NERVOUS SYSTEM
... – Single process arises from body – Branches into an axon and dendrite – e.g., Present in spinal and cranial ganglia (sensory neuron) Bipolar: – Single axon and single dendrite on opposite ends of the soma. e.g., interneuron Multipolar; – Single axon & multiple dendrites – Most common type in men – ...
... – Single process arises from body – Branches into an axon and dendrite – e.g., Present in spinal and cranial ganglia (sensory neuron) Bipolar: – Single axon and single dendrite on opposite ends of the soma. e.g., interneuron Multipolar; – Single axon & multiple dendrites – Most common type in men – ...
Slide ()
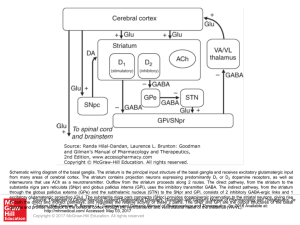
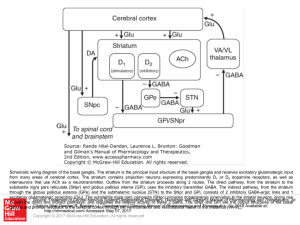
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
The Nervous System
... Central Nervous System The Brain • 100 billion neurons • Protected by skull bones • Wrapped in three layers of connective tissue called meninges. • Bathed in cerebrospinal ...
... Central Nervous System The Brain • 100 billion neurons • Protected by skull bones • Wrapped in three layers of connective tissue called meninges. • Bathed in cerebrospinal ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Brief period of time between the triggering of an impulse and when it is available for another. ...
... Brief period of time between the triggering of an impulse and when it is available for another. ...
The Nervous System
... response to a stimulus – Response travels to spinal column instead of all the way to the brain ...
... response to a stimulus – Response travels to spinal column instead of all the way to the brain ...
JARINGAN SYARAF TIRUAN
... This may make machines more powerful, relieve humans of tedious tasks, and may even improve upon human performance. ...
... This may make machines more powerful, relieve humans of tedious tasks, and may even improve upon human performance. ...
Sprint Adaptive Swimwear - Post
... For more information about this suit, and other creative products that address the needs of those who utilize pools for physical therapy as well as recreation, visit www.sprintaquatics.com or call 800-235-2156. s ...
... For more information about this suit, and other creative products that address the needs of those who utilize pools for physical therapy as well as recreation, visit www.sprintaquatics.com or call 800-235-2156. s ...
Concept Mapping Back Print
... answer: Two factors that influence the speed with which an impulse is conducted are the diameter of the axon and whether or not it is myelinated. In the absence of myelination, increasing the diameter of the axon will increase the speed of impulse conduction. The large axons in the organisms are res ...
... answer: Two factors that influence the speed with which an impulse is conducted are the diameter of the axon and whether or not it is myelinated. In the absence of myelination, increasing the diameter of the axon will increase the speed of impulse conduction. The large axons in the organisms are res ...
Exploring the Human Nervous System
... Layered membranes that lie between bony coverings and the soft tissues of the CNS Act to protect the brain and spinal cord. ...
... Layered membranes that lie between bony coverings and the soft tissues of the CNS Act to protect the brain and spinal cord. ...
File
... Neurons either fire maximally or not at all, this is referred to as the “all or none” response Increasing neuronal stimulation beyond a critical level will not result in an increased response Neurons response to increased stimulation by increasing the frequency of firing, not the intensity at wh ...
... Neurons either fire maximally or not at all, this is referred to as the “all or none” response Increasing neuronal stimulation beyond a critical level will not result in an increased response Neurons response to increased stimulation by increasing the frequency of firing, not the intensity at wh ...
PDF
... Analysis of propulsive motor activity in isolated segments of guinea pig distal colon revealed that peristalsis and spontaneous motility patterns are impeded specifically at sites of ulceration. Peristalsis is, however, enhanced in regions adjacent to ulcers, possibly due to sensitization of motilit ...
... Analysis of propulsive motor activity in isolated segments of guinea pig distal colon revealed that peristalsis and spontaneous motility patterns are impeded specifically at sites of ulceration. Peristalsis is, however, enhanced in regions adjacent to ulcers, possibly due to sensitization of motilit ...
Chapter 3: The Nervous System
... substance that is found in both the CNS and in the PNS. •In the PNS, it is the NT released at synapses on skeletal muscles and is also found in the cell bodies of the autonomic nervous system. •In the brain, it appears to be involved in learning/memory, attention as well as sleeping and dreaming. ...
... substance that is found in both the CNS and in the PNS. •In the PNS, it is the NT released at synapses on skeletal muscles and is also found in the cell bodies of the autonomic nervous system. •In the brain, it appears to be involved in learning/memory, attention as well as sleeping and dreaming. ...
Neuron and Brain Review Handout
... branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. 2. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotransmitters are excitatory (create a new action potential) while others are inhibitory. 3 ...
... branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. 2. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotransmitters are excitatory (create a new action potential) while others are inhibitory. 3 ...
Artificial Neural Networks - Texas A&M University
... principles of computations. This computer consists of those elements which can be called the biological neuron prototypes, which are interconnected by direct links called connections and which cooperate to perform parallel distributed processing (PDP) in order to solve a desired computational task. ...
... principles of computations. This computer consists of those elements which can be called the biological neuron prototypes, which are interconnected by direct links called connections and which cooperate to perform parallel distributed processing (PDP) in order to solve a desired computational task. ...
The Nervous System - Riverside Preparatory High School
... A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ floods into cell E. Stimulus triggers membrane depolarization ...
... A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ floods into cell E. Stimulus triggers membrane depolarization ...
presentation
... Two astrocytic microdomains connected to two networks are able to interact with each other. The network connected to M1 spikes at a higher frequency and is able to trigger SICs (Slow Inward Currents) in b ...
... Two astrocytic microdomains connected to two networks are able to interact with each other. The network connected to M1 spikes at a higher frequency and is able to trigger SICs (Slow Inward Currents) in b ...