signal xj. A typical directed link originates at node j and terminates on node k. It has an associated transfer function (transmittance) that specifies t ...
Dopamine control of pyramidal neuron activity in the primary motor
... (Alexander et al., 1986; Lang and Lozano, 1998; Murer et al., 2002; Dejean et al., 2012). In addition, neuroanatomical studies have shown the existence of a direct DA innervation from the midbrain to M1 that could directly modulate M1 neuronal activity (Descarries et al., 1987; Gaspar et al., 1991; ...
... (Alexander et al., 1986; Lang and Lozano, 1998; Murer et al., 2002; Dejean et al., 2012). In addition, neuroanatomical studies have shown the existence of a direct DA innervation from the midbrain to M1 that could directly modulate M1 neuronal activity (Descarries et al., 1987; Gaspar et al., 1991; ...
A Model for Delay Activity Without Recurrent Excitation
... that a moderately higher potentiation of a relatively small fraction of its input synapses can lead to a firing rate which is significantly higher than baseline activity. Hence, it is possible that spontaneous firing rates significantly above baseline could emerge in such a population, if there is no co ...
... that a moderately higher potentiation of a relatively small fraction of its input synapses can lead to a firing rate which is significantly higher than baseline activity. Hence, it is possible that spontaneous firing rates significantly above baseline could emerge in such a population, if there is no co ...
neurons - haltliappsych
... biological battery ready to be discharged. It takes about onethousandth of a second for a neuron to fire an impulse and return to its resting level. A maximum of 1,000 nerve impulses per second is possible. However, firing rates of 1 per second to 300-400 per second are more typical. ...
... biological battery ready to be discharged. It takes about onethousandth of a second for a neuron to fire an impulse and return to its resting level. A maximum of 1,000 nerve impulses per second is possible. However, firing rates of 1 per second to 300-400 per second are more typical. ...
Which Model to Use for the Liquid State Machine?
... Liquid computing efficiency has been investigated principally for integrate-and-fire neurons [2], and some experiments have been conducted for the sophisticated and numerically demanding Hodgkin-Huxley cells [4][5]. In this work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational pe ...
... Liquid computing efficiency has been investigated principally for integrate-and-fire neurons [2], and some experiments have been conducted for the sophisticated and numerically demanding Hodgkin-Huxley cells [4][5]. In this work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational pe ...
Artificial Intelligence
... to the network is processed by the entire network and an output (or multiple outputs) produced. • There is no central processing or control mechanism, the entire network is involved in every piece of computation that takes place. ...
... to the network is processed by the entire network and an output (or multiple outputs) produced. • There is no central processing or control mechanism, the entire network is involved in every piece of computation that takes place. ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.