Exploring the Human Nervous System
... Layered membranes that lie between bony coverings and the soft tissues of the CNS Act to protect the brain and spinal cord. ...
... Layered membranes that lie between bony coverings and the soft tissues of the CNS Act to protect the brain and spinal cord. ...
Chapter 13 - Integration
... o the orientation of the head relative to the ground and in response to movements o the location and rate of movement of one body part in relation to others So we can walk, type, or dress without using our eyes It allows us to estimate the weight of objects and determine the muscular effect nece ...
... o the orientation of the head relative to the ground and in response to movements o the location and rate of movement of one body part in relation to others So we can walk, type, or dress without using our eyes It allows us to estimate the weight of objects and determine the muscular effect nece ...
3cf1482f14bbaf7
... Change the Timing and to Scale the Intensity of Movements. Two important capabilities of the brain in controlling movement are: (1) to determine how rapidly the movement is to be performed and (2) to control how large the movement will be. For instance, a person may write the letter "a" slowly or ra ...
... Change the Timing and to Scale the Intensity of Movements. Two important capabilities of the brain in controlling movement are: (1) to determine how rapidly the movement is to be performed and (2) to control how large the movement will be. For instance, a person may write the letter "a" slowly or ra ...
Local Copy - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... Note that these reagents can be expressed in practically any cell type. Given that cardiac, immune, pancreatic, and other kinds of cells can be electrically modulated, we can perform ‘synthetic physiology’ on these cells, controlling their state to assess how they contribute to organism or system-le ...
... Note that these reagents can be expressed in practically any cell type. Given that cardiac, immune, pancreatic, and other kinds of cells can be electrically modulated, we can perform ‘synthetic physiology’ on these cells, controlling their state to assess how they contribute to organism or system-le ...
Neurotransmitters
... processed by the brain, sent back down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
... processed by the brain, sent back down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
Central Nervous System
... the central nervous system. These nerves coordinate messages between all parts of the body and the central nervous system (brain and spine) ...
... the central nervous system. These nerves coordinate messages between all parts of the body and the central nervous system (brain and spine) ...
Neural Pathways
... • routes traveled by nerve impulses are called neural pathways • one type of neural pathway is a reflex arc • the simplest and quickest • consists only of 2 neurons • bypasses the brain ...
... • routes traveled by nerve impulses are called neural pathways • one type of neural pathway is a reflex arc • the simplest and quickest • consists only of 2 neurons • bypasses the brain ...
Objectives included for the test File
... Explain how psychoactive drugs affect the brain and personality by either increasing or decreasing postsynaptic transmission. List three examples of excitatory and three examples of inhibitory psychoactive drugs. Explain the effects of THC and cocaine in terms of their action at synapses in the brai ...
... Explain how psychoactive drugs affect the brain and personality by either increasing or decreasing postsynaptic transmission. List three examples of excitatory and three examples of inhibitory psychoactive drugs. Explain the effects of THC and cocaine in terms of their action at synapses in the brai ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... • Nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another across synapses, or spaces inbetween the cells. • The “jumping across” the synapse is facilitated by chemicals called ...
... • Nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another across synapses, or spaces inbetween the cells. • The “jumping across” the synapse is facilitated by chemicals called ...
Biology 360: Motor Behaviors and Review 1) What is a central
... 5) The connection between cell 1 and cell 2a is called? ______synapse_____________ 6) What happens in this region? Electrical information passing through the axon of cell 1 will be transduced into a chemical signal. This occurs when the action potential has reached the synapse (presynaptic terminal) ...
... 5) The connection between cell 1 and cell 2a is called? ______synapse_____________ 6) What happens in this region? Electrical information passing through the axon of cell 1 will be transduced into a chemical signal. This occurs when the action potential has reached the synapse (presynaptic terminal) ...
Motor Areas - Motlow State Community College
... usually receive input from both primary sensory areas and other brain regions integrate sensory experiences to generate meaningful patterns of recognition and ...
... usually receive input from both primary sensory areas and other brain regions integrate sensory experiences to generate meaningful patterns of recognition and ...
Chapter 13: Peripheral Nervous System and Reflexes
... A reflex is a rapid, predictable motor response to a stimulus. Can be either inborn (involuntary and intrinsic) or learned (still involuntary, though). Many spinal reflexes occur without the involvement of higher brain centers. Muscle spindles: receptors in skeletal muscle that are sensitive to stre ...
... A reflex is a rapid, predictable motor response to a stimulus. Can be either inborn (involuntary and intrinsic) or learned (still involuntary, though). Many spinal reflexes occur without the involvement of higher brain centers. Muscle spindles: receptors in skeletal muscle that are sensitive to stre ...
The Nervous System
... – causes partial depolarization bringing neuron closer to firing – one EPSP is probably too weak to trigger an action potential – EPSPs can be added together (summation) – results in firing of neuron ...
... – causes partial depolarization bringing neuron closer to firing – one EPSP is probably too weak to trigger an action potential – EPSPs can be added together (summation) – results in firing of neuron ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... muscles to properly focus light on the retina) ...
... muscles to properly focus light on the retina) ...
Commentary on slides for lecture 15
... fiber length. However, the dynamic range of length over which stretch information can be provided can e increased if the gamma motor neurons fire at the same time as the alpha motor neurons; this scenario is called alpha-gamma co-activation. 8. The second sense organs related to muscle function is t ...
... fiber length. However, the dynamic range of length over which stretch information can be provided can e increased if the gamma motor neurons fire at the same time as the alpha motor neurons; this scenario is called alpha-gamma co-activation. 8. The second sense organs related to muscle function is t ...
pharm chapter 8 [3-16
... Cellular Organization of the Nervous System Cellular organization of autonomic and peripheral nervous system involves limited number of neurons that make few connections o Somatic and sensory info carried directly between spinal cord and periphery o Autonomic nerves – signal must undergo synaptic ...
... Cellular Organization of the Nervous System Cellular organization of autonomic and peripheral nervous system involves limited number of neurons that make few connections o Somatic and sensory info carried directly between spinal cord and periphery o Autonomic nerves – signal must undergo synaptic ...
The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 2003 • 23(11):4657– 4666
... was evident that labeled neurons were confined to a tight column within lamina IX of the L4 and L5 spinal cord levels. At higher magnification (inset to the right), it was observed that presumed gastrocnemius motoneurons had a soma diameter of _40 – 70 _m and extensive dendritic arborizations. B ill ...
... was evident that labeled neurons were confined to a tight column within lamina IX of the L4 and L5 spinal cord levels. At higher magnification (inset to the right), it was observed that presumed gastrocnemius motoneurons had a soma diameter of _40 – 70 _m and extensive dendritic arborizations. B ill ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
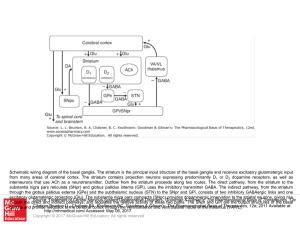
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
The Nervous System
... (CNS)/ Brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Ø Bundles of nerve fibers or axons that conduct information to and from the central nervous system Ø Includes sensory neurons and motor neurons ...
... (CNS)/ Brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Ø Bundles of nerve fibers or axons that conduct information to and from the central nervous system Ø Includes sensory neurons and motor neurons ...